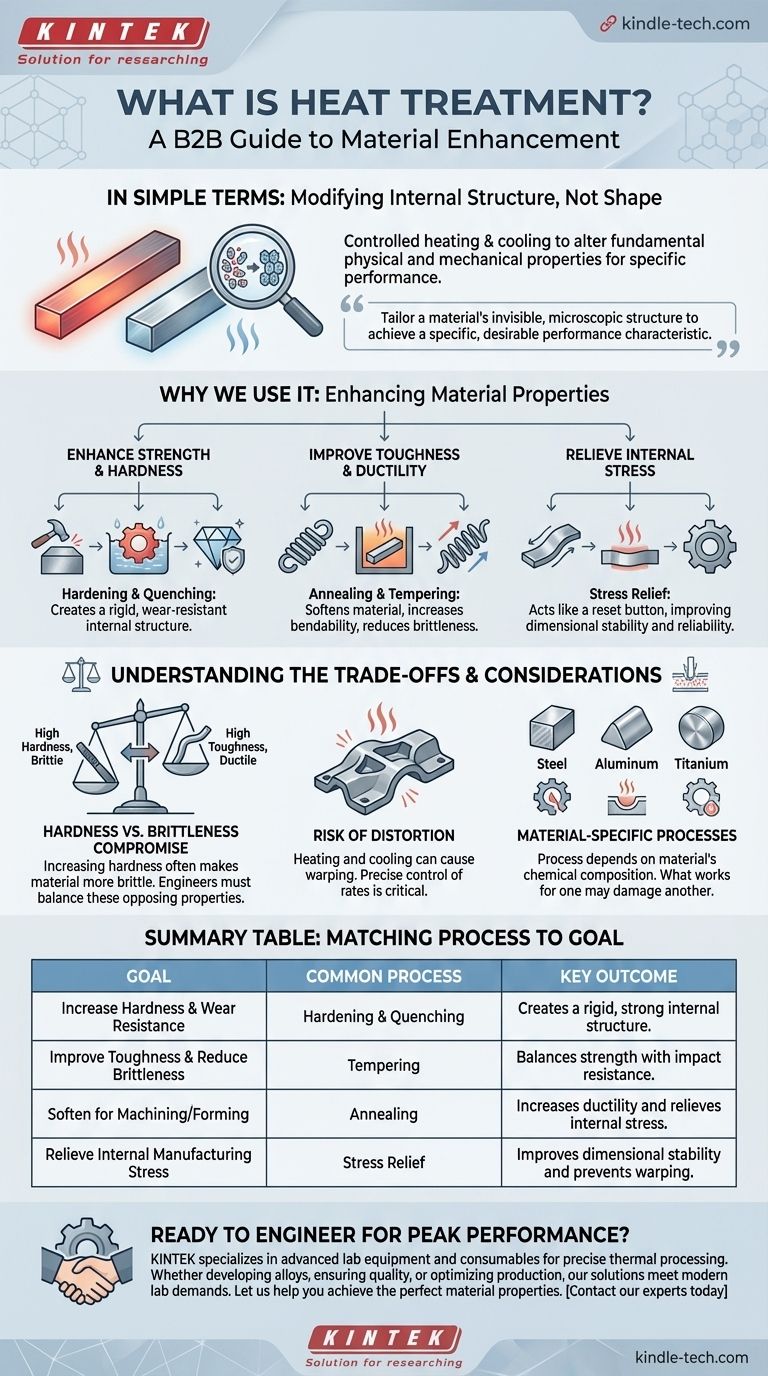
In simple terms, heat treatment is the process of using carefully controlled heating and cooling to change the internal structure of a material, most often a metal like steel. It's not about changing the material's shape, but about altering its fundamental physical and mechanical properties to make it stronger, tougher, or easier to work with.
The core purpose of heat treatment is to tailor a material's invisible, microscopic structure to achieve a specific, desirable performance characteristic—such as making a drill bit hard enough to cut steel or making a car frame tough enough to absorb impact.
