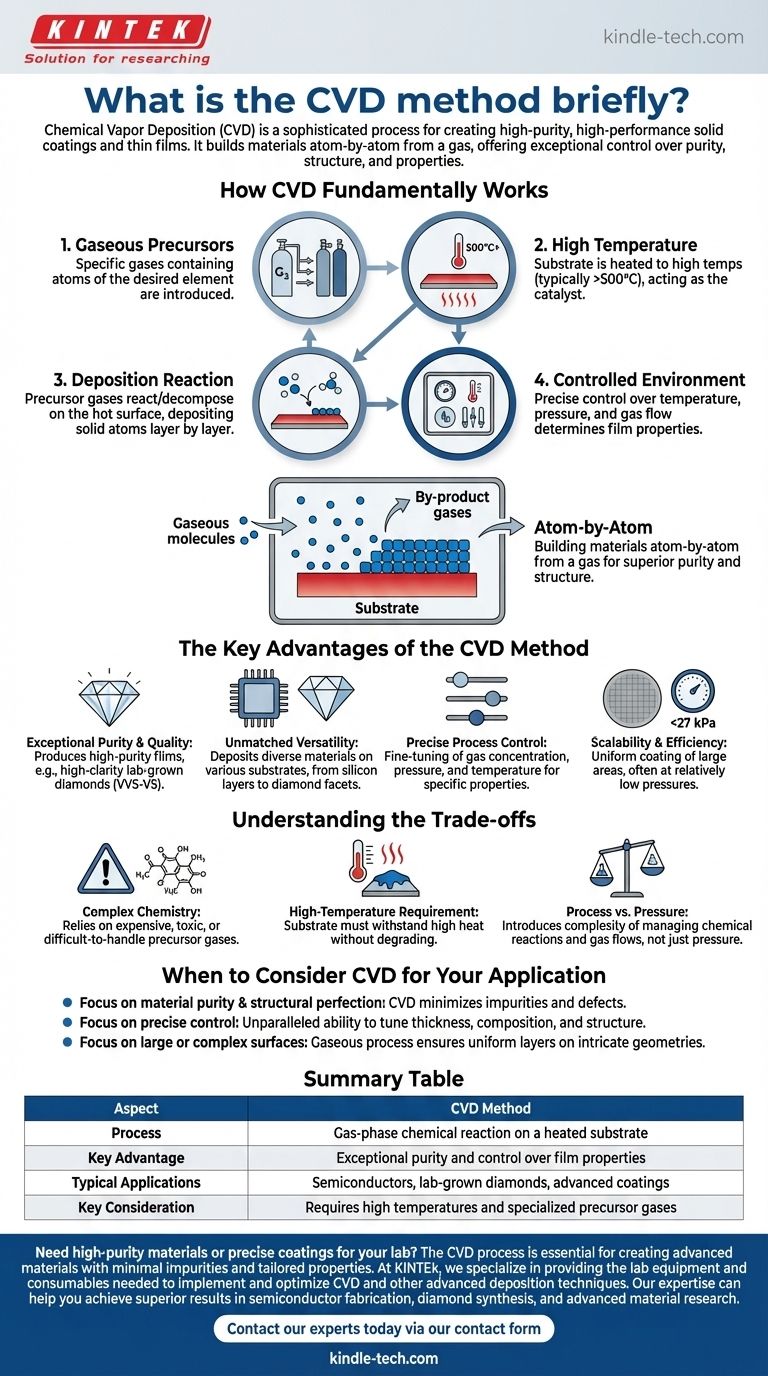
In short, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated process used to create high-purity, high-performance solid coatings and thin films. It works by introducing reactive gases into a chamber containing a heated object (substrate), where a chemical reaction or decomposition occurs on the object's surface, depositing the desired material layer by layer.
The core principle of CVD is not about melting or physically applying a material, but about building it atom-by-atom from a gas. This gives engineers exceptional control over the final material's purity, structure, and properties, making it a cornerstone for manufacturing advanced materials like semiconductors and lab-grown diamonds.
