At its core, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is an additive manufacturing process that builds three-dimensional objects by selectively depositing melted material in a predetermined path, layer by layer. A thermoplastic filament is fed from a spool into a heated extruder, which melts the material and forces it through a small nozzle as it traces the object's cross-section. Once a layer is complete, the build platform moves down to begin the next layer, fusing it to the one below.
The FDM process is best understood as a highly precise, computer-controlled hot glue gun. Grasping this simple analogy is the key to understanding how parts are built, what gives them strength, and what causes common printing failures.
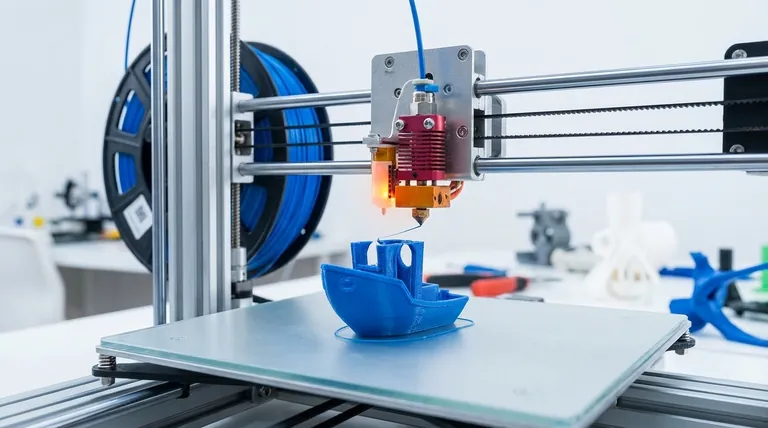
The Core Mechanics of FDM: From Spool to Object
To truly understand FDM, we must break the process down into its four distinct stages, which happen continuously during a print.
The Filament Feed System
The process begins with a spool of solid plastic wire, called filament. A motor-driven gear system, known as the extruder, grips this filament and pushes it from the spool toward the heating element. The speed and reliability of this feed system are critical for consistent material flow.
The "Hot End": Melting the Material
The filament is fed into the "hot end," which consists of a heater block and a nozzle. The heater block raises the temperature of the material past its melting point, turning the solid filament into a molten, viscous liquid ready for deposition.
Precision Deposition: The Gantry System
The molten plastic is then forced out of the nozzle onto a build platform. The nozzle is mounted on a gantry system that controls its movement with high precision along the X and Y axes (horizontally). This movement traces the exact shape of a single layer.
Layer-by-Layer Adhesion
Once a layer is complete, the build platform moves down along the Z-axis by a tiny, specific increment (the layer height). The hot end then begins depositing the next layer. The heat from the newly extruded plastic slightly melts the surface of the layer below it, causing the two layers to fuse together as they cool, forming a solid bond. This process repeats hundreds or thousands of times to create the final object.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Extrusion
The layer-by-layer nature of FDM is both its greatest strength and the source of its primary limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for successful engineering and design.
Strength and Anisotropy
Because parts are built from fused layers, they are anisotropic. This means their mechanical properties are not the same in all directions. FDM parts are significantly stronger against forces applied along the printed layers (X/Y axes) than they are against forces that try to pull the layers apart (Z-axis).
Resolution and Layer Lines
The process inherently creates visible layer lines on the surface of the part. The final resolution and smoothness are determined by the nozzle diameter and the chosen layer height. A smaller layer height produces a more detailed part but dramatically increases the printing time.
Speed vs. Detail
There is a direct trade-off between print speed and visual quality. Using a larger nozzle and thicker layers allows for very fast material deposition, which is ideal for rapid prototyping. Achieving fine details, however, requires a smaller nozzle and thinner layers, which is a much slower process.
How This Process Impacts Your Prints
Understanding the fundamentals of extrusion allows you to make deliberate choices to match your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Orient your model so that critical forces are applied parallel to the layer lines, not in a direction that could pull the layers apart.
- If your primary focus is visual detail: Use the smallest practical layer height and ensure your printer's motion system is well-calibrated to produce clean, consistent surfaces.
- If your primary focus is speed and rapid prototyping: Use a larger nozzle and thicker layer heights to produce functional parts quickly, accepting that the surface finish will be rougher.
By understanding how FDM stacks these simple molten layers, you gain complete control over the quality, strength, and speed of your 3D printed creations.
Summary Table:
| FDM Process Stage | Key Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Filament Feed | Extruder Motor & Gears | Pushes solid filament from the spool into the hot end. |
| Melting | Heater Block & Nozzle | Heats the filament past its melting point for deposition. |
| Deposition | Gantry System (X/Y Axes) | Moves the nozzle to trace the object's cross-section. |
| Layer Adhesion | Build Platform (Z-Axis) | Lowers after each layer, fusing new material to the layer below. |
Ready to bring precision and reliability to your additive manufacturing or prototyping projects? The principles of controlled material deposition and thermal management are at the heart of FDM and many lab processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables that deliver the accuracy and consistency your work demands.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to MIC testing? Ensure Precision in Stainless Steel Specimens
- What is the general procedure and what precautions should be taken during the polishing process? Achieve a Flawless Electrode Finish
- What is the process of mounting in metallurgy? A Guide to Perfect Specimen Preparation
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly
- What role do laboratory grinding and polishing systems play in nitriding? Ensure Superior Mirror-Finish & Ion Penetration











