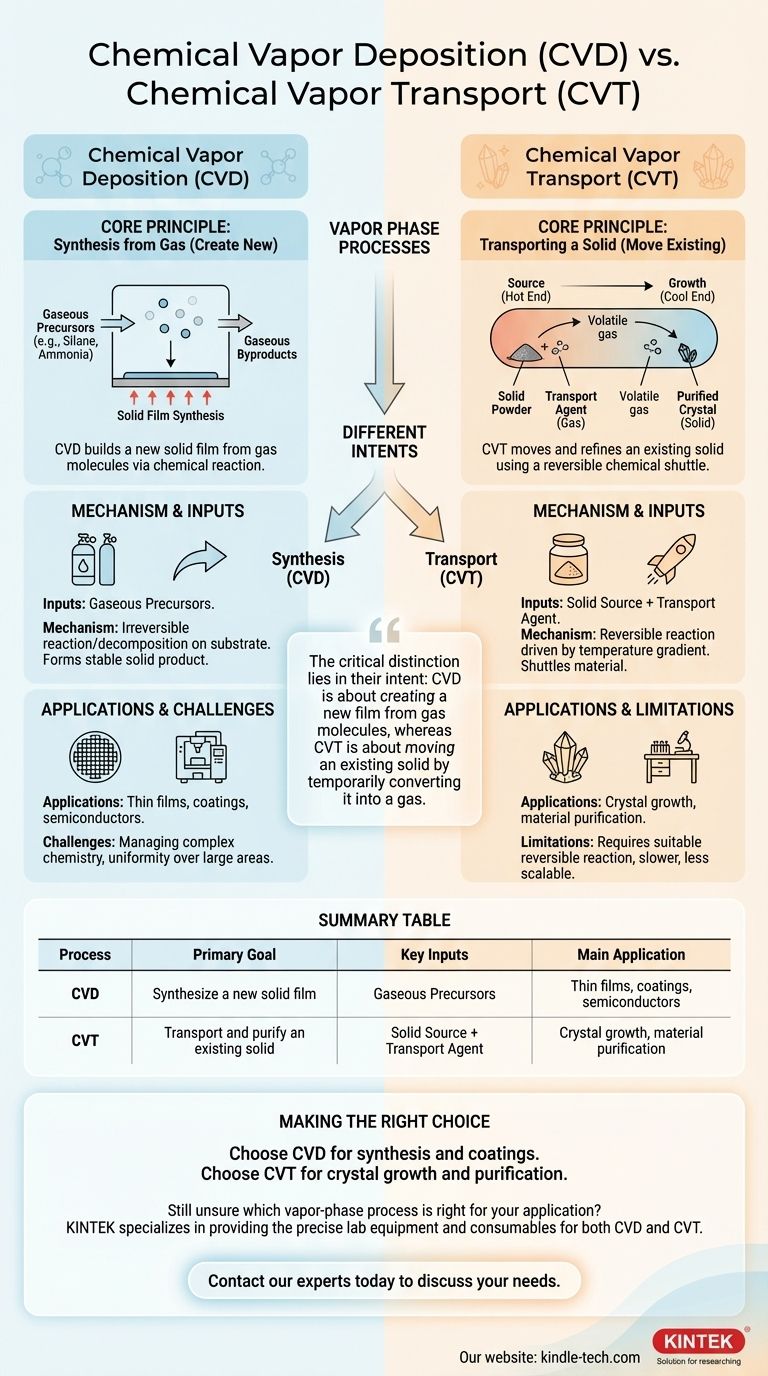
The fundamental difference is their primary purpose. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process that synthesizes a new, solid material directly from gaseous precursors onto a substrate. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) is a process used to transport and purify an existing solid material from one location to another using a reversible chemical reaction.
While both processes operate in the vapor phase, the critical distinction lies in their intent: CVD is about creating a new film from gas molecules, whereas CVT is about moving an existing solid by temporarily converting it into a gas.

Deconstructing Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a versatile and widely used technique for producing high-quality thin films and coatings. Its foundation is the synthesis of a new material directly on a surface.
The Core Principle: Synthesis from Gas
The goal of CVD is to build a solid film from the ground up. This is achieved by introducing one or more reactive gases, known as precursors, into a reaction chamber containing the object to be coated (the substrate).
The Mechanism of Deposition
The process involves a series of carefully controlled steps. Gaseous precursors are transported to the substrate's surface, where the heat (or plasma) provides the energy for a chemical reaction or decomposition to occur.
This reaction forms a stable solid product that deposits and grows on the surface, creating the desired film. Gaseous byproducts from the reaction are then transported away and exhausted from the chamber.
Key Inputs: Gaseous Precursors
In CVD, the starting materials are the gases themselves. For example, to deposit a silicon nitride film, gaseous precursors like silane (SiH₄) and ammonia (NH₃) might be used. These gases react to form solid Si₃N₄ on the substrate.
Deconstructing Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT)
CVT is a more specialized technique, often used in research and for producing high-purity single crystals. Its purpose is not to create a new material but to move and refine an existing one.
The Core Principle: Transporting a Solid
Imagine you have a solid powder of a material and you want to grow a perfect, large crystal of that same material. CVT is the process to achieve this. It uses a chemical "shuttle" to pick up the material at one end and drop it off at the other.
The Reversible Reaction Mechanism
CVT relies entirely on a reversible chemical reaction. The process occurs in a sealed tube with a temperature gradient (one end is hotter than the other).
- Forward Reaction (Source): At the "source" end, the solid material you want to transport reacts with a gaseous transport agent. This reaction converts the solid into a new, volatile gas molecule.
- Reverse Reaction (Growth): This new gas molecule diffuses to the other end of the tube (the "growth" end), which is at a different temperature. The temperature change causes the reaction to reverse, re-depositing the original solid material—often in a much purer, crystalline form. The transport agent gas is released and is free to shuttle more material.
Key Inputs: Solid Source + Transport Agent
The starting materials for CVT are the solid powder of the substance you wish to transport and a separate transport agent gas. The transport agent's only job is to act as a temporary chemical taxi for the solid material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The fundamental difference in mechanism dictates where these processes are used and what challenges they present.
CVD Applications and Challenges
CVD is an industrial workhorse for creating protective coatings, semiconductor layers, and optical films. Its main challenge lies in managing the complex chemistry of precursors and ensuring uniform temperature and gas flow to achieve a consistent film over a large area.
CVT Applications and Limitations
CVT is primarily a laboratory technique for crystal growth and material purification. Its major limitation is the need for a suitable, reversible chemical reaction and a compatible transport agent for the specific material, which is not always available. The process is generally slower and less scalable than CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines which process is appropriate.
- If your primary focus is applying a new coating or thin film onto a substrate (e.g., depositing titanium nitride on a tool bit): CVD is the correct choice because its purpose is to synthesize a new material layer from gaseous precursors.
- If your primary focus is purifying an existing solid or growing a large, high-quality single crystal of a specific compound (e.g., growing a MoS₂ crystal from powder): CVT is the appropriate method because it is designed to transport and recrystallize an existing material.
Ultimately, understanding this core difference between synthesis and transport is the key to mastering vapor-phase material processing.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Inputs | Main Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Synthesize a new solid film | Gaseous Precursors | Thin films, coatings, semiconductors |
| Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) | Transport and purify an existing solid | Solid Source + Transport Agent | Crystal growth, material purification |
Still unsure which vapor-phase process is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for both CVD and CVT processes. Whether you are developing new thin films or growing high-purity crystals, our expertise can help you achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material processing needs and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application



















