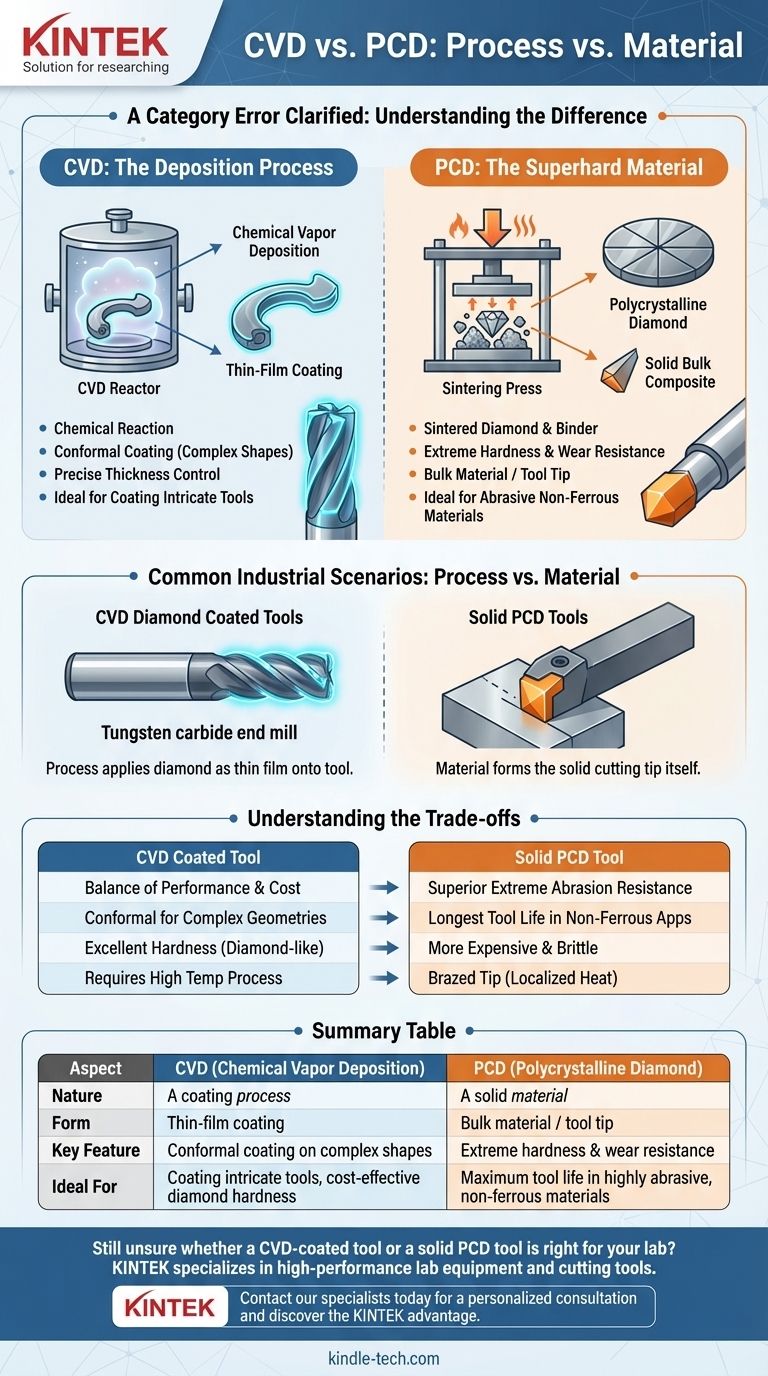
At its core, the comparison is a category error. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process used to apply a thin film coating, while Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) is a material used to create superhard cutting tools. You don't choose between them; rather, you might use the CVD process to apply a diamond coating to a tool, or you might use a tool made from solid PCD material.
The central point of confusion is thinking of CVD and PCD as direct alternatives. The correct way to frame it is: CVD is a method of application, whereas PCD is a type of superhard material. Understanding this distinction is the key to selecting the right technology for your application.

What is CVD? The Deposition Process
Chemical Vapor Deposition, or CVD, is a technique that uses chemical reactions to create high-performance, thin-film coatings on a substrate.
