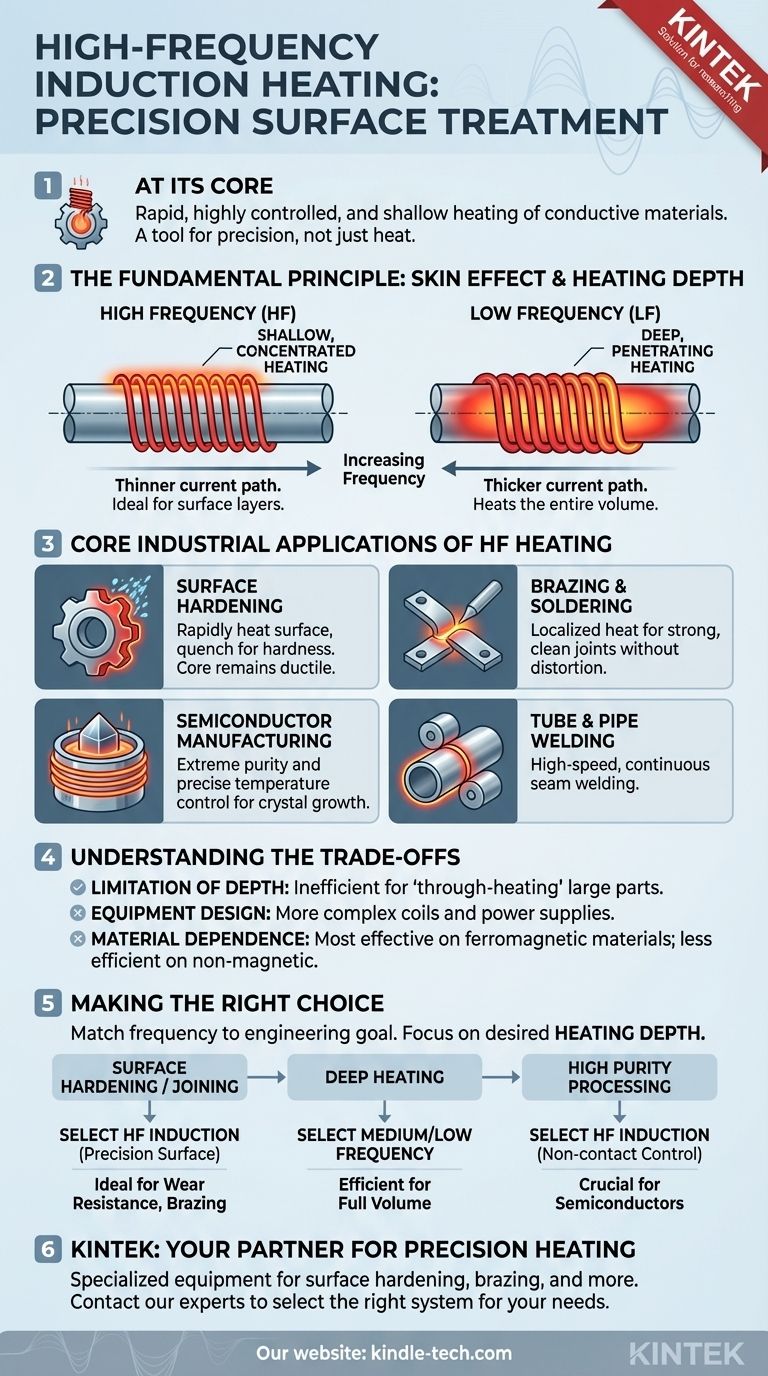
At its core, high-frequency induction heating is a tool for precision surface treatment. It is used for industrial processes that require rapid, highly controlled, and shallow heating of conductive materials. Key applications include surface hardening of steel parts like gears and shafts, brazing and soldering of small components, and specialized processes in semiconductor manufacturing that demand extreme purity and control.
The critical factor in induction heating is not just the heat itself, but the depth at which that heat is generated. High frequency is used specifically for applications where only the surface layer of a part needs to be heated, leaving the core material's properties unchanged.
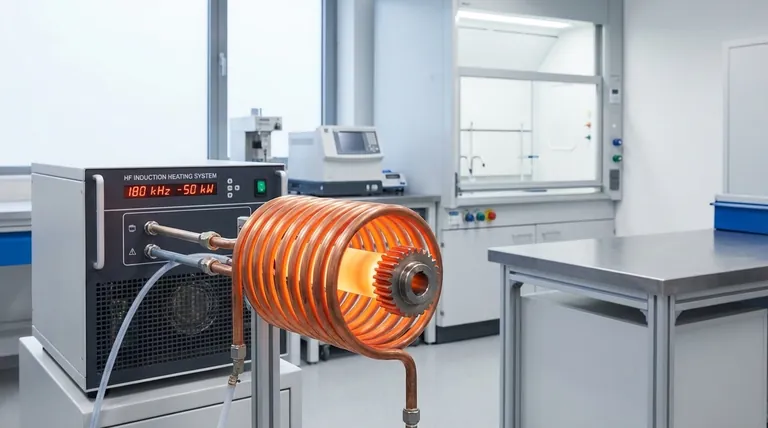

The Fundamental Principle: Frequency and Heat Depth
To understand why high frequency is used, you must first understand its direct relationship with heating depth. This physical principle, known as the "skin effect," is the key to selecting the right process for your goal.
