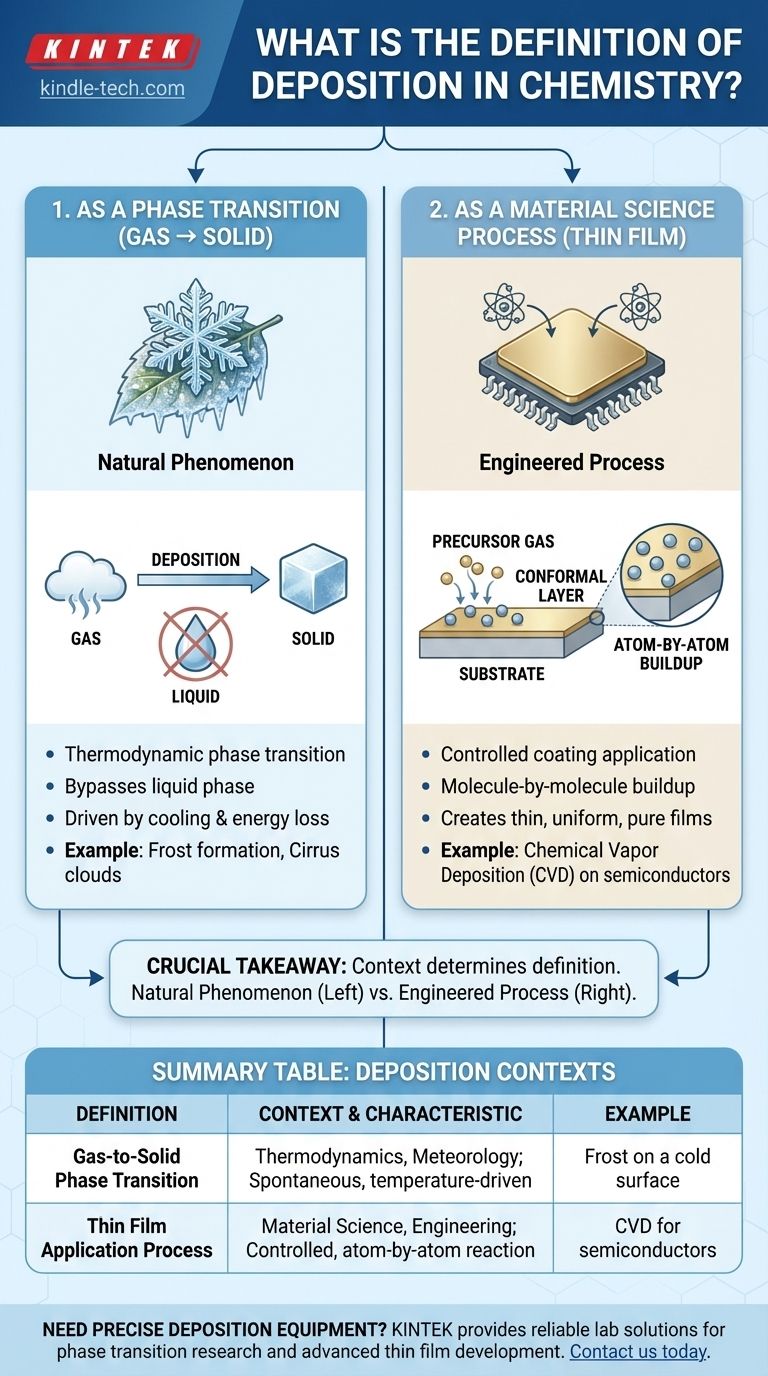
In chemistry, the term "deposition" has two primary meanings. It most commonly refers to the thermodynamic phase transition where a substance in a gaseous state changes directly into a solid, bypassing the liquid phase. It also describes a set of processes in material science where a substance is deposited, often molecule by molecule, onto a surface to form a thin, solid film.
The crucial takeaway is that "deposition" can describe either a natural phase change (like frost forming) or a highly controlled industrial process (like coating a computer chip). The specific context determines which definition applies.

Understanding Deposition as a Phase Transition
From Gas Directly to Solid
Deposition is the reverse process of sublimation (solid to gas). This phase change occurs when gas molecules cool and lose enough thermal energy to settle into a rigid, crystalline structure without first condensing into a liquid.
Common Examples in Nature
A classic example is the formation of frost on a cold surface. Water vapor in the air (a gas) comes into contact with a surface below freezing point and turns directly into ice crystals (a solid).
Another large-scale example is the formation of high-altitude cirrus clouds, which are composed of ice crystals that formed directly from water vapor in the upper atmosphere.
Deposition as a Material Science Process
What is Chemical Deposition?
In manufacturing and engineering, deposition refers to a family of techniques used to apply a coating to a surface, known as a substrate.
These processes typically involve a fluid precursor, often a gas, which undergoes a chemical reaction at the substrate's surface. This reaction leaves behind a solid layer, creating a thin or thick film.
The Goal: Creating Thin Films
The objective is to build a new layer on the substrate, atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule. This highly controlled method allows for the creation of extremely thin, pure, and uniform coatings that alter the substrate's properties, such as its electrical conductivity, hardness, or resistance to corrosion.
Key Characteristic: Conformal Layers
A significant advantage of many chemical deposition techniques, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), is that the resulting films are conformal. This means the coating uniformly covers the entire surface topography, including any microscopic crevices or bumps, rather than just settling on the top surfaces.
Why Context Is Critical
Natural Phenomenon vs. Engineered Process
The two definitions describe fundamentally different scales and intentions. One is a macroscopic, often spontaneous, natural phenomenon driven by changes in temperature and pressure.
The other is a precise, engineered process used in high-tech applications like manufacturing semiconductors, solar cells, and protective tool coatings.
Different Mechanisms at Play
While both involve molecules settling from a fluid onto a solid surface, the mechanisms are distinct. The phase transition is a physical process governed by thermodynamics.
Chemical deposition, however, is a complex process involving controlled chemical reactions at a surface to deliberately build a specific material with desired properties.
Applying the Correct Definition
To interpret the term correctly, always consider the field of study.
- If your primary focus is thermodynamics or meteorology: Deposition almost always refers to the gas-to-solid phase transition.
- If your primary focus is material science, engineering, or manufacturing: Deposition refers to the controlled process of applying a thin film to a substrate.
Understanding both definitions provides a complete picture of how chemical processes operate, from the natural world to advanced technology.
Summary Table:
| Definition | Context | Key Characteristic | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas-to-Solid Phase Transition | Thermodynamics, Meteorology | Spontaneous process driven by temperature/pressure change | Frost formation on a cold surface |
| Thin Film Application Process | Material Science, Engineering | Controlled, atom-by-atom coating via chemical reaction | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for semiconductors |
Need precise deposition equipment for your lab? Whether you're researching phase transitions or developing advanced thin films, KINTEK provides the reliable lab equipment and consumables you need. From basic research to high-tech manufacturing, our solutions ensure accuracy and repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific deposition requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is argon used in magnetron sputtering? Unlock the Secret to Efficient, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is the trend in Synthetic Diamonds? Exponential Growth Reshaping the Gemstone Market
- How can you improve corrosion resistance? Extend Equipment Life with Proven Strategies
- What is the thermal debinding process? A Guide to Safe Binder Removal for MIM & Ceramics
- How does the sputtering process work? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- How can we make plastic more sustainable? A Strategic Guide to Recycling, Bioplastics, and Reduction
- What are the advantages of using a centrifuge? Achieve Rapid, High-Resolution Sample Separation
- What is a pyrolysis fluidized bed reactor? Maximize Bio-Oil Yield with Superior Heat Transfer



















