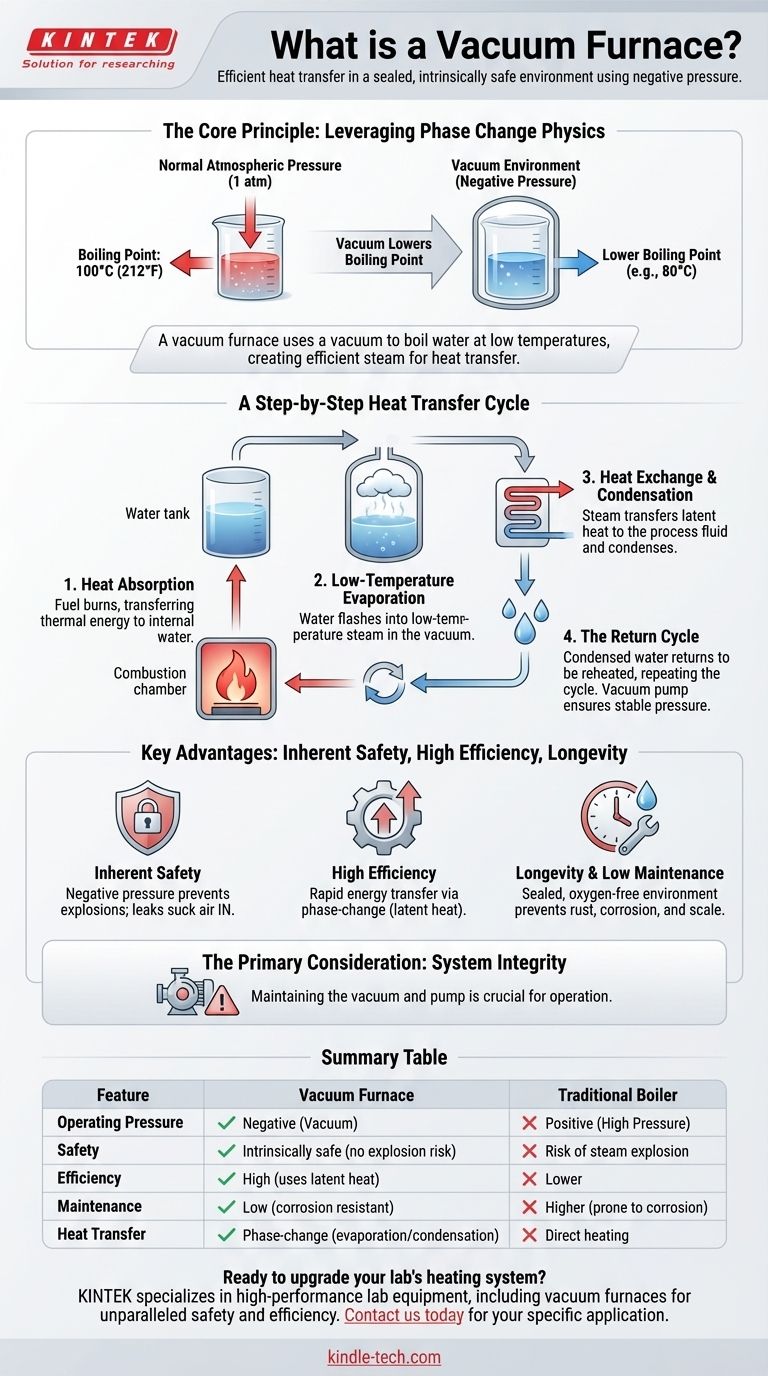
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized type of boiler or heater that operates under negative pressure. Instead of heating a target substance directly, it uses a vacuum to boil a small amount of water at a very low temperature. This low-temperature steam then serves as an incredibly efficient vehicle to transfer heat from a combustion source to a separate system, all within a sealed, intrinsically safe environment.
The defining principle of a vacuum furnace is not the vacuum itself, but its effect on water. By creating a vacuum, the furnace forces an internal water reserve to boil at a much lower temperature (e.g., 80°C), enabling rapid, safe, and efficient heat transfer through a continuous cycle of evaporation and condensation.

The Core Principle: Leveraging Phase Change Physics
To truly understand a vacuum furnace, you must look past the mechanics and focus on the physics it manipulates. The system is designed to exploit the relationship between pressure and the boiling point of a liquid.
Why a Vacuum is Essential
Under normal atmospheric pressure at sea level, water boils at 100°C (212°F). By removing most of the air from a sealed vessel, a vacuum furnace creates a low-pressure environment.
