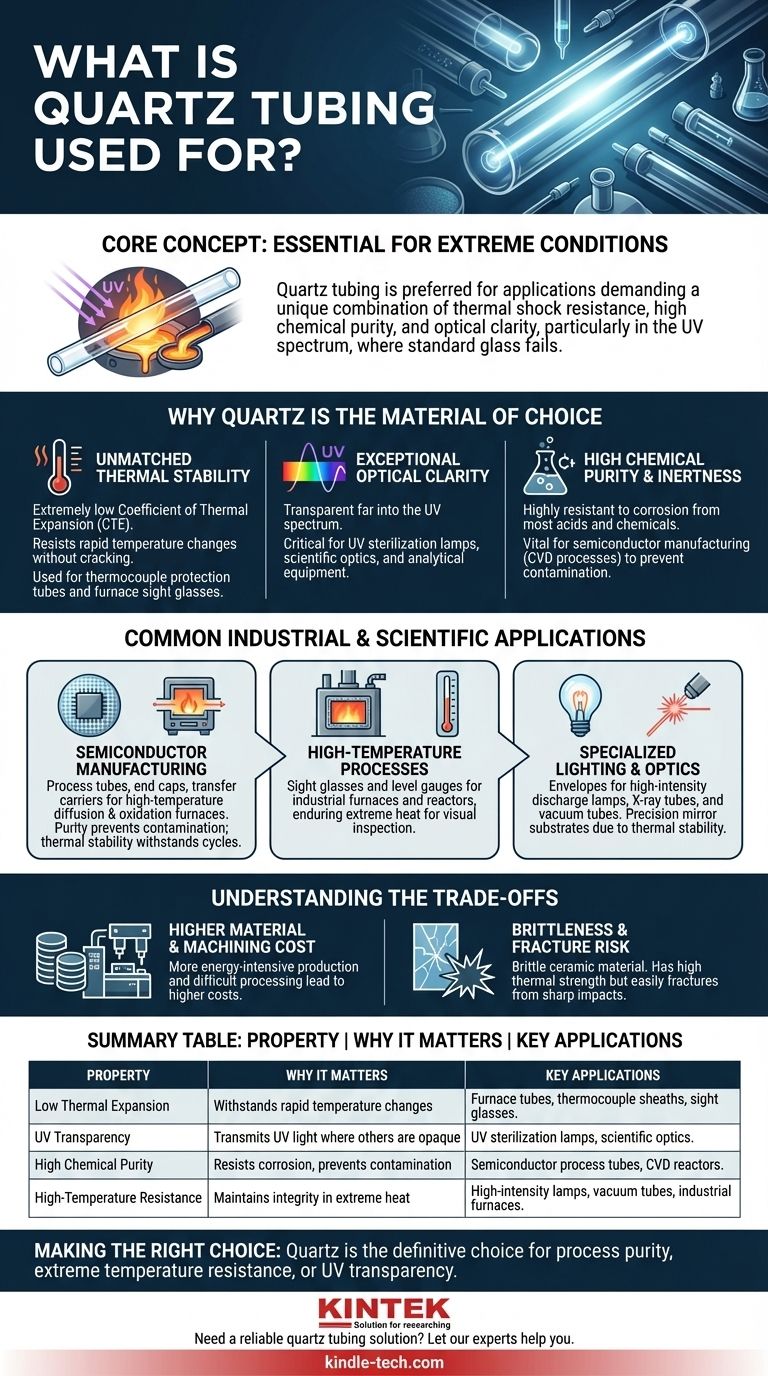
At its core, quartz tubing is an essential material for scientific and industrial applications that operate under extreme conditions. It is used in everything from semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature furnaces to specialized lighting and optical systems where standard glass or plastic would fail catastrophically.
The use of quartz tubing is not about the tube itself, but about its fundamental properties. It is chosen when an application demands an exceptional combination of thermal shock resistance, high chemical purity, and specific optical clarity, particularly in the ultraviolet spectrum.

Why Quartz is the Material of Choice
Engineers and scientists specify quartz tubing when performance under stress is non-negotiable. Its value comes from a unique set of properties that make it superior to other transparent materials like borosilicate glass.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). This means it barely expands or contracts when subjected to rapid and extreme temperature changes, preventing it from cracking.
This property makes it indispensable for components like thermocouple protection tubes, which are plunged into molten metals, or for furnace sight glasses that must endure intense heat.
Exceptional Optical Clarity
Fused quartz is transparent far into the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum, a range where most other types of glass are opaque.
This UV transmission is critical for applications like UV sterilization lamps, scientific optics, and analytical equipment that rely on the unimpeded passage of ultraviolet light.
High Chemical Purity and Inertness
Quartz is one of the purest materials available for industrial use. It is highly resistant to corrosion from most acids and chemicals, even at high temperatures.
This inertness is vital in semiconductor manufacturing, where processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and diffusion require an environment free of contaminants that could ruin silicon wafers.
Common Industrial and Scientific Applications
The properties of quartz directly translate into its use in some of the most demanding technical fields.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
This is one of the largest applications for quartz tubing. It is used to create process tubes, end caps, and transfer carriers (boats) that hold silicon wafers inside high-temperature diffusion and oxidation furnaces.
Its high purity prevents contamination of the wafers, while its thermal stability allows it to withstand the process cycles without failing.
High-Temperature Processes
Quartz is used for sight glasses and level gauges on industrial furnaces and chemical reactors, allowing for visual inspection of processes occurring at hundreds or even thousands of degrees.
Its ability to protect thermocouples from both extreme heat and chemical attack makes it a standard material for temperature measurement in harsh environments.
Specialized Lighting and Optics
Because it can withstand high temperatures and is transparent to UV light, quartz tubing forms the envelope for high-intensity discharge lamps, X-ray tubes, and vacuum tubes.
It is also the material of choice for precision mirror substrates in telescopes and lasers, as its thermal stability ensures the mirror's shape remains constant despite temperature fluctuations.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost and Brittleness
While its performance is exceptional, quartz is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Higher Material and Machining Cost
Producing and shaping fused quartz is a more energy-intensive and difficult process than working with standard glass. This results in a significantly higher cost for both raw material and finished components.
Brittleness and Fracture Risk
Like all ceramic materials, quartz is brittle. It has excellent thermal and compressive strength but can easily fracture from a sharp impact. It is not suitable for applications that require high durability against physical shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material always depends on the primary requirement of your project.
- If your primary focus is process purity: Quartz is the definitive choice for applications like semiconductor manufacturing where preventing contamination is the most critical factor.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature resistance: Quartz is essential for components that must survive rapid thermal cycling or constant high-heat exposure, such as furnace tubes and sensor sheaths.
- If your primary focus is UV transparency: Quartz is one of the few practical materials that allows for efficient transmission of ultraviolet light for optical or sterilization systems.
Ultimately, quartz tubing is the enabling material for technologies that function where others simply cannot survive.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Thermal Expansion | Withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking. | Furnace tubes, thermocouple sheaths, sight glasses. |
| UV Transparency | Transmits ultraviolet light where other glasses are opaque. | UV sterilization lamps, scientific optics. |
| High Chemical Purity | Resists corrosion and prevents contamination. | Semiconductor process tubes, CVD reactors. |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Maintains integrity in extreme heat. | High-intensity lamps, vacuum tubes, industrial furnaces. |
Need a reliable quartz tubing solution for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our quartz tubing is engineered to meet the stringent requirements of semiconductor fabrication, high-temperature research, and precision optics. We provide the material purity and thermal stability your processes demand.
Let our experts help you select the right components to enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure process integrity. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















