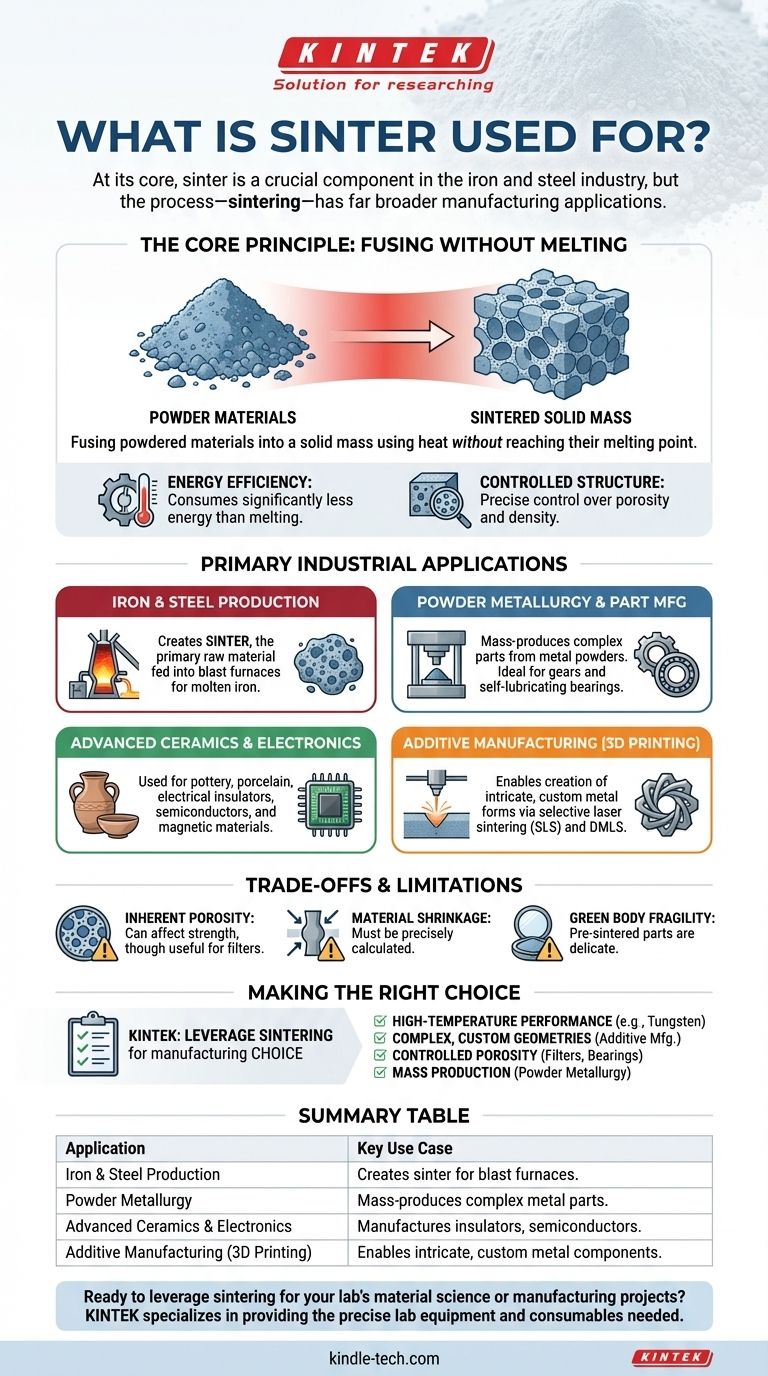
At its core, sinter is a crucial component in the iron and steel industry, serving as the primary raw material fed into a blast furnace. However, the underlying process, sintering, has far broader applications across manufacturing, used to create everything from ceramic pottery and metal parts to advanced electronics and 3D-printed custom components.
The true value of sintering is its ability to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass using heat without reaching their melting point. This single principle unlocks the ability to work with high-temperature metals, create unique material blends, and precisely control the final object's density and porosity.
