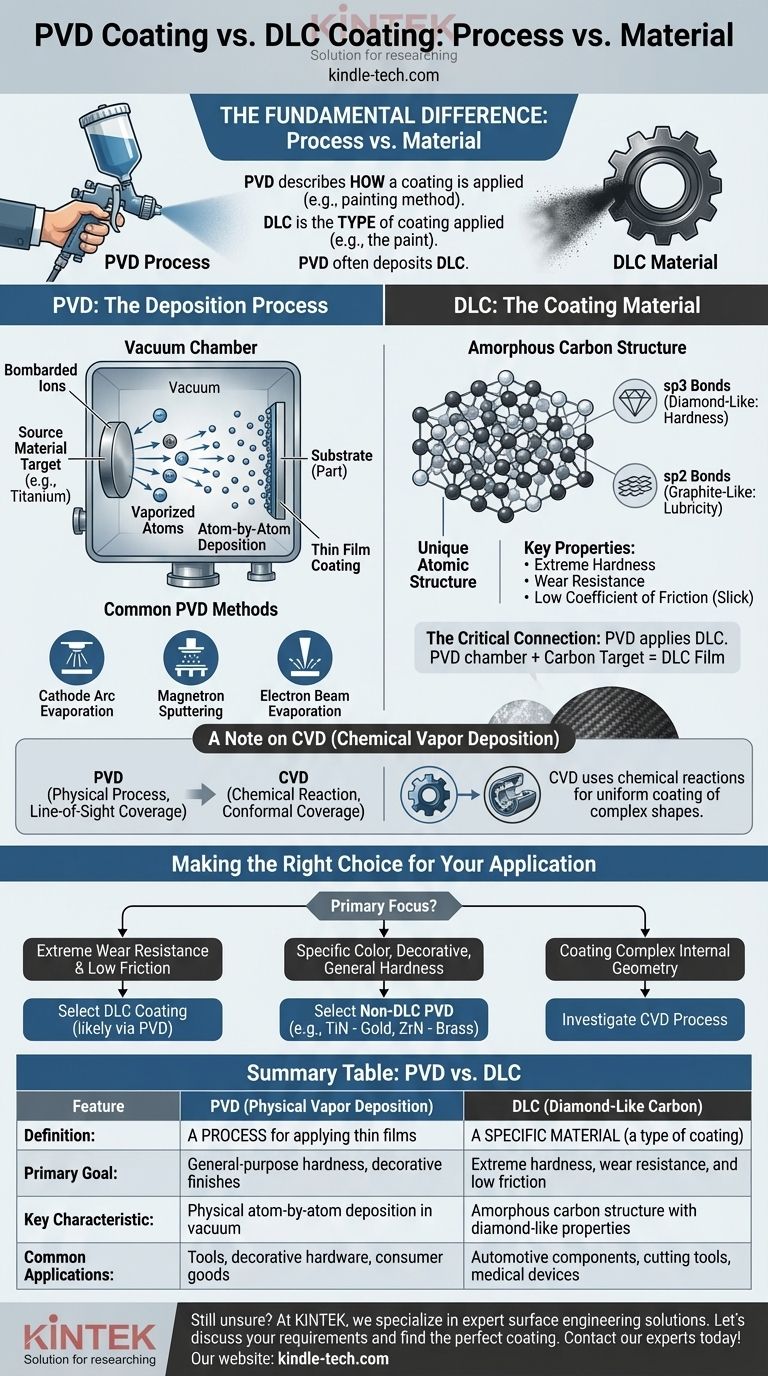
The fundamental difference is that Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a process, while Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a specific material. PVD is a method used to apply a thin film coating to a surface, whereas DLC is one of the many types of coatings that can be applied. In fact, PVD is a very common method used to deposit DLC coatings.
Think of it this way: PVD describes how a coating is applied, like a method of painting. DLC is the type of coating being applied, like the specific paint itself. The two are not mutually exclusive; they work together.
What is PVD? The Deposition Process
PVD is a category of vacuum deposition methods used to produce high-performance thin films. The general principle involves transforming a solid material into a vapor, transporting it through a vacuum, and condensing it onto a target substrate.
The Core Principle: A Vacuum Chamber
The entire PVD process takes place under a high vacuum. This controlled environment is critical to ensure the purity of the coating and prevent contamination from atmospheric gases.
Vaporizing the Source Material
A solid source material, often a metal like titanium or chromium known as a "target," is vaporized. This is achieved through high-energy physical processes like sputtering (bombarding the target with ions) or arc discharge (using a high-current electric arc).
Atom-by-Atom Deposition
The vaporized material travels through the vacuum chamber and deposits onto the part's surface. This deposition happens atom by atom, creating an extremely thin, bonded, and durable layer. Sometimes, a reactive gas like nitrogen is introduced to form metal-ceramic compounds.
Common PVD Methods
PVD is not a single technique but a family of processes. Common methods include cathode arc evaporation, magnetron sputtering, and electron beam evaporation.
What is DLC? The Coating Material
DLC, or Diamond-Like Carbon, is a specific class of amorphous carbon material. It is not pure diamond, but it exhibits many of the valuable properties of diamond.
The Core Principle: Amorphous Carbon
DLC is a unique material that lacks a rigid crystal structure. This amorphous nature is key to its performance, allowing it to be dense and smooth.
Unique Atomic Structure
Its exceptional properties come from a mixture of two types of carbon bonds: sp3 bonds (the hard, tetrahedral bonds found in diamond) and sp2 bonds (the planar, lubricating bonds found in graphite).
Key Properties: Hardness and Lubricity
The high percentage of sp3 bonds gives DLC coatings extreme hardness and wear resistance. The presence of sp2 bonds provides a very low coefficient of friction, making the surface naturally slick or "lubricious."
The Critical Connection to PVD
PVD is one of the primary industrial processes used to apply DLC coatings. A solid carbon target is vaporized in the PVD chamber and deposited onto the substrate to form the diamond-like film.
A Note on CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
While your question focused on PVD, it's important to briefly distinguish it from Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), as they are the two major coating process families.
The Key Difference is Chemistry
Unlike PVD, which is a physical process, CVD uses chemical reactions. Precursor gases are introduced into a chamber where they react and decompose on the substrate's surface, forming the desired coating.
Where CVD Excels
CVD provides excellent conformal coverage. This means it can uniformly coat highly complex shapes and even internal surfaces, which can be challenging for the line-of-sight nature of PVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right surface treatment requires understanding your primary goal. The "PVD vs. DLC" question is better framed as, "What kind of PVD coating do I need?"
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and low friction: A DLC coating, likely applied via a PVD process, is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is a specific color, decorative finish, or general-purpose hardness: A non-DLC PVD coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN, gold color) or Zirconium Nitride (ZrN, brass color) is the correct path.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex internal geometry: You should investigate CVD as a potential process, as PVD may not provide adequate coverage.
Understanding this distinction between process and material empowers you to select the precise surface engineering solution your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A process for applying thin films | A specific material (a type of coating) |
| Primary Goal | General-purpose hardness, decorative finishes | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, and low friction |
| Key Characteristic | Physical atom-by-atom deposition in a vacuum | Amorphous carbon structure with diamond-like properties |
| Common Applications | Tools, decorative hardware, consumer goods | Automotive components, cutting tools, medical devices |
Still unsure which coating is right for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing expert solutions for all your laboratory equipment and consumable needs. Our team can help you navigate the complexities of surface engineering to select the ideal PVD or DLC coating for your specific project, ensuring superior performance and durability.
Let's discuss your requirements and find the perfect solution. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer



















