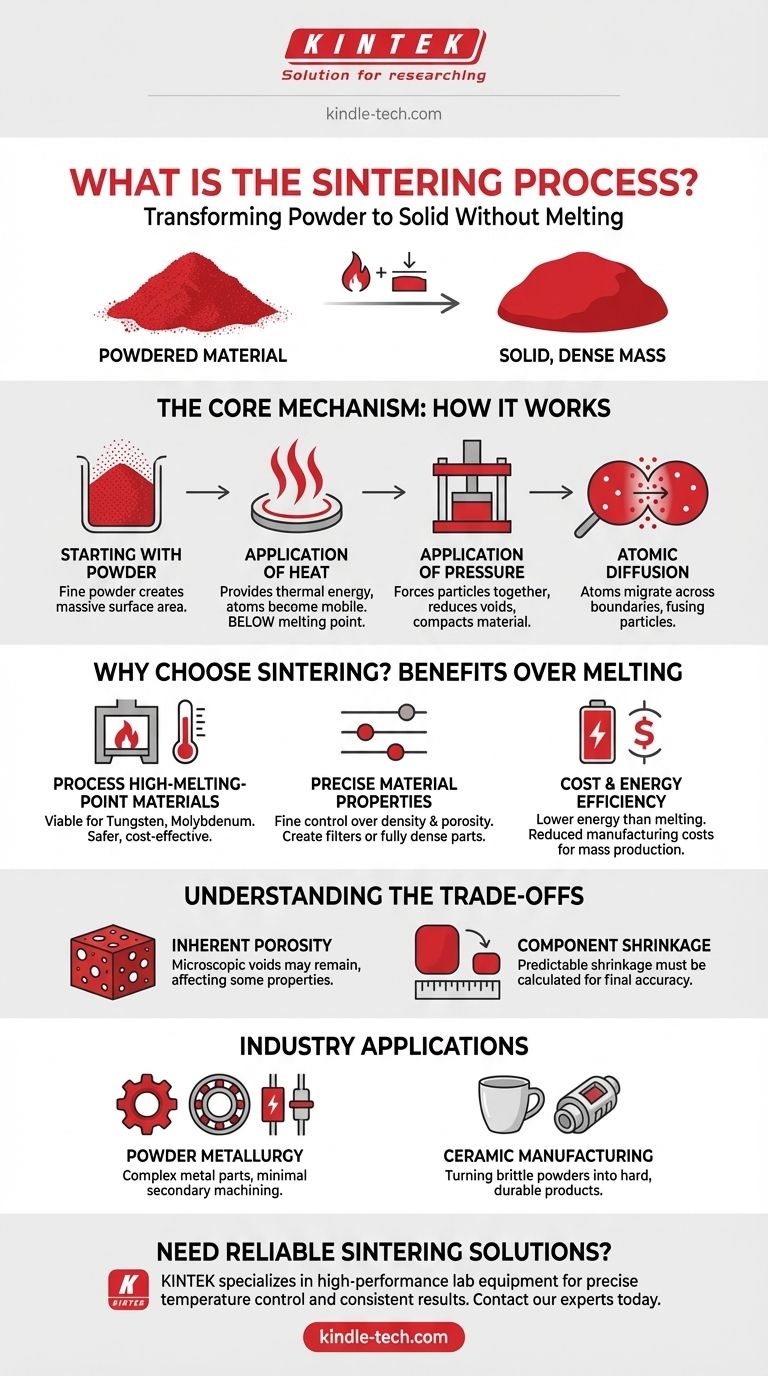
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a powder into a solid, dense mass using heat and pressure. Crucially, this is achieved without ever melting the material to the point of liquefaction. Instead of becoming a liquid, the individual particles fuse together on an atomic level, creating a strong, unified piece.
The fundamental goal of sintering is not to melt a material, but to give its atoms enough energy and proximity to diffuse across particle boundaries, effectively welding them together in a solid state. This makes it possible to form parts from materials with exceptionally high melting points.
