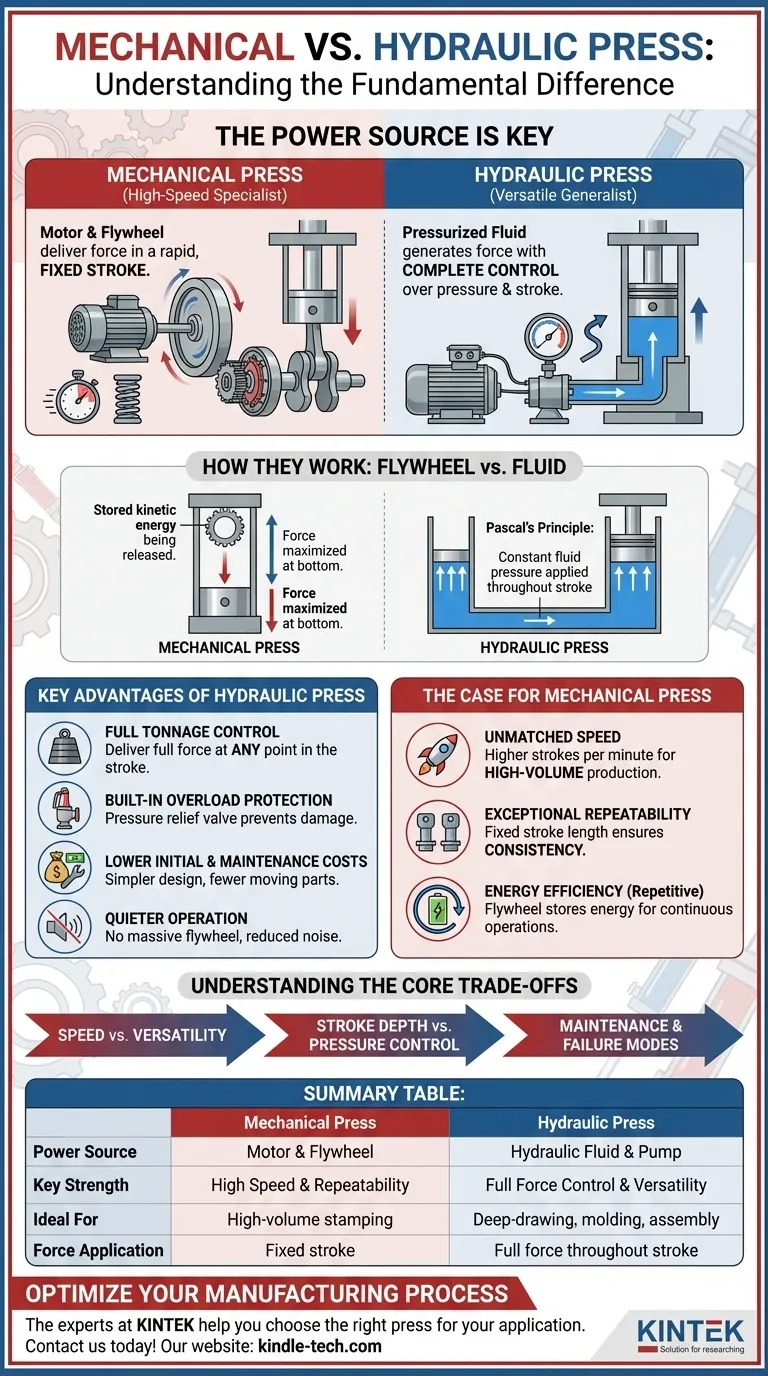
The fundamental difference between a mechanical and hydraulic press lies in its power source. A mechanical press uses a motor and flywheel to deliver force in a rapid, fixed stroke, making it a high-speed specialist. In contrast, a hydraulic press uses pressurized fluid to generate force, allowing for complete control over pressure and stroke length, making it a powerful and versatile generalist.
The choice is not about which press is "better," but which is right for the job. Mechanical presses excel at high-speed, repeatable stamping, while hydraulic presses offer superior force control and versatility for forming, molding, and deep-drawing tasks.
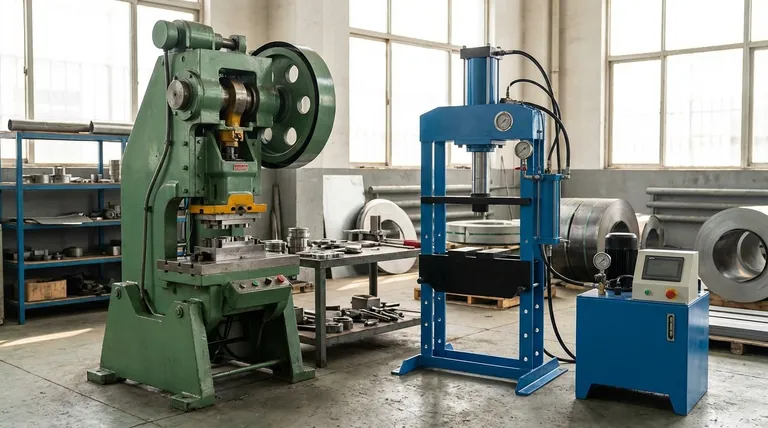

How They Work: Flywheel vs. Fluid
The method of force generation is the core distinction that drives every other difference between these two technologies.
