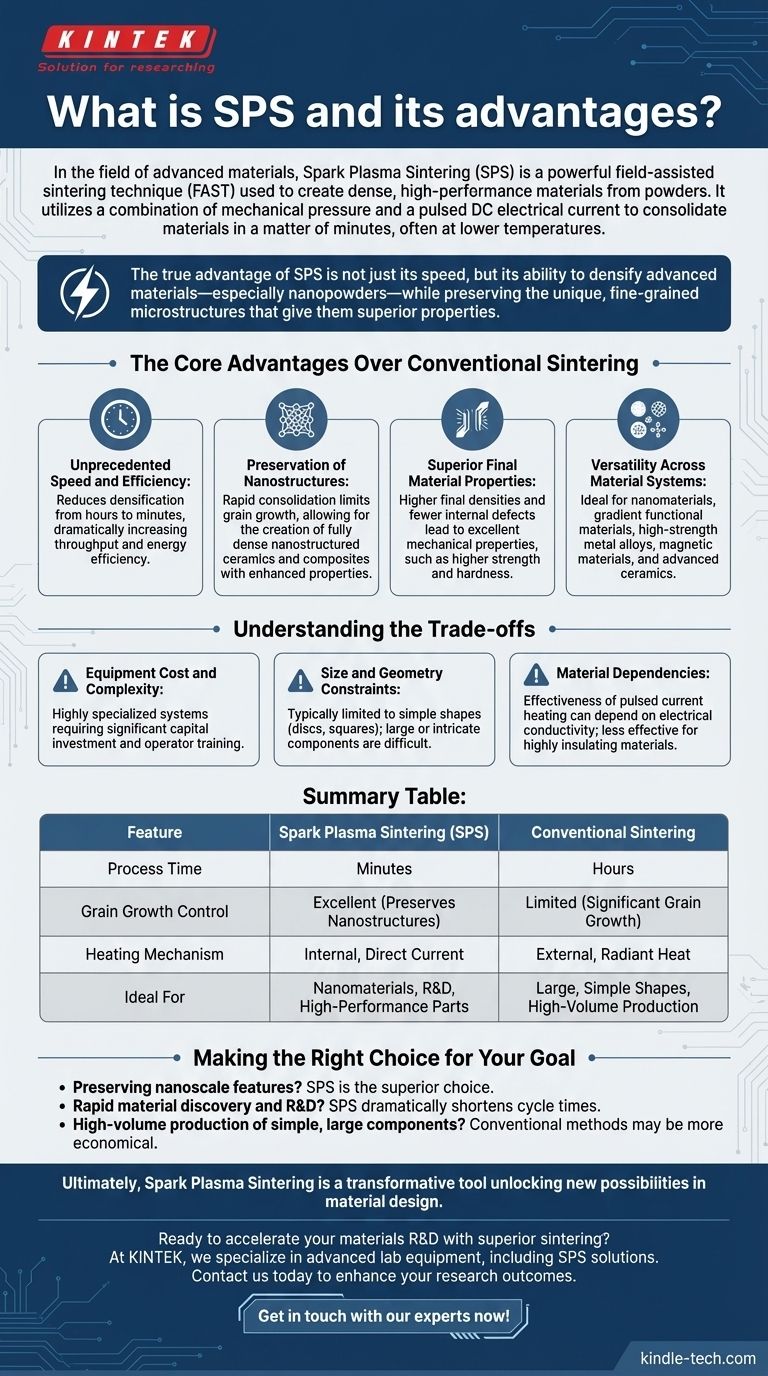
In the field of advanced materials, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a powerful field-assisted sintering technique (FAST) used to create dense, high-performance materials from powders. Unlike conventional methods that take hours, SPS uses a combination of mechanical pressure and a pulsed DC electrical current to consolidate materials in a matter of minutes, often at significantly lower temperatures.
The true advantage of SPS is not just its speed, but its ability to densify advanced materials—especially nanopowders—while preserving the unique, fine-grained microstructures that give them superior properties. It overcomes the limitations of traditional heating that often destroys these delicate features.

