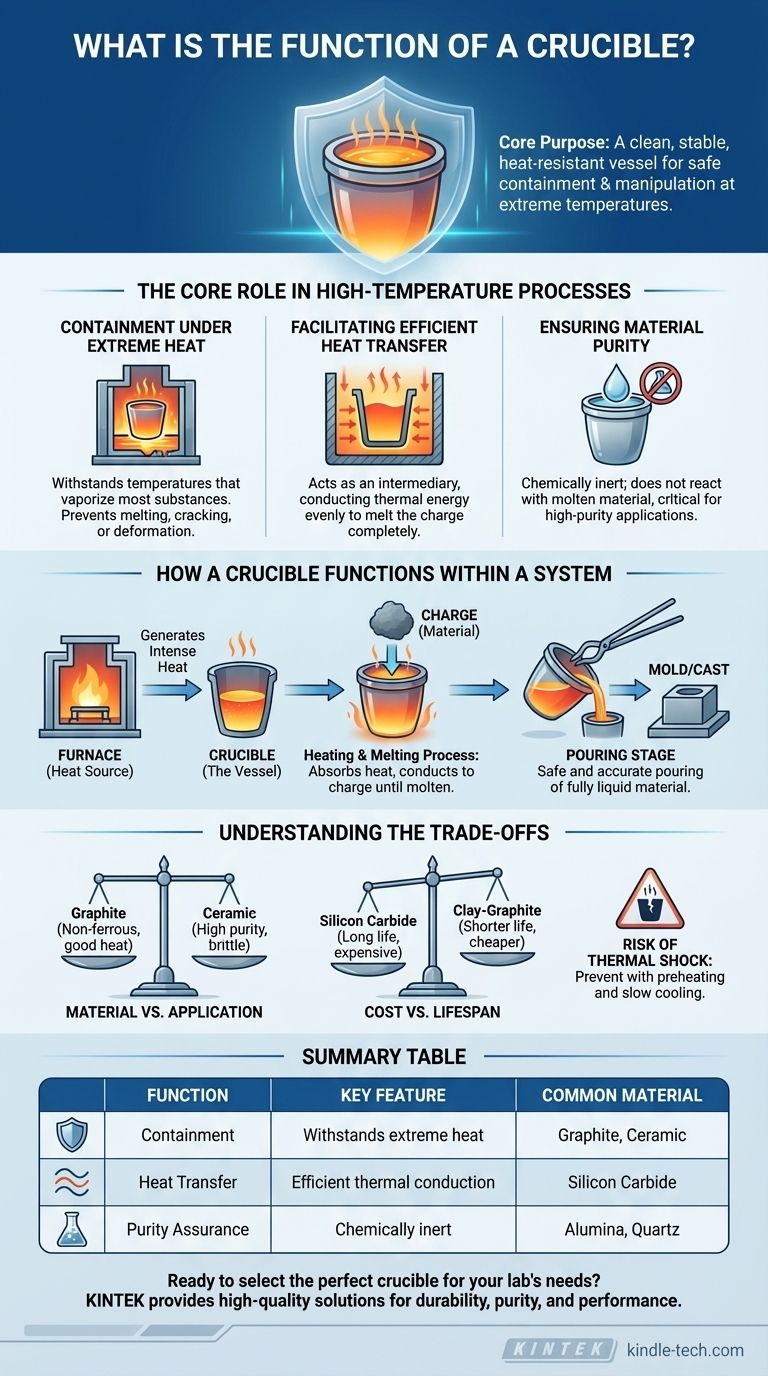
In essence, a crucible is a specialized container engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures. Its primary function is to hold materials, such as metals or chemical compounds, while they are being melted, calcined, or otherwise chemically altered. Unlike an ordinary pot, a crucible is constructed from materials that maintain their structural integrity and chemical stability at temperatures that would vaporize or destroy most other substances.
The core purpose of a crucible is to act as a clean, stable, and heat-resistant vessel. It enables the safe containment and manipulation of materials at extreme temperatures, ensuring the purity of the substance being heated and the integrity of the process.

The Core Role in High-Temperature Processes
A crucible's function goes beyond simple containment. It is an active component in a larger thermal system, such as a furnace, and its properties are critical to achieving the desired outcome.
Containment Under Extreme Heat
The most fundamental job of a crucible is to hold a solid or liquid material at very high temperatures. Whether melting aluminum at 660°C (1220°F) or iron at 1538°C (2800°F), the crucible must not melt, crack, or deform.
Facilitating Efficient Heat Transfer
The crucible serves as the intermediary between the heat source (like a furnace) and the material inside. It must conduct thermal energy efficiently from its outer wall to the charge within, allowing the material to heat up evenly and melt completely.
Ensuring Material Purity
A crucial function of a crucible is to be chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the molten material it holds. This prevents contamination, which is critical in metallurgy, laboratory analysis, and manufacturing, where even small impurities can ruin a batch.
How a Crucible Functions Within a System
A crucible is rarely used in isolation. It is the heart of a system, most commonly a crucible furnace, which provides the necessary heat.
The Crucible and the Furnace
Think of the furnace as the oven and the crucible as the high-performance baking dish. The furnace generates the intense heat, and the crucible is placed inside to hold the material safely as it is heated.
The Heating and Melting Process
First, the material to be melted (the "charge") is placed inside the crucible. The furnace is then activated, transferring heat to the crucible. The crucible absorbs this heat and conducts it into the charge until it reaches its melting point and becomes molten.
The Pouring Stage
Once the material is fully liquid, the crucible itself is often lifted from the furnace using specialized tongs. Its design allows the molten material to be safely and accurately poured into a mold, cast, or other container.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single crucible is perfect for every task. The selection of a crucible involves balancing material properties, cost, and the specific requirements of the application.
Material vs. Application
The material of the crucible dictates its use. Graphite crucibles are excellent for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and gold but can be consumed in oxygen-rich environments at high temperatures. Ceramic crucibles (like alumina or zirconia) offer superior chemical inertness for high-purity applications but can be more brittle.
Cost vs. Lifespan
High-performance crucibles made from materials like silicon carbide are more expensive but offer a long service life and excellent thermal shock resistance. Cheaper clay-graphite crucibles are effective but may have a shorter lifespan, especially under harsh conditions.
Risk of Thermal Shock
A significant pitfall is thermal shock, where a crucible cracks due to rapid changes in temperature. Preheating the crucible before adding the charge and allowing it to cool slowly are critical steps to maximize its life and prevent catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible is fundamental to the success and safety of your work. Your choice should be guided by the material you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is casting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible provides the best balance of durability, thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory analysis: An alumina, quartz, or porcelain crucible is essential to prevent contamination that could compromise your results.
- If your primary focus is melting precious metals like gold and silver: A graphite crucible is often preferred for its smooth, non-stick surface and excellent heat transfer.
Ultimately, understanding the function of a crucible is to see it as a critical tool that makes high-temperature chemistry and metallurgy possible.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Common Material |
|---|---|---|
| Containment | Withstands extreme heat | Graphite, Ceramic |
| Heat Transfer | Efficient thermal conduction | Silicon Carbide |
| Purity Assurance | Chemically inert | Alumina, Quartz |
Ready to select the perfect crucible for your lab's high-temperature needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles designed for durability, purity, and performance. Whether you're melting precious metals, conducting high-purity analysis, or casting non-ferrous metals, we have the right solution to ensure your process is safe, efficient, and contamination-free.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts help you find the ideal crucible for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity



















