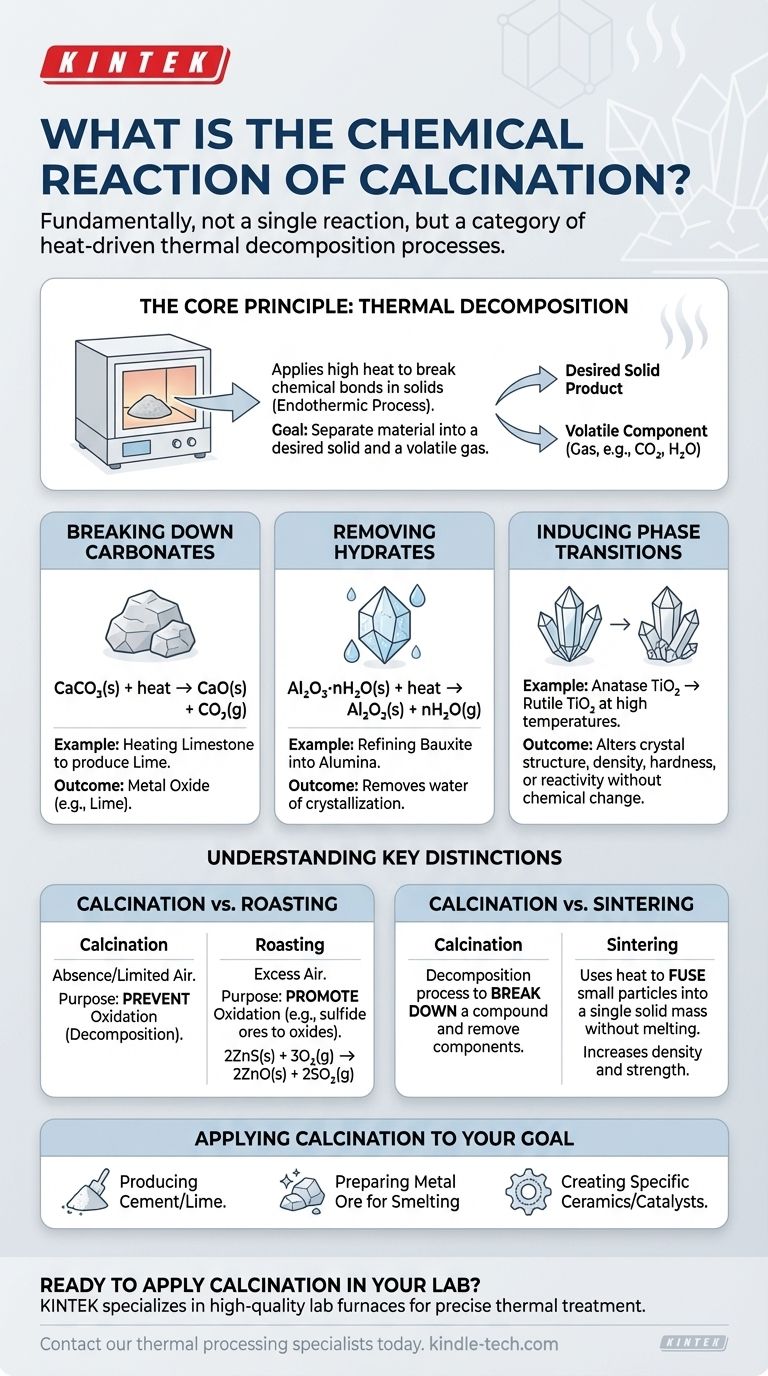
Fundamentally, calcination is not a single chemical reaction but rather a category of heat-driven processes defined by a specific outcome: thermal decomposition. While many reactions fall under this umbrella, the most common example is the breakdown of a carbonate, such as heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide gas.
Calcination is a thermal treatment process that uses high heat in a controlled atmosphere to break down a material. Its primary purpose is to drive off a volatile component—like carbon dioxide or water—to purify or alter the chemical and physical properties of the remaining solid.

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
Calcination works by applying enough thermal energy to a solid to break its chemical bonds. This process is always endothermic, meaning it requires an input of energy (heat) to proceed. The goal is to separate the material into a desired solid product and a volatile component that can be driven off as a gas.
Breaking Down Carbonates
This is the classic and most widespread application of calcination, particularly in the production of cement. When a metal carbonate is heated, it decomposes into a metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas.
For limestone, the reaction is:
CaCO₃(s) + heat → CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
Here, solid calcium carbonate breaks down into solid calcium oxide (lime) and gaseous carbon dioxide.
Removing Hydrates (Water of Crystallization)
Many minerals exist as hydrates, meaning water molecules are incorporated into their crystal structure. Calcination is used to drive this water off, a process often called "drying," though it is a chemical decomposition.
For example, refining bauxite ore into alumina involves calcining hydrated aluminum oxide:
Al₂O₃·nH₂O(s) + heat → Al₂O₃(s) + nH₂O(g)
This step removes the water, concentrating the aluminum oxide, which is a necessary precursor for producing aluminum metal.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Less commonly, calcination can refer to a process where heat doesn't cause decomposition but instead changes the crystal structure (phase) of a material. This alters its physical properties, like density, hardness, or reactivity, without changing its chemical formula.
An example is the conversion of anatase, a form of titanium dioxide (TiO₂), into its more stable rutile phase at high temperatures.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
The value of calcination becomes clearer when contrasted with other common thermal processes. The specific conditions—particularly the atmosphere—define the outcome.
Calcination vs. Roasting
This is the most critical distinction. Calcination occurs in the absence or limited supply of air to purposefully prevent oxidation.
Roasting, by contrast, is done in an excess of air specifically to promote oxidation. It is typically used on sulfide ores, converting them to oxides. For example, roasting zinc sulfide:
2ZnS(s) + 3O₂(g) → 2ZnO(s) + 2SO₂(g)
Calcination vs. Sintering
These processes have opposite goals. Calcination is a decomposition process used to break down a compound and remove a component.
Sintering, however, uses heat (below the melting point) to fuse small particles into a single, solid mass. It increases density and strength, essentially "welding" the material together without melting it.
Applying Calcination to Your Goal
The specific calcination reaction you care about depends entirely on your starting material and desired end product.
- If your primary focus is producing cement or lime: You are using calcination to decompose calcium carbonate into reactive calcium oxide.
- If your primary focus is preparing a metal ore for smelting: You are likely using calcination to remove water (from hydrates) or carbon dioxide (from carbonates) to enrich the metal content.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific ceramic or catalyst: You may be using calcination to achieve a desired crystal phase and surface area in a material like alumina or titania.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational tool in materials science for transforming raw solids into more useful, concentrated, or reactive forms.
Summary Table:
| Calcination Reaction Type | Example Reaction | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonate Decomposition | CaCO₃(s) + heat → CaO(s) + CO₂(g) |
Produces metal oxide (e.g., lime) |
| Hydrate Decomposition | Al₂O₃·nH₂O(s) + heat → Al₂O₃(s) + nH₂O(g) |
Removes water of crystallization |
| Phase Transition | Anatase TiO₂ → Rutile TiO₂ | Alters crystal structure & properties |
Ready to apply calcination in your lab?
Whether you are developing new catalysts, processing ores, or synthesizing advanced ceramics, precise thermal treatment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for reliable calcination processes.
We provide the tools you need to achieve uniform heating, precise temperature control, and consistent results. Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific material and application.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















