While there is no single frequency for all induction furnaces, they operate across a wide spectrum, typically from standard line frequencies (50-60 Hz) up to several hundred kilohertz (kHz). The specific frequency used is not arbitrary; it is the most critical design parameter that dictates the furnace's heating characteristics, efficiency, and its intended application, from melting massive tons of iron to processing small, high-purity alloys.
The operating frequency of an induction furnace is a fundamental variable that controls how energy transfers to the metal. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper and stir more vigorously, ideal for large melts, while higher frequencies provide shallower, more controlled heating for smaller or specialized applications.

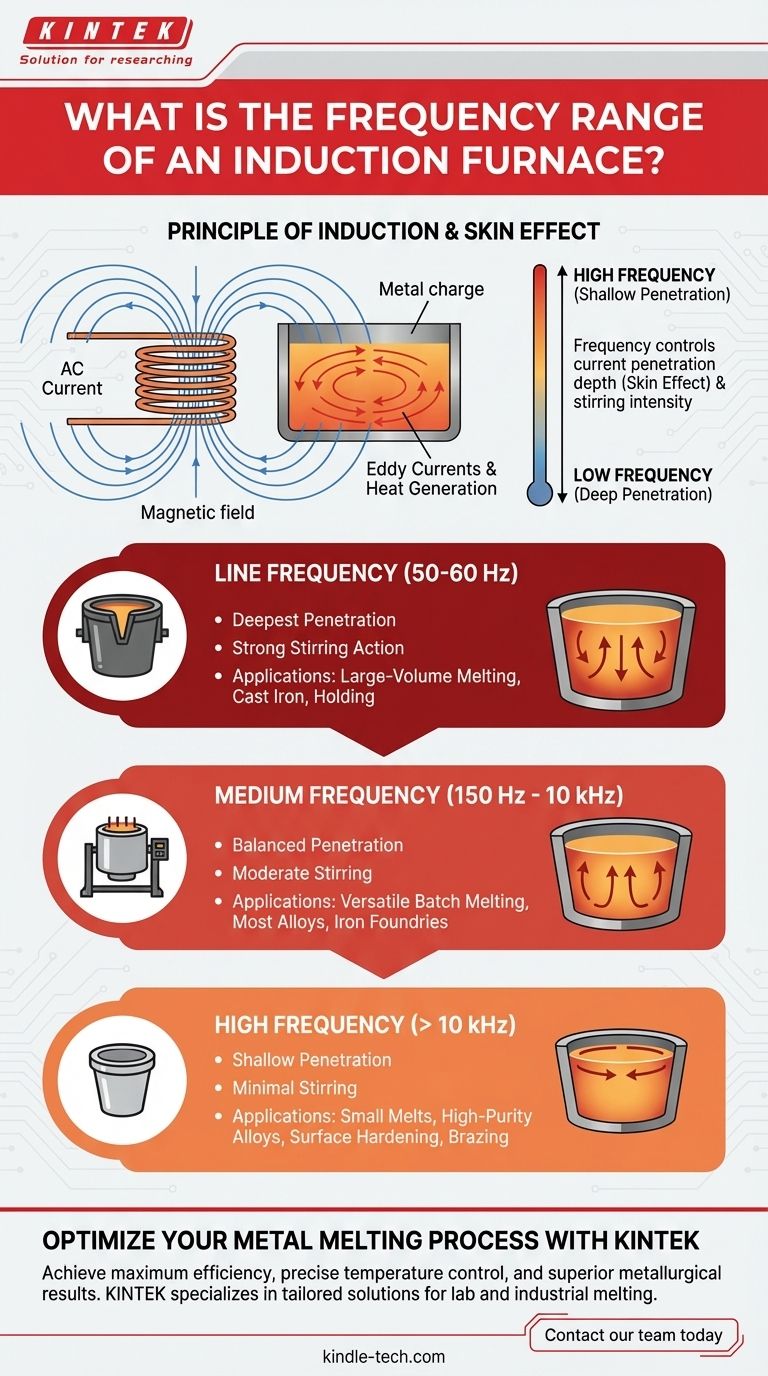
The Role of Frequency in Induction Heating
To understand the different frequency ranges, we must first understand the physics at play. An induction furnace is essentially a large transformer where the primary coil is the water-cooled copper coil, and the metal to be melted (the charge) acts as a single-turn secondary coil.
