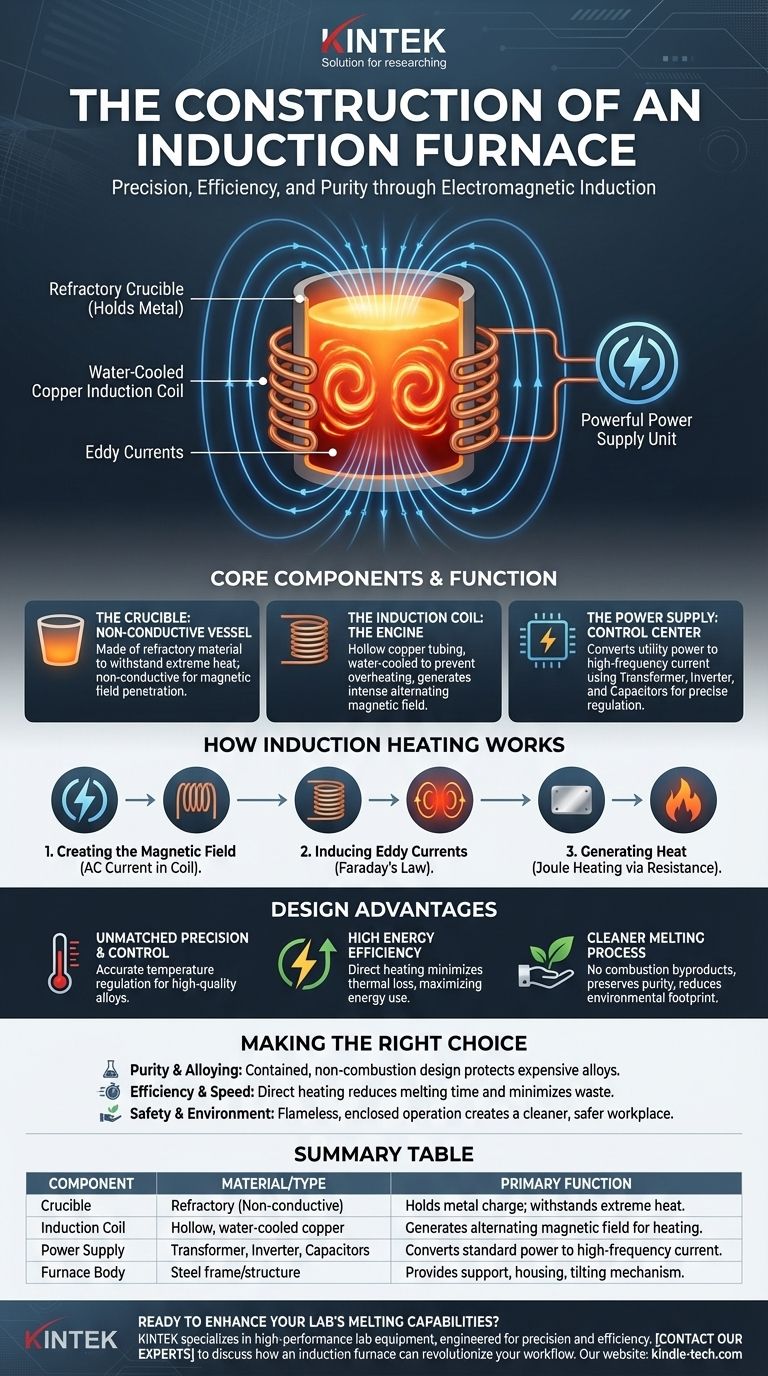
At its core, an induction furnace is constructed from three primary components: a non-conductive crucible to hold the metal, a copper coil surrounding it, and a powerful power supply. This design uses a powerful, alternating current in the coil to create a magnetic field that heats the metal directly, without any external flame or heating element.
The genius of an induction furnace lies not in its parts, but in its principle. Its construction is engineered to use electromagnetic induction to generate heat inside the target metal, making it an inherently precise, efficient, and clean method for melting.

The Core Components and Their Function
An induction furnace is a system where each component serves a distinct and critical purpose in the melting process. Understanding these parts reveals how the technology achieves its results.
The Crucible (The Containment Vessel)
The crucible is the central container that holds the charge, which is the metal to be melted. It is made from a refractory material, meaning it can withstand extreme temperatures without melting, reacting with the metal, or conducting electricity.
This non-conductive property is crucial. It ensures that the magnetic field passes through the crucible and only induces heat in the conductive metal charge inside.