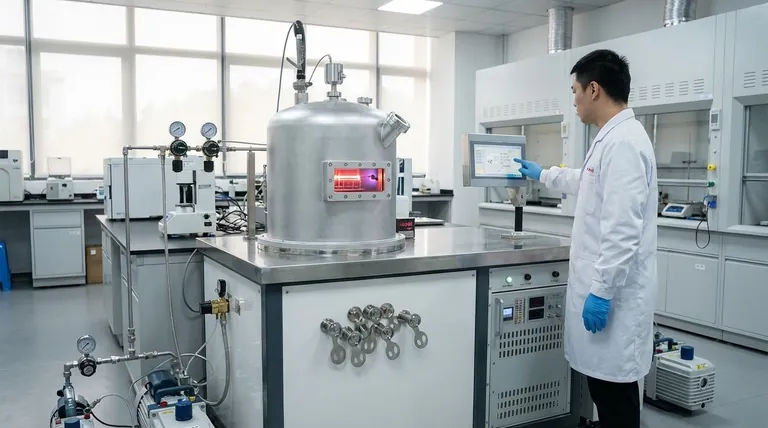

How CVD Fundamentally Works
The CVD process can be broken down into a few essential stages, all occurring within a controlled chamber or reactor.
The Gaseous Precursors
The process begins by introducing specific gases, known as precursors, into the chamber. These gases contain the atoms of the element you wish to deposit.
The Role of High Temperature
The substrate—the object being coated—is heated to a high temperature, typically above 500°C. This thermal energy is the catalyst that drives the entire process.
The Deposition Reaction
When the precursor gases come into contact with the hot substrate, the thermal energy causes them to react or decompose. The solid atoms from this reaction then bond to the surface, forming a thin, solid film.
A Controlled Environment
This entire sequence takes place under carefully managed conditions. Parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates are precisely controlled to dictate the final properties of the deposited film.
The Key Advantages of the CVD Method
Engineers choose CVD when the quality and specific properties of the final material are paramount.
Exceptional Purity and Quality
CVD can produce extremely high-purity films, whether they are single-crystal, polycrystalline, or amorphous. In applications like diamond synthesis, this results in very high clarity (VVS-VS grades) and an absence of the metallic inclusions common in other methods.
Unmatched Versatility
The technique is remarkably versatile, capable of depositing a wide range of pure and complex materials onto many different types of substrates. It is used to create everything from the silicon layers in microchips to the brilliant facets of lab-grown diamonds.
Precise Process Control
The final chemical and physical properties of the film can be finely tuned. By adjusting the gas concentration, pressure, and temperature, operators can precisely engineer the coating for a specific application.
Scalability and Efficiency
CVD allows for the uniform coating of large surface areas. Furthermore, it often operates at relatively low pressures (under 27 kPa), which can make the equipment setup less costly compared to extreme high-pressure alternatives like HPHT.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is a specialized technique with its own set of considerations.
Complex Chemistry
The "chemical" aspect of CVD means the process relies on precursor gases that can be expensive, toxic, or difficult to handle, requiring sophisticated safety and delivery systems.
High-Temperature Requirement
The need for high temperatures means the substrate material must be able to withstand the heat without deforming or degrading. This can limit the types of materials that can be coated.
Process vs. Pressure
CVD is distinct from physical methods. While it avoids the immense pressures of techniques like HPHT, it introduces the complexity of managing chemical reactions, gas flows, and by-product removal.
When to Consider CVD for Your Application
Choosing the right deposition method depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity and structural perfection: CVD is a superior choice for creating films and crystals with minimal impurities or defects.
- If your primary focus is precise control over film properties: CVD offers unparalleled ability to tune characteristics like thickness, composition, and crystal structure.
- If your primary focus is coating large or complex-shaped surfaces uniformly: The gaseous nature of the process allows it to deposit even layers on intricate geometries.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition is a foundational technology that enables the creation of materials that would be impossible to produce by other means.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Method |
|---|---|
| Process | Gas-phase chemical reaction on a heated substrate |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional purity and control over film properties |
| Typical Applications | Semiconductors, lab-grown diamonds, advanced coatings |
| Key Consideration | Requires high temperatures and specialized precursor gases |
Need high-purity materials or precise coatings for your lab?
The CVD process is essential for creating advanced materials with minimal impurities and tailored properties. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to implement and optimize CVD and other advanced deposition techniques.
Our expertise can help you achieve superior results in semiconductor fabrication, diamond synthesis, and advanced material research. Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems



