How It Works: A Chemical Reaction
The process involves placing a part (the substrate) in a vacuum chamber and introducing volatile precursor gases.
When heated, these gases react or decompose on the part's surface, forming a new, solid layer of material. This is a purely chemical bonding process, resulting in an exceptionally strong and durable coating.
Key Characteristics of the CVD Process
The primary strength of CVD is its ability to create a conformal coating. This means the film perfectly follows every contour of a complex or three-dimensional shape, including internal surfaces.
The process also allows for precise control over the coating's thickness and uniformity, making it ideal for applications that demand high precision.
What is PCD? The Superhard Material
Polycrystalline Diamond, or PCD, is not a coating process but a solid composite material.
How It's Made: Sintering Diamond Crystals
PCD is produced by sintering—fusing together micron-sized diamond particles with a metallic binder (often cobalt) under immense heat and pressure.
The result is a solid wafer or "blank" of diamond material. These blanks are then typically cut and brazed onto a carbide tool body to form the cutting edge of a tool.
Key Characteristics of PCD Material
PCD is valued for its extreme hardness and wear resistance, second only to natural diamond. It provides exceptional tool life when working with highly abrasive materials.
It is considered a bulk material or a tool "tip," not a thin-film coating applied over the entire tool.
Clarifying the Relationship: Process vs. Material
The confusion between CVD and PCD arises because both are associated with "diamond" tooling. The key is to separate the "how" from the "what."
CVD is the "How," PCD is the "What"
You use a process (like CVD) to apply a material (like diamond) as a thin film.
Alternatively, you can make the tool itself out of a solid material (like PCD).
Common Industrial Scenarios
There are two distinct applications:
- Solid PCD Tools: A piece of PCD material is brazed onto a tool, acting as the cutting tip. This is common for machining abrasive non-ferrous materials like high-silicon aluminum or carbon composites.
- CVD Diamond Coated Tools: A standard tool (often tungsten carbide) is placed in a reactor, and the CVD process is used to grow a thin layer of pure diamond directly onto its surface.
Furthermore, it is sometimes beneficial to use the CVD process to apply a different type of coating onto a PCD tool to enhance other properties like thermal stability or corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a solid PCD tool and a CVD diamond-coated tool involves a direct trade-off between performance, application, and cost.
When to Choose a Solid PCD Tool
Solid PCD is the superior choice for extreme abrasion resistance. Its thick, solid diamond edge offers the longest possible tool life in demanding, non-ferrous applications. However, it is typically more expensive and can be more brittle.
When to Choose a CVD Diamond Coated Tool
A CVD diamond coating provides an excellent balance of performance and cost. It imparts diamond-like hardness to a tougher and less expensive substrate like carbide. The conformal nature of CVD also makes it suitable for coating complex tool geometries, like drills or end mills with intricate flutes.
Limitations to Consider
The high temperatures required for the CVD process (often >700°C) can potentially affect the underlying substrate material, which must be considered during tool design. In contrast, brazing a PCD tip occurs at a localized point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven entirely by your specific application and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum tool life in highly abrasive non-ferrous materials: A solid PCD tool is almost always the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is adding diamond hardness to complex tools at a lower cost: A CVD diamond-coated carbide tool is the more practical solution.
- If your primary focus is coating intricate internal or 3D surfaces uniformly: The CVD process itself is uniquely capable of meeting this need, regardless of the coating material.
Ultimately, understanding that you are choosing between a solid material and a coating process empowers you to select the technology that will deliver the best performance for your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | A coating process | A solid material |
| Form | Thin-film coating | Bulk material / tool tip |
| Key Feature | Conformal coating on complex shapes | Extreme hardness & wear resistance |
| Ideal For | Coating intricate tools, cost-effective diamond hardness | Maximum tool life in highly abrasive, non-ferrous materials |
Still unsure whether a CVD-coated tool or a solid PCD tool is right for your lab's specific materials and application?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced cutting tools. Our experts can help you analyze your needs and select the perfect solution to maximize efficiency, tool life, and cost-effectiveness.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK advantage.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers



















