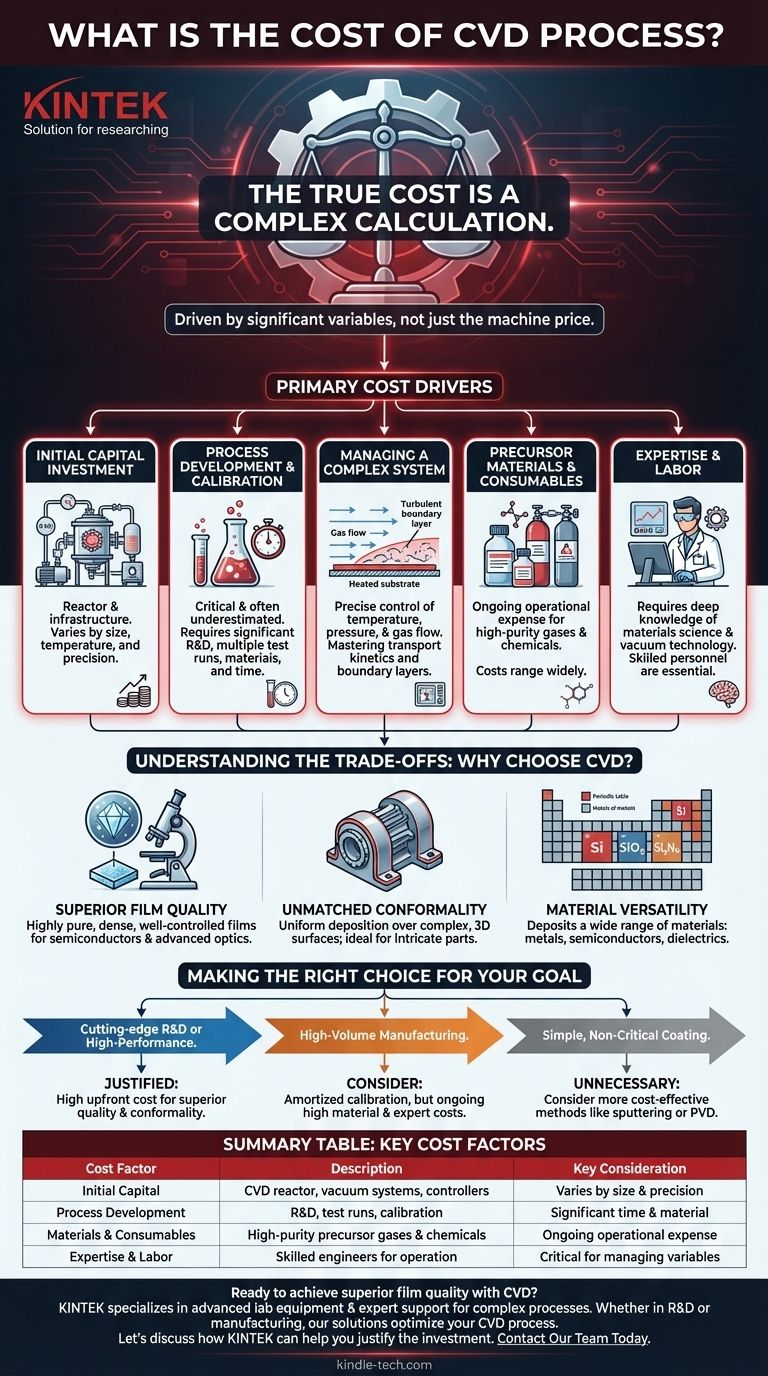
The true cost of a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is not a single number, but a complex calculation driven by significant variables. While the initial equipment can be expensive, the dominant costs often arise from the intricate process development and operational expertise required, a direct result of the complex physics and chemistry involved in managing gas transport and surface reactions.
The cost of CVD is defined less by the price of the machine and more by the investment in time, materials, and expertise needed to overcome its inherent operational complexity and calibrate it for a specific application.

The Primary Cost Drivers in CVD
Understanding the cost of CVD requires looking beyond the initial purchase price and examining the factors that contribute to the total cost of ownership over the lifetime of a project or product.
Initial Capital Investment
The most obvious cost is the CVD reactor and its supporting infrastructure. This includes the reaction chamber, vacuum systems, gas delivery controllers, and heating elements. The price of this equipment varies dramatically based on size, temperature range, and precision.
Process Development and Calibration
This is a critical, often underestimated cost driver. As the underlying process is incredibly complex, achieving a successful, repeatable film deposition requires significant R&D.
The need for multiple test runs to calibrate the system is a direct operational cost. These runs consume valuable precursor materials, energy, and, most importantly, the time of highly skilled engineers.
Managing a Complex System
The CVD process involves a delicate balance of intertwined factors. Parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates must be precisely controlled.
Furthermore, managing the transport kinetics of gas species—the complex convection and diffusion of chemicals—is a non-trivial challenge. A phenomenon known as the stagnant boundary layer, a layer of slow-moving gas just above the substrate, can impede uniform deposition and requires careful process design to manage.
Precursor Materials and Consumables
CVD relies on high-purity precursor gases and chemicals, which are an ongoing operational expense. The cost of these materials can range from moderate to extremely high, depending on the desired film composition.
Expertise and Labor
Operating and maintaining a CVD system is not a push-button operation. It requires personnel with a deep understanding of materials science, chemistry, and vacuum technology. The cost of hiring and retaining this expertise is a significant factor.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Choose CVD?
Given these complexities and costs, the decision to use CVD is based on the unique advantages it offers over simpler deposition techniques. The investment is justified when the final film quality is the highest priority.
Superior Film Quality
CVD is renowned for its ability to produce highly pure, dense, and well-controlled films. It allows for precise control over the material's crystalline structure and stoichiometry, which is critical for applications in semiconductors and advanced optics.
Unmatched Conformality
One of CVD's defining features is its ability to deposit a uniform film over complex, three-dimensional surfaces. The gaseous precursors can reach and react on all exposed surfaces, making it ideal for coating intricate components where line-of-sight techniques like sputtering would fail.
Material Versatility
The CVD process is exceptionally versatile, capable of depositing a wide range of materials, including metals, semiconductors (like silicon), and dielectrics (like silicon nitride or silicon dioxide).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to invest in CVD should be weighed against your specific technical and commercial requirements.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge R&D or high-performance components: The high upfront cost and process development effort of CVD are justified by the superior film quality, purity, and conformality it delivers.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: The initial calibration costs can be amortized, but the ongoing expense of high-purity materials and expert oversight remains a key consideration.
- If your primary focus is a simple, non-critical coating on a flat surface: The complexity and expense of CVD are likely unnecessary; more cost-effective methods like sputtering or physical vapor deposition (PVD) should be considered.
Ultimately, choosing CVD is an investment in achieving material properties that other methods simply cannot provide.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Capital | CVD reactor, vacuum systems, gas controllers | Varies by size, temperature, and precision |
| Process Development | R&D, multiple test runs, calibration | Significant time and material investment |
| Materials & Consumables | High-purity precursor gases and chemicals | Ongoing operational expense |
| Expertise & Labor | Skilled engineers for operation and maintenance | Critical for managing complex system variables |
Ready to achieve superior film quality and conformality with CVD?
The cost of CVD is an investment in unparalleled performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support needed to master complex processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether you're in R&D or high-volume manufacturing, our solutions are designed to meet the precise demands of your laboratory.
Let's discuss how KINTEK's expertise can help you optimize your CVD process and justify the investment. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