In this vacuum, the boiling point of water drops significantly. This is the entire key to the furnace's operation. It allows for the creation of steam (water vapor) without needing to reach high temperatures.
The Heat Medium: Water as an Energy Vehicle
The furnace contains a small, fixed amount of highly pure, deaerated water. This water is not the final product; it is the heat transfer medium.
When this water turns into steam, it absorbs a massive amount of energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization. This makes steam an exceptionally effective way to transport thermal energy from one place to another.
The Combustion Chamber and Heat Exchanger
A vacuum furnace has two distinct major components. A combustion chamber at the bottom burns fuel (like natural gas or oil) to heat the sealed vessel.
Inside the upper part of this vessel is a separate tube bundle, known as a heat exchanger. The water or fluid you actually want to heat flows through this exchanger, never mixing with the furnace's internal water.
A Step-by-Step Look at the Heat Transfer Cycle
The process is a continuous, closed loop that efficiently moves heat from the fuel source to your target application (e.g., a building's heating system).
Step 1: Heat Absorption
Fuel is burned in the combustion chamber. The hot gases from this combustion pass over tubes containing the furnace's internal heat medium water, transferring thermal energy into that water.
Step 2: Low-Temperature Evaporation
As the water's temperature rises, it quickly reaches its low boiling point due to the vacuum. It flashes into a large volume of low-temperature steam, filling the vacuum chamber.
Step 3: Heat Exchange and Condensation
This steam makes contact with the cooler surfaces of the heat exchanger. The steam instantly transfers its latent heat to the fluid inside the heat exchanger, causing the steam to condense back into liquid water. This is the critical step where useful work is done.
Step 4: The Return Cycle
The condensed water, having released its energy, simply falls back to the bottom of the vessel. Here, it is reheated by the combustion process, and the cycle begins again. A vacuum pump ensures the internal pressure remains stable throughout.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
No technology is a universal solution. The design of a vacuum furnace presents clear benefits but also specific considerations.
Key Advantage: Inherent Safety
This is the most significant benefit over traditional pressurized boilers. Because the system operates at a negative pressure, a leak or crack will cause outside air to be sucked in, not cause an explosion of high-pressure steam out. This eliminates the risk of catastrophic failure.
Key Advantage: High Efficiency
Phase-change heat transfer is one of the most efficient thermal processes in nature. The furnace rapidly moves large quantities of energy with minimal thermal loss, as the energy is "locked" in the steam until it condenses.
Key Advantage: Longevity and Low Maintenance
The sealed, oxygen-free environment inside the furnace virtually eliminates the potential for rust, corrosion, and mineral scale buildup. This dramatically extends the lifespan of the equipment and reduces maintenance requirements compared to atmospheric or pressurized systems.
The Primary Consideration: System Integrity
The core advantage of the vacuum is also its primary operational demand. The vessel must remain perfectly sealed, and the vacuum pump must be properly maintained to ensure the system holds its negative pressure. A loss of vacuum will stop the low-temperature boiling cycle, rendering the furnace ineffective until the leak is fixed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding if a vacuum furnace is appropriate depends entirely on your primary goal for the heating system.
- If your primary focus is safety: A vacuum furnace is an unparalleled choice, as it completely designs out the risk of a steam explosion inherent in pressurized boilers.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational cost: The high efficiency and dramatically reduced maintenance from corrosion and scale make it a superior long-term investment.
- If your primary focus is process heating for an industrial application: The precise temperature control and rapid response time of a vacuum furnace are highly advantageous.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace represents a shift from brute-force heating to an intelligent method of manipulating physics for safer, more durable, and more efficient thermal management.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Furnace | Traditional Boiler |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | Negative (Vacuum) | Positive (High Pressure) |
| Safety | Intrinsically safe (no explosion risk) | Risk of steam explosion |
| Efficiency | High (uses latent heat of vaporization) | Lower |
| Maintenance | Low (corrosion and scale-resistant) | Higher (prone to corrosion and scaling) |
| Heat Transfer | Phase-change (evaporation/condensation) | Direct heating |
Ready to upgrade your lab's heating system with unparalleled safety and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces designed for durability and precise thermal management. Our solutions are ideal for laboratories seeking to eliminate explosion risks, reduce long-term maintenance costs, and enhance process control. Contact us today to find the perfect vacuum furnace for your specific application and experience the KINTEK difference in reliability and support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components



















