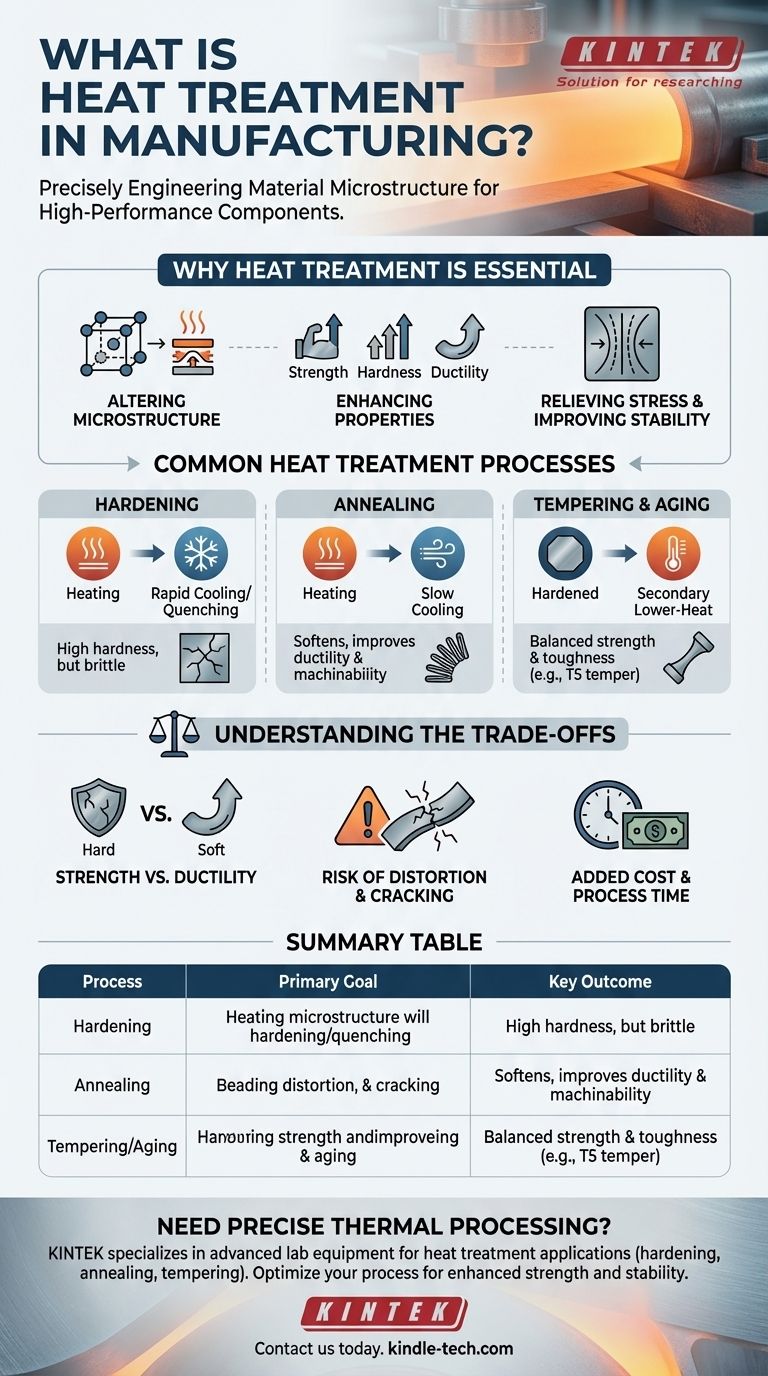
In manufacturing, heat treatment is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling a material to deliberately change its internal structure. This is not done to simply shape the material, but to alter its fundamental physical and mechanical properties, making it stronger, more durable, or easier to work with for a specific application.
The core purpose of heat treatment is not to change a part's shape, but to precisely engineer its microscopic internal structure. This transforms a standard material into a high-performance component tailored for a specific operational demand.