The Core Advantages Over Conventional Sintering
SPS represents a fundamental shift from traditional furnace-based sintering. The primary benefits stem directly from its unique heating mechanism, which provides unprecedented control over the final material structure.
Unprecedented Speed and Efficiency
Conventional methods like hot pressing or pressureless sintering slowly heat a material from the outside in, requiring long soak times of several hours. SPS passes a current directly through the powder and die, generating rapid, uniform, and internal heat.
This distinction reduces the entire densification process from several hours to mere minutes, dramatically increasing throughput for research and development while also being more energy-efficient.
Preservation of Nanostructures
Perhaps the most significant advantage of SPS is its ability to limit grain growth. In traditional sintering, the long exposure to high temperatures causes small grains to coarsen and grow, destroying the unique properties of nanomaterials.
Because SPS is so fast, it consolidates the powder into a dense solid before the grains have time to grow. This allows for the creation of fully dense nanostructured ceramics and composites with enhanced strength, hardness, and other desirable mechanical properties.
Superior Final Material Properties
The combination of speed and limited grain growth results in materials with higher final densities and fewer internal defects. This near-theoretical density is critical for applications where performance cannot be compromised.
The resulting materials exhibit excellent mechanical properties, such as higher strength and hardness, directly attributable to their fine-grained, uniform microstructure.
Versatility Across Material Systems
The benefits of SPS are not limited to a single class of materials. Its unique capabilities make it an ideal processing method for a wide range of advanced applications.
This includes nanomaterials, gradient functional materials, high-strength metal alloys, magnetic materials, and advanced ceramics, making it a cornerstone technology in modern materials science.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SPS is a specialized technique with its own set of considerations. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations compared to more established industrial methods.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
SPS systems are highly specialized and represent a significant capital investment compared to standard industrial furnaces. The complexity of the equipment also requires more specialized operator training.
Size and Geometry Constraints
The process is typically limited to consolidating relatively simple shapes, such as discs or squares, within a graphite die. Producing large or intricately shaped components via SPS is often impractical or impossible, a domain where other methods like pressureless sintering excel.
Material Dependencies
The effectiveness of the pulsed current heating mechanism can depend on the electrical conductivity of the material being processed. While it is highly effective for conductive materials, its application to highly insulating materials can be more complex.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering method depends entirely on the desired outcome, balancing material properties against manufacturing constraints like cost, volume, and complexity.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanoscale features: SPS is the superior choice, as its speed minimizes the grain growth that plagues conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is rapid material discovery and R&D: The dramatically shorter cycle times of SPS can accelerate your development process by an order of magnitude.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple, large components: The cost and scalability of traditional methods like hot pressing may be more economical.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering is a transformative tool that unlocks new possibilities in material design by overcoming the kinetic barriers of traditional processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Grain Growth Control | Excellent (Preserves Nanostructures) | Limited (Significant Grain Growth) |
| Heating Mechanism | Internal, Direct Current | External, Radiant Heat |
| Ideal For | Nanomaterials, R&D, High-Performance Parts | Large, Simple Shapes, High-Volume Production |
Ready to accelerate your materials R&D with superior sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including Spark Plasma Sintering solutions, to help you achieve dense, high-performance materials with preserved nanostructures. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics, metal alloys, or composite materials, our expertise and products are designed to meet the precise needs of your laboratory.
Contact us today to discuss how our SPS technology can enhance your research and development outcomes. Let's unlock new possibilities in material design together.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in diamond/copper composites? Master Densification & Bonding
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What advantages does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace offer over traditional sintering? Achieve Fine Grain Control
- What is the effect of pressure during sintering? Achieve Higher Density and Finer Microstructures Faster
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets
- What conditions does a vacuum hot pressing furnace provide for LLZTO? Achieving 99% Density for Solid Electrolytes
- Why is the vacuum environment provided by a vacuum hot pressing furnace critical for A356 sintering? Maximize Density
- What effect does pressure have on sintering? Accelerate Densification and Boost Material Performance



