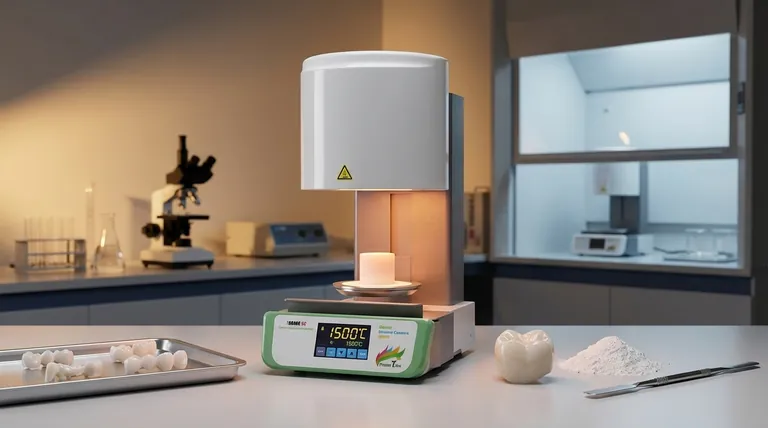

The Core Mechanism: How Sintering Works
To understand why sintering is so effective, we must look at the process on a microscopic level. It's a precise orchestration of material science, heat, and pressure.
Starting with a Powder
The process begins with the raw material in a powdered form. This could be metal, ceramic, plastic, or other materials. The fine particles create a massive amount of surface area, which is key to the next steps.
The Role of Heat
Heat is applied to the powdered mass, but always kept below the material’s melting point. This heat isn't for melting; it's to provide thermal energy. This energy makes the atoms within the particles vibrate and become more mobile.
The Role of Pressure
Simultaneously, pressure is often applied to compact the powder. This serves two purposes: it forces the particles into close contact and begins to reduce the porous spaces, or voids, between them.
Atomic Diffusion at the Boundaries
This is the central principle of sintering. With the atoms energized by heat and the particles pressed tightly together, atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This atomic diffusion creates strong metallic or covalent bonds, effectively fusing the particles into a single, solid piece.
Why Choose Sintering Over Melting?
Sintering is not just an alternative to casting (melting and pouring); for many applications, it is the superior or only viable option.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
Many advanced materials, like tungsten and molybdenum, have melting points so high that melting and casting them is impractical, unsafe, and extremely expensive. Sintering allows us to form these materials into solid, usable shapes at significantly lower temperatures.
Achieving Precise Material Properties
Sintering gives engineers fine control over the final product's density and porosity. By adjusting temperature, pressure, and time, you can create parts that are intentionally porous (like for filters) or almost fully dense for maximum strength. This level of control is difficult to achieve with casting.
Cost and Energy Efficiency
Heating a material to just below its melting point requires far less energy than melting it completely. For mass production of components, this reduction in energy consumption translates directly into lower manufacturing costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any engineering process, sintering has specific limitations that are important to understand.
Inherent Porosity
Because the material never reaches a liquid state, microscopic voids or pores can remain in the final product. While this can be controlled, a sintered part may not achieve the absolute 100% density of a perfectly cast part, which can affect certain mechanical properties.
Component Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the gaps between them close, the entire component shrinks. This shrinkage is predictable but must be precisely calculated and accounted for during the initial design and mold-making stage to ensure final dimensional accuracy.
Application in Industry
The versatility and efficiency of sintering have made it a cornerstone process across many industries.
Powder Metallurgy
This is one of the most common applications. Sintering is used to produce a vast range of complex metal parts, including gears, bearings, sprockets, rotors, and electrical contacts, often with no need for secondary machining.
Ceramic Manufacturing
From traditional pottery to advanced technical ceramics, sintering is the fundamental process used to turn brittle ceramic powders into hard, durable finished products.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is working with extremely high-melting-point metals like tungsten: Sintering is often the only practical and cost-effective method for creating solid components.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex metal parts: Sintering, via powder metallurgy, offers a highly efficient path for items like gears and bearings that minimizes waste and secondary operations.
- If your primary focus is controlling the final density and porosity of a ceramic part: Sintering provides the necessary process control that traditional melting and casting cannot offer.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage sintering to create strong, precise components from materials that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to form.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Fuse powder particles into a solid mass via atomic diffusion, without melting. |
| Key Advantage | Enables shaping of high-melting-point materials (e.g., tungsten, ceramics). |
| Main Limitation | Final parts may have inherent porosity and require precise shrinkage calculations. |
| Common Applications | Powder metallurgy (gears, bearings), ceramic manufacturing, filters. |
Need to source reliable sintering equipment or consumables for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment for powder metallurgy and ceramic sintering. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our solutions ensure precise temperature control and consistent results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering process and help you achieve superior material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia



