The Mechanical Press: Stored Kinetic Energy
A mechanical press operates using a motor that spins a heavy flywheel.
When activated, a clutch connects this spinning flywheel to a crankshaft, which drives a ram down in a single, rapid motion. The force is greatest at the very bottom of this fixed-length stroke.
The Hydraulic Press: Pascal's Principle in Action
A hydraulic press uses an electric motor to power a pump that pressurizes fluid (typically oil) within a cylinder.
This pressure acts on a piston, driving the ram down. Because the force is generated by constant fluid pressure, it can be applied and held at any point throughout the stroke.
Key Advantages of the Hydraulic Press
Hydraulic systems are known for their flexibility and control, which stem directly from their fluid-power design.
Full Tonnage Control
A hydraulic press can deliver its full, rated force at any point during its stroke. This is essential for applications like deep-drawing, where constant pressure is needed over a long distance.
Built-in Overload Protection
These presses have a pressure relief valve. If the force exceeds a set limit, the valve opens, preventing damage to the press or the tooling. This safety feature is inherent to the design.
Lower Initial and Maintenance Costs
According to industry analysis, hydraulic presses generally have a simpler design with fewer moving parts. This often translates to a lower purchase price and less complex maintenance requirements over the machine's life.
Quieter Operation
The absence of a massive, spinning flywheel and clutched crankshaft makes hydraulic presses significantly quieter than their mechanical counterparts. The operator has more control over the ram speed, further managing noise levels.
The Case for the Mechanical Press
While hydraulic presses are versatile, mechanical presses are the undisputed champions of speed and certain types of precision.
Unmatched Speed for High-Volume Production
The flywheel-based mechanism allows a mechanical press to achieve significantly higher strokes per minute. This makes it the ideal choice for high-volume, repetitive tasks like blanking or shallow stamping.
Exceptional Repeatability
The fixed stroke length of a mechanical press is a key advantage. It ensures that the ram stops at the exact same position on every cycle, providing unparalleled consistency in part depth and coining operations.
Energy Efficiency in Repetitive Tasks
For continuous, high-speed operations, the flywheel acts as an energy reservoir. It stores energy between strokes, leading to high efficiency for its specialized tasks.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Choosing between these technologies means balancing speed against control and simplicity against complexity.
Speed vs. Versatility
A mechanical press is a specialist built for speed. A hydraulic press is a generalist built for versatility and control over the entire pressing process.
Stroke Depth vs. Pressure Control
Mechanical presses offer extreme precision in their final stroke depth. Hydraulic presses offer granular control over the pressure applied throughout the stroke.
Maintenance and Failure Modes
Mechanical presses have more complex components like clutches and bearings that wear over time. Hydraulic presses are simpler but are susceptible to fluid leaks, contamination, or pump issues.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct press technology is critical for optimizing your production process, cost, and final part quality.
- If your primary focus is high-volume stamping or blanking: A mechanical press is the superior choice for its speed and repeatable stroke depth.
- If your primary focus is deep-drawing, molding, or assembly: A hydraulic press provides the necessary constant force and precise pressure control throughout the entire stroke.
- If your primary focus is budget and versatility for varied jobs: A hydraulic press often presents a lower initial cost and greater flexibility for tasks requiring different pressures and stroke lengths.
Understanding these core differences in power delivery empowers you to select the ideal tool for your specific manufacturing goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanical Press | Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Motor & Flywheel | Hydraulic Fluid & Pump |
| Key Strength | High Speed & Repeatability | Full Force Control & Versatility |
| Ideal For | High-volume stamping, blanking | Deep-drawing, molding, assembly |
| Force Application | Fixed stroke, peak force at bottom | Full force at any point in the stroke |
Optimize your manufacturing process with the right press technology.
Choosing between a mechanical and hydraulic press is a critical decision that impacts your production speed, part quality, and overall efficiency. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate this choice.
We specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables, including press solutions tailored to your specific application—whether you require the high-speed precision of a mechanical press or the versatile force control of a hydraulic press.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your needs. Let KINTEK provide the reliable equipment and expert support that your laboratory or production facility deserves.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