What is the Skin Effect?
In induction heating, an alternating magnetic field induces an electrical current within a conductive part, and the resistance to this current flow generates heat. The skin effect describes the tendency of this alternating current to flow primarily near the surface of the conductor.
How Frequency Controls Heating Depth
The depth of this current flow—and therefore the heating—is inversely proportional to the frequency.
- High Frequency = Thinner current path = Shallow, concentrated heating.
- Low Frequency = Thicker current path = Deep, penetrating heating.
This control is what makes induction heating such a precise manufacturing tool. By selecting the frequency, an engineer can decide exactly how much of the part gets hot.
Defining "High Frequency"
While ranges vary by manufacturer, "high frequency" (HF) for induction heating typically refers to a range between 60 kHz and 200 kHz. Some specialized applications can use frequencies well into the megahertz (MHz) range.
Core Industrial Applications of HF Heating
The shallow heating depth of high-frequency induction makes it the ideal choice for processes where surface properties are paramount.
Surface and Case Hardening
This is the most common application. HF heating can rapidly bring the surface of a steel component, like a gear tooth or a bearing race, to a critical temperature. When this heated surface is then rapidly cooled (quenched), it becomes extremely hard and wear-resistant, while the core of the part remains softer and more ductile to absorb shock.
Brazing and Soldering
HF induction is perfect for joining components, especially thin or delicate ones. It delivers intense, localized heat directly to the joint area, melting the brazing alloy quickly without overheating or distorting the rest of the assembly. This creates strong, clean joints with minimal thermal stress.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Processes like Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining, which are used to create the ultra-pure silicon crystals for computer chips, rely on the precise and clean heating of induction. HF is often used in these setups because of the exceptional temperature control it provides, which is critical for achieving the required material purity.
Tube and Pipe Welding
High-frequency induction is widely used to weld seams on steel tubes and pipes. As a flat strip of steel is formed into a tube, HF current is applied to its edges, heating them to a welding temperature in milliseconds. The edges are then forged together by pressure rollers, creating a continuous, strong weld seam at high speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, high-frequency induction is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is defined by its limitations.
The Limitation of Depth
The primary strength of HF heating is also its main weakness. It is highly inefficient for applications that require heating the entire volume of a large part, such as forging a large billet or melting a full crucible of metal. For these "through-heating" tasks, lower frequencies are necessary.
Equipment and Coil Design
High-frequency power supplies and the associated induction coils (inductors) can be more complex to design and build than their low-frequency counterparts. The coil's geometry is critical, as it must be precisely shaped and positioned to deliver energy efficiently to the target area.
Material Dependence
Induction heating is most effective on ferromagnetic materials like steel and iron below their Curie temperature. It is less efficient on non-magnetic but conductive materials like aluminum and copper, often requiring higher power or different frequency configurations to achieve the desired heating rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct frequency is about matching the physics of the process to your engineering goal. The required heating depth should be your primary guide.
- If your primary focus is creating a wear-resistant surface: HF induction is the standard and most effective method for surface and case hardening.
- If your primary focus is joining small or thin components: HF provides the rapid, localized heat needed for precise brazing and soldering without damaging the parts.
- If your primary focus is heating the entire volume of a large part: You should investigate medium or low-frequency induction, as HF is inefficient for deep heating.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing: HF offers the unmatched, non-contact control required for applications like semiconductor crystal growth.
Understanding the direct link between frequency and depth empowers you to select induction heating not just as a heat source, but as a precision manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Typical Frequency Range |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Hardening | Creates a hard, wear-resistant surface on gears and shafts | 60 kHz - 200 kHz |
| Brazing & Soldering | Fast, localized heating for strong joints without distortion | 60 kHz - 200 kHz |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Extreme purity and temperature control for crystal growth | Up to MHz range |
| Tube & Pipe Welding | High-speed, continuous seam welding | 60 kHz - 200 kHz |
Ready to implement precision heating in your lab or manufacturing process? KINTEK specializes in high-frequency induction heating equipment and solutions for surface hardening, brazing, and specialized industrial applications. Our experts can help you select the right system for your specific material and depth requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your manufacturing capabilities and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does bond strength depend on in braze welding? Master the 3 Keys to a Strong Joint
- What products are made by hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Density and Performance for Your Components
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What is vacuum hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Density & Purity in Advanced Materials
- What is the effect of increasing the pressure during sintering? Achieve Maximum Density and Superior Performance



