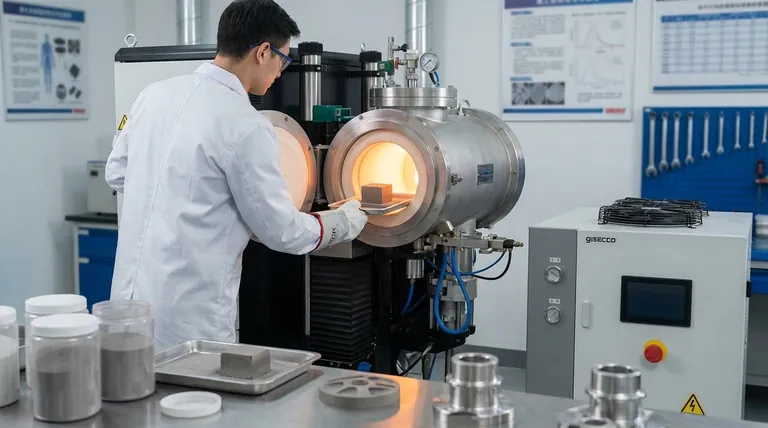

The Core Principle: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering is a thermal process that applies heat and often pressure to a mass of particles, causing them to bond and form a coherent, solid piece.
The Key Advantage Over Melting
By operating below the material's melting point, sintering consumes significantly less energy. This makes it the only practical method for shaping materials with exceptionally high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum, which are difficult and expensive to melt and cast.
Control Over the Final Structure
Because the material never becomes a liquid, sintering allows for precise control over the final product's internal structure. This includes managing its porosity, or the amount of empty space within the material.
Primary Industrial Applications
The versatility of sintering has led to its adoption in a vast range of industries, from heavy manufacturing to high-tech electronics.
Iron and Steel Production
In its most specific industrial use, sinter is the product created by heating fine iron ore particles with other materials like limestone and coke. This process creates porous, solid lumps that are ideal for use in a blast furnace to produce molten iron, the precursor to steel.
Powder Metallurgy and Part Manufacturing
Sintering is the cornerstone of powder metallurgy, a process used to mass-produce complex metal parts. Metal powders are compressed into a shape (called a "green body") and then sintered to create finished components like structural steel parts, gears, and self-lubricating bearings.
Advanced Ceramics and Electronics
Many familiar items are made through sintering. This includes traditional applications like pottery and porcelain, as well as modern uses in producing electrical insulators, semiconductors, and magnetic materials.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Modern 3D printing techniques like selective laser sintering (SLS) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) use lasers to fuse layers of powder together. This allows for the creation of intricate, custom metal forms that would be impossible to make with traditional methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every manufacturing challenge. Understanding its inherent trade-offs is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity
Even in "fully dense" sintered parts, microscopic pores can remain. While sometimes a desired feature (for filters or self-lubrication), this residual porosity can make sintered parts less strong than components forged or cast from a fully molten state.
Material Shrinkage
As the particles fuse during sintering, the overall part will shrink. This change in dimension must be precisely calculated and controlled to ensure the final product meets required tolerances, adding a layer of complexity to the design process.
Green Body Fragility
The pre-sintered component, often called a "green body," is merely compacted powder. It is typically very fragile and must be handled with extreme care before it enters the furnace, which can complicate automated manufacturing lines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is chosen when its unique benefits directly address a specific manufacturing or material science challenge.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Sintering is the optimal choice for processing metals like tungsten for applications such as filaments and cutting tools.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, custom geometries: Additive manufacturing methods based on sintering are unparalleled for producing intricate, one-off metal parts.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity: Sintering is the only method to intentionally create porous metal or plastic structures for products like filters and self-lubricating bearings.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex metal parts: Powder metallurgy using sintering is a highly efficient and economical method for creating components like automotive gears.
Ultimately, sintering offers a powerful method for engineering materials from the particle level up, unlocking properties and forms that conventional melting and casting cannot achieve.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Case |
|---|---|
| Iron & Steel Production | Creates sinter, the primary raw material for blast furnaces. |
| Powder Metallurgy | Mass-produces complex, strong metal parts like gears and bearings. |
| Advanced Ceramics & Electronics | Manufactures insulators, semiconductors, and magnetic materials. |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Enables creation of intricate, custom metal components (SLS/DMLS). |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material science or manufacturing projects? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced thermal processing. Whether you are developing new materials or optimizing production, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific sintering applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness



