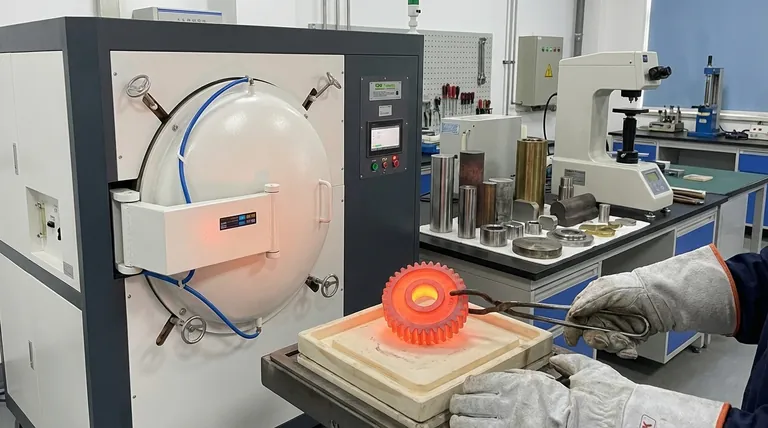

Why We Use Heat Treatment: Modifying a Material's Properties
Think of a metal's internal crystal structure like a set of building blocks. Heat treatment is the process of rearranging those blocks into a more optimal configuration for a specific job.
Enhancing Strength and Hardness
One of the most common goals is to make a material harder and more resistant to wear.
Processes like hardening involve heating a metal to a high temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching). This locks the internal structure in a very rigid, strong state.
Improving Toughness and Ductility
Sometimes, a material that is too hard is also too brittle, meaning it will shatter under impact.
Heat treatment processes like annealing or tempering are used to soften a material, increase its ability to bend without breaking (ductility), and improve its overall toughness.
Relieving Internal Stress
Manufacturing processes like welding, bending, or machining can create invisible stress inside a part, which can lead to warping or cracking over time.
A stress-relief heat treatment acts like a reset button, gently heating the part to allow its internal structure to relax, dramatically improving its stability and reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it involves critical compromises and requires precise control to be successful.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Increasing a metal's hardness almost always makes it more brittle.
A file needs to be extremely hard to cut other metals, but this makes it so brittle that it will snap if you try to bend it. Engineers must always balance these opposing properties.
The Risk of Distortion
Heating and cooling materials, especially in complex shapes, can cause them to warp or distort.
Controlling the heating and cooling rates is critical to ensure the part maintains its required dimensions and tolerances after treatment.
Material-Specific Processes
You cannot apply the same heat treatment to all materials. The specific temperatures, times, and cooling methods are entirely dependent on the material's chemical composition.
What works for a high-carbon steel would be ineffective or even damaging for an aluminum alloy or a different grade of steel.
Matching the Process to the Goal
The right heat treatment is always determined by the final application of the part.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A hardening and quenching process is necessary to create a rigid internal structure.
- If your primary focus is making a part easy to machine or form: An annealing process is used to make the material as soft and stress-free as possible.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and toughness: A tempering process is typically used after hardening to reduce brittleness while retaining most of the strength.
Ultimately, heat treatment is how we transform a basic material into a high-performance component engineered for a specific task.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Common Heat Treatment Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Wear Resistance | Hardening & Quenching | Creates a rigid, strong internal structure. |
| Improve Toughness & Reduce Brittleness | Tempering | Balances strength with impact resistance. |
| Soften for Machining/Forming | Annealing | Increases ductility and relieves internal stress. |
| Relieve Internal Manufacturing Stress | Stress Relief | Improves dimensional stability and prevents warping. |
Ready to engineer your materials for peak performance?
The principles of heat treatment are fundamental to creating reliable, high-quality components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise thermal processing. Whether you are developing new alloys, ensuring quality control, or optimizing production processes, our solutions are designed to meet the exacting demands of modern laboratories.
Let us help you achieve the perfect material properties for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific heat treatment challenges and discover how KINTEK can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high-energy homogenizers required for high-performance microbial biopolymers? Achieving Superior Dispersion
- What are the different types of melting process? From Smelting to Suspension for Ultimate Purity
- What is deposition methods? Choose the Right Thin-Film Technique for Your Lab
- Why is precise temperature-controlled heating equipment required for chitosan synthesis? Ensure High-Quality Deacetylation
- Does melting point ever change? Unlock the Secrets of Pressure and Purity
- What is the difference between cannabis extract and distillate? A Guide to Potency vs. Full-Spectrum Effects
- Is oil sludge hazardous? Understanding the Critical Risks and Regulations
- What is the purpose of reactive sputtering? Synthesize High-Performance Compound Thin Films



