The Principle of Induction
When alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field inside the furnace. This magnetic field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal charge. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes these eddy currents to generate immense heat, leading to melting.
The "Skin Effect": Current Penetration Depth
Crucially, these eddy currents do not flow uniformly through the entire metal charge. They tend to concentrate on the outer surface in a phenomenon known as the skin effect. The operating frequency directly controls the depth of this current-carrying "skin."
The relationship is inverse:
- Higher frequency results in a shallower penetration depth.
- Lower frequency results in a deeper penetration depth.
Stirring vs. Concentrated Heating
This penetration depth dictates the furnace's behavior. A deeper current path (low frequency) interacts with more of the metal, creating stronger electromagnetic forces that result in a vigorous, natural stirring action. A shallower current path (high frequency) concentrates energy on the surface for rapid heating with minimal stirring.
Typical Frequency Ranges and Their Applications
The choice of frequency is a deliberate engineering decision based on the desired outcome. Furnaces are built to operate in one of three general ranges.
Line Frequency (50 – 60 Hz)
These furnaces operate at the standard frequency available from the electrical grid. The very low frequency causes the deepest energy penetration, which is ideal for melting large-diameter charges and holding massive volumes of molten metal. The strong stirring action is excellent for homogenizing alloys like cast iron. Channel furnaces, which are often used as holders, typically operate at line frequency.
Medium Frequency (150 Hz – 10 kHz)
This is the most common and versatile range for modern coreless induction furnaces. Medium-frequency systems offer an excellent balance between heating efficiency and stirring action. They are suitable for a wide variety of melt sizes and applications, from iron foundries to non-ferrous metals, providing rapid melting without the extreme stirring of a line-frequency unit.
High Frequency (Above 10 kHz)
High-frequency furnaces produce a very shallow penetration depth. This is ideal for melting small quantities of metal very quickly or for applications where minimal stirring is desired, such as with high-purity or specialty alloys where gas absorption is a concern. This range is also used for non-melting applications like surface hardening, brazing, and soldering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a frequency involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" frequency, only the most appropriate one for the job.
Efficiency vs. Stirring Action
Vigorous stirring from low-frequency operation is excellent for mixing and temperature uniformity in large baths. However, this same turbulence can increase oxidation (slag formation) and accelerate the erosion of the furnace's refractory lining. High-frequency heating is less turbulent but may not provide enough stirring to properly homogenize certain alloys.
Melt Size and Power Coupling
For induction heating to be efficient, the penetration depth should be significantly smaller than the diameter of the material being heated. Using a low frequency with a very deep penetration depth on a small piece of metal is highly inefficient, as the magnetic field "misses" the target. The frequency must be matched to the charge size.
Capital Cost and Complexity
Generally, power supply systems that convert line frequency to medium or high frequencies are more complex and have a higher initial cost than simple line-frequency transformers. However, their flexibility and efficiency for batch melting operations often justify the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal frequency is directly tied to your operational objective. When evaluating an induction furnace, the frequency tells you its purpose.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of ferrous metals (e.g., cast iron): A line or low-frequency furnace is optimal for deep energy penetration and strong metallurgical stirring.
- If your primary focus is flexible batch melting for various alloys: A medium-frequency furnace offers the best balance of heating speed, efficiency, and controlled stirring.
- If your primary focus is small, high-purity melts or surface heat treatment: A high-frequency system provides precise, rapid heating with minimal stirring.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between frequency, penetration, and stirring empowers you to select a system perfectly matched to your process.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Range | Penetration Depth | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Line (50-60 Hz) | Deepest | Large-volume melting, cast iron, strong stirring |
| Medium (150 Hz - 10 kHz) | Moderate | Versatile batch melting, most alloys, balanced stirring |
| High (>10 kHz) | Shallow | Small melts, high-purity alloys, surface treatments |
Optimize Your Metal Melting Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right induction furnace frequency is critical for achieving maximum efficiency, precise temperature control, and superior metallurgical results in your lab or production facility. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for laboratory and industrial melting applications.
Our experts will help you select the ideal induction furnace configuration to match your specific material, batch size, and process requirements—ensuring faster melt times, reduced energy costs, and consistent, high-quality outcomes.
Ready to enhance your melting capabilities? Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's reliable equipment can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















