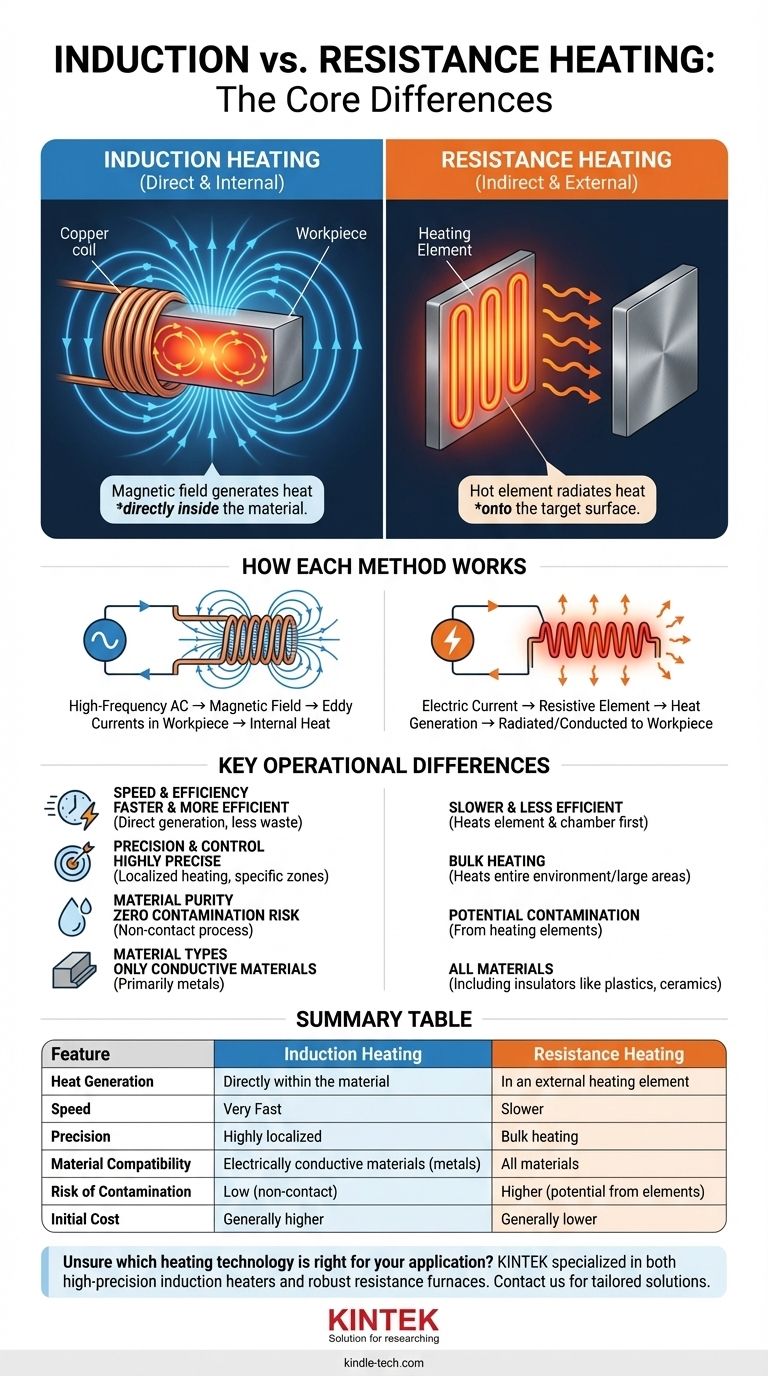
At its core, the difference is simple: resistance heating uses a hot element to radiate heat onto a target, much like a conventional oven. In contrast, induction heating uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly inside the target material itself. This fundamental distinction in how and where heat is generated dictates the efficiency, speed, precision, and ideal applications for each method.
The critical distinction is that resistance heating is an indirect process that heats an external element, while induction heating is a direct process that uses magnetic fields to make the material heat itself from within. This makes induction faster, more precise, and often more efficient for specific tasks.
How Each Method Works
To truly grasp the difference, you must understand the underlying physics of heat generation in each system. They are fundamentally distinct approaches to achieving the same goal.
The Principle of Resistance Heating
Resistance heating is the most familiar form of electric heat. It works by passing an electrical current through a material with high electrical resistance, often called a heating element.