Why Heat Treatment is an Essential Step
Heat treatment unlocks the full potential of a material. A single type of steel, for example, can be configured for dozens of different applications—from a flexible spring to a rigid cutting tool—based entirely on how it is heat treated.
Altering the Material Microstructure
At a microscopic level, heat treatment forces the atoms within the metal's crystal lattice to rearrange themselves. The speed of heating, the maximum temperature reached, the time held at that temperature, and the speed of cooling all dictate the final arrangement of these crystals, which in turn defines the material's properties.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
The primary goal is often to improve specific mechanical traits. Controlled heating and cooling can significantly increase a material's strength (resistance to bending), hardness (resistance to scratching and wear), and ductility (ability to deform without fracturing).
Relieving Stress and Improving Stability
Manufacturing processes like welding, machining, or forming (like extrusion) can introduce internal stresses into a material. A specific heat treatment cycle, such as annealing or stress-relieving, can relax these stresses, preventing future distortion or premature failure and improving the part's dimensional stability.
Common Heat Treatment Processes
While there are many specific recipes, most heat treatments fall into a few key categories. The chosen process depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
Hardening
This process increases a material's strength and wear resistance. It involves heating the metal to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling it (a process known as quenching), typically by submerging it in water, oil, or air. This "freezes" the atoms in a hard, strong microstructure.
Annealing
Annealing is essentially the opposite of hardening. The material is heated and then cooled very slowly. This process softens the metal, increases its ductility, and relieves internal stresses, making it easier to machine or form in subsequent steps.
Tempering and Aging
After hardening, a material can often be too brittle. Tempering (for steels) or Aging (for non-ferrous alloys) is a secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment that reduces this brittleness and improves toughness.
The T5 temper condition for aluminum is a perfect example of artificial aging. After being formed at a high temperature (like in an extrusion press), the part is "artificially aged" in an oven to increase its strength and stabilize its dimensions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it involves critical engineering compromises that must be managed carefully.
The Strength vs. Ductility Dilemma
The most fundamental trade-off is between strength and ductility. As you make a metal harder and stronger, it almost always becomes more brittle and less able to deform without cracking. The goal is to find the optimal balance for the part's function.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
Rapid temperature changes are inherently stressful for materials. If not controlled with extreme precision, the quenching process can cause a part to warp, distort, or even develop microscopic cracks that can lead to catastrophic failure under load.
Added Cost and Process Time
Heat treatment is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized furnaces, precise controls, and extra time. This adds to the overall cost and lead time of producing a finished part, a factor that must be justified by the required performance improvement.
Applying This to Your Project
Choosing the right heat treatment begins with defining the single most important performance characteristic your part needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and surface hardness: A hardening process like quenching is necessary, but you will likely need a follow-up tempering step to reduce brittleness.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or preparing for extensive forming: An annealing cycle will soften the material and relieve internal stresses, making it easier to work with.
- If your primary focus is achieving a balanced blend of strength and toughness: A combination process, such as hardening followed by tempering or an aging treatment like the T5 condition, is the correct path.
Ultimately, viewing heat treatment as an integral part of material selection empowers you to design and build components that perform exactly as intended.
Summary Table:
| Heat Treatment Process | Primary Goal | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Increase strength & wear resistance | High hardness, but can be brittle |
| Annealing | Soften material, relieve stress | Improved ductility & machinability |
| Tempering/Aging | Reduce brittleness, improve toughness | Balanced strength & ductility (e.g., T5 temper) |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for heat treatment applications. Whether you are hardening, annealing, or tempering, our reliable furnaces and expert support ensure you achieve the exact material properties your project demands—from enhanced strength to improved stability.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your manufacturing process and deliver high-performance components.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- What is the difference between melting and sintering temperatures? A Guide to Material Processing Methods
- What is the purpose of calcination? Transform and Purify Materials for Industrial Use
- What are the precautions for heat in the laboratory? Essential Safety Rules to Prevent Burns and Fires
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace? Achieve High-Purity Heating for Your Lab



