The Induction Coil (The Engine)
Wrapped around the outside of the crucible is the induction coil, typically made of hollow copper tubing. A powerful, high-frequency alternating current is passed through this coil.
This coil's function is to generate the intense, rapidly reversing magnetic field that is the basis of induction heating. Because of the immense electrical currents involved, the copper tubing is water-cooled to prevent the coil itself from overheating and melting.
The Power Supply Unit (The Control Center)
The power supply is far more than a simple connection to the electrical grid. It is a sophisticated unit consisting of a transformer, an inverter, and a bank of capacitors.
This unit takes standard utility power and converts it into the high-amperage, high-frequency current required by the induction coil. The control system allows operators to precisely regulate this power, giving them exact control over the melting rate and final temperature.
The Furnace Body and Support Structure
The entire assembly of the crucible and coil is housed within a sturdy steel shell or frame. This body provides structural integrity, protects the components, and often includes a tilting mechanism to allow for the safe pouring of molten metal. Fume extraction hoods are also integrated to manage any vapors released from the melt.
How the Construction Enables Induction Heating
The physical arrangement of these components is designed specifically to leverage a fundamental law of physics: electromagnetic induction.
1. Creating the Magnetic Field
When the power supply sends high-frequency alternating current into the copper coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field that penetrates the area inside the coil.
2. Inducing Eddy Currents
This magnetic field passes through the crucible and into the metallic charge. According to Faraday's Law of Induction, the changing magnetic field induces small, circular electrical currents within the metal itself. These are known as eddy currents.
3. Generating Heat via Resistance
As these eddy currents swirl through the metal, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This friction generates intense heat through a process called Joule heating. The metal effectively becomes its own heating element, melting rapidly and uniformly from the inside out.
Understanding the Design Advantages
The unique construction of an induction furnace directly leads to several significant operational advantages over traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
Unmatched Precision and Temperature Control
Because the heat is generated by a tightly controlled electrical current, operators can increase, decrease, or hold the temperature with a level of accuracy that is difficult to achieve with combustion. This results in minimal temperature difference throughout the melt and is vital for producing high-quality alloys.
High Energy Efficiency
Traditional furnaces heat a chamber and rely on radiation and convection to transfer that heat to the metal, losing a significant amount of energy to the surrounding environment. Induction heating is direct, generating heat only where it is needed—within the metal itself. This minimizes thermal loss and makes the process highly energy-efficient.
A Cleaner Melting Process
Induction melting is a completely clean process from an energy standpoint. There is no combustion, which means no byproducts like smoke, ash, or carbon dioxide are introduced into the melt or the atmosphere. This helps preserve the purity of valuable metals and significantly reduces the facility's environmental footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The construction of an induction furnace is a direct reflection of its intended function. Its design offers specific advantages depending on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material purity and alloying: The non-combustion, contained design is ideal for preserving expensive alloys and preventing contamination of the melt.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and speed: The direct heating via eddy currents minimizes energy waste, reduces melting time, and allows for quicker operational cycles.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact and workplace safety: The enclosed, flameless operation creates a cleaner, cooler, and safer working environment while eliminating direct fossil fuel emissions.
Ultimately, the construction of an induction furnace represents a sophisticated solution engineered for modern, precise, and efficient metal processing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material / Type | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible | Refractory (non-conductive) | Holds the metal charge; withstands extreme heat. |
| Induction Coil | Hollow, water-cooled copper | Generates the alternating magnetic field for heating. |
| Power Supply | Transformer, Inverter, Capacitors | Converts standard power to high-frequency current for the coil. |
| Furnace Body | Steel frame/structure | Provides support, housing, and often a tilting mechanism. |
Ready to enhance your lab's melting capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for precision, efficiency, and purity. Whether you are working with precious metals, advanced alloys, or require a cleaner melting process, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an induction furnace can revolutionize your workflow and deliver superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does high frequency induction heating work? Unlock Fast, Precise, and Efficient Heat
- What type of furnace do I need to melt steel? The Definitive Guide to Induction Furnaces
- How accurate is vacuum casting? Achieve High-Fidelity Prototypes and Low-Volume Production
- How efficient is induction heating? Discover the Power of Direct, Internal Heating
- What metals cannot be induction heated? A guide to material suitability and heating efficiency.
- How can I increase the efficiency of my induction furnace? A Holistic Guide to Lower Costs & Higher Output
- How to choose an induction furnace? A Guide to Matching Capacity, Power, and Frequency
- What is the process of melting in an induction furnace? Harnessing Electromagnetic Power for Efficient Metal Melting



