As electrons are forced through this resistive material, they collide with atoms, creating friction and generating intense heat. This heat is then transferred to the target workpiece via conduction, convection, or radiation. Think of a toaster, an electric stovetop, or a large industrial furnace with glowing coils.
The Principle of Induction Heating
Induction heating is a non-contact process. It begins with a high-frequency alternating current (AC) passed through a copper coil, known as the inductor.
This AC creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil. When a conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed within this field, the field induces electrical currents, called eddy currents, to flow directly within the workpiece. The material's own internal resistance fights against these eddy currents, generating precise, internal heat.
Key Operational Differences
The "direct vs. indirect" nature of these methods leads to significant differences in performance, control, and application suitability.
Speed and Efficiency
Induction heating is almost always faster because it does not waste time or energy heating an element or a surrounding chamber. Heat is generated instantly within the part itself.
This direct generation makes induction highly energy-efficient for many processes, as nearly all the electrical energy is converted to useful heat within the workpiece, with minimal loss to the environment.
Precision and Control
Induction allows for exceptionally precise and localized heating. By designing the shape of the coil and controlling the frequency, you can heat a specific zone of a part—like the tip of a screwdriver or a single gear tooth—without affecting the rest of it.
Resistance heating is typically a bulk heating process. It heats the entire environment within a furnace, making it difficult to target small, specific areas with any degree of accuracy.
Material Purity and Contamination
In processes like melting high-purity metals, induction holds a significant advantage. Because it is a non-contact method, the workpiece never touches a heating element.
This eliminates the risk of contamination. In contrast, resistance heating in some furnace types (like electric arc furnaces which use graphite electrodes) can introduce impurities, such as carbon, into the melt. This makes induction essential for producing alloys with very low carbon content.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior. The choice depends entirely on a project's specific constraints and goals.
The Limitations of Induction Heating
Induction's primary limitation is that it only works on electrically conductive materials, primarily metals. It cannot directly heat plastics, ceramics, or other insulators.
The equipment is also more complex and generally has a higher initial capital cost than a comparable resistance heating system. Furthermore, the induction coil often needs to be designed and shaped for a specific part geometry to be efficient.
The Limitations of Resistance Heating
Resistance heating is often slower and less energy-efficient than induction, as significant energy is lost heating the furnace chamber and insulation.
Achieving very high temperatures can be challenging, requiring complex and expensive high-temperature insulation to prevent massive heat loss. As mentioned, there is also a potential for material contamination from the heating elements themselves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on your specific requirements for speed, precision, material compatibility, and budget.
- If your primary focus is rapid, precise, and repeatable heating of metal parts: Induction heating offers superior control and efficiency for tasks like surface hardening, brazing, or annealing specific zones.
- If your primary focus is melting high-purity alloys with zero contamination: Induction heating is the superior, and often only, viable option.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating of various materials at a lower initial cost: Resistance heating in a furnace is often the more practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials like plastics or ceramics: Resistance heating is your default method, as induction requires a conductive target.
By understanding whether you need to heat the environment or the workpiece itself, you can confidently select the right technology for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Resistance Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Directly within the material | In an external heating element |
| Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Precision | Highly localized | Bulk heating |
| Material Compatibility | Electrically conductive materials (metals) | All materials |
| Risk of Contamination | Low (non-contact) | Higher (potential from elements) |
| Initial Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Unsure which heating technology is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, from high-precision induction heaters to robust resistance furnaces, tailored to your specific material and process requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your efficiency, precision, and results. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How do multiple cartridge heaters and K-type thermocouples work together? Achieve Optimal Temperature Uniformity
- Why does the heating element in a circuit get hot? Discover the Science of Joule Heating
- Why is tungsten so heat resistant? Unlocking Its Atomic Secrets for Extreme Temperatures
- Why tungsten is not used as heating element? Discover the critical role of oxidation resistance.
- How does an electric oven heating element work? The Science of Resistive Heating Explained
- Why use SiC heating elements for Li2ZrO3-MgO synthesis at 1300°C? Achieve Precise Thermal Stability
- Which is better nichrome or tungsten? Choose the Right Heating Element for Your Application
- How long should a heating element last? Maximize your oven's lifespan with these key insights.



















