In analytical chemistry, potassium bromide (KBr) serves as a specialized matrix material for preparing solid samples for analysis by Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The sample is finely ground with KBr powder and pressed under high pressure to form a thin, transparent disc or "pellet." This pellet acts as a solid-state "window," allowing infrared light to pass through the sample so its molecular vibrations can be measured.
KBr is not a chemical reactant; it is an ideal optical window for solid-state FTIR. Its critical function stems from its unique properties: it is transparent to infrared light and can be pressed into a glass-like disc, which minimizes light scattering and allows for a clear, high-quality measurement of the solid sample embedded within it.

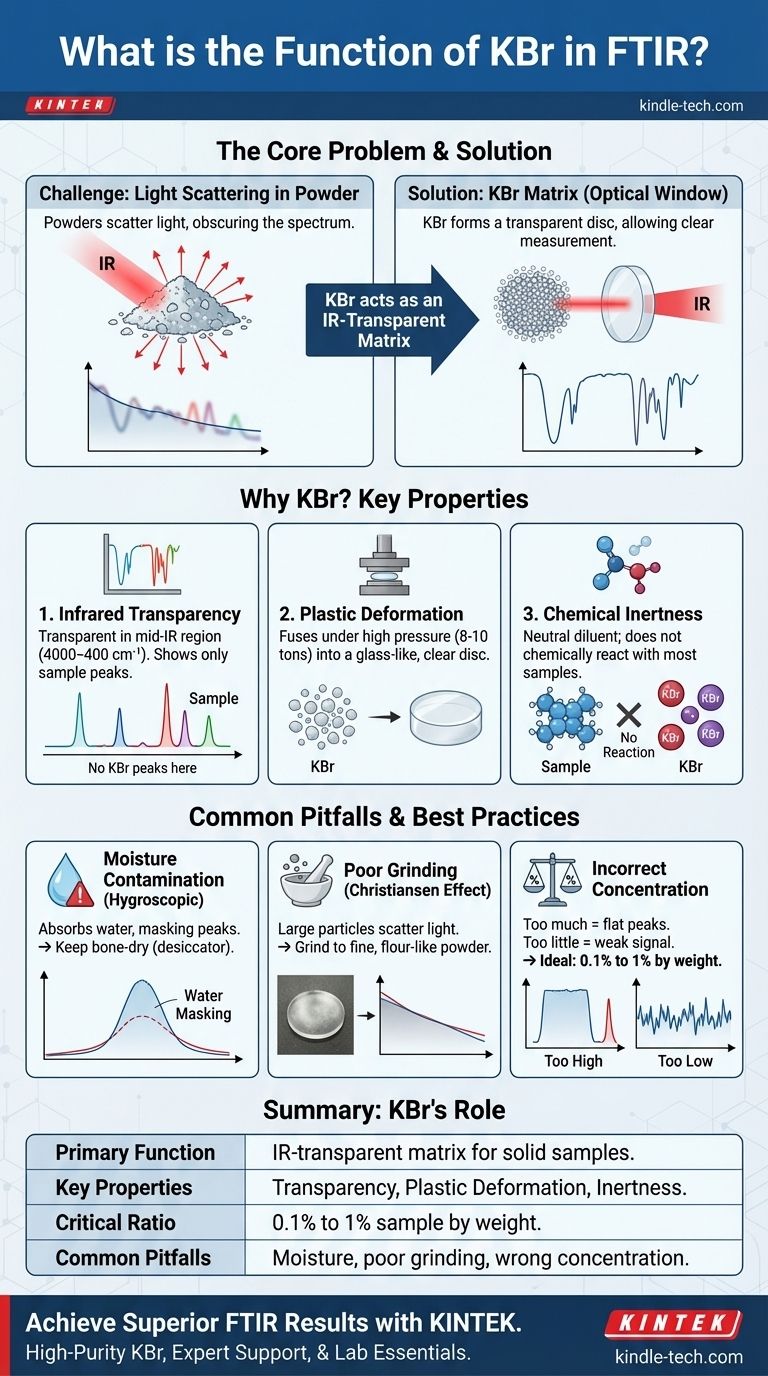
The Core Problem: Analyzing Solids with Light
To understand the function of KBr, we must first understand the fundamental challenge of using light to analyze a solid powder.
The Challenge of Light Scattering
If you shine an infrared beam directly at a fine powder, most of the light will scatter in all directions rather than passing through it. This scattering effect obscures the true absorption spectrum of the material, resulting in a poor-quality, unusable measurement with a sloping baseline and distorted peaks.
The Need for an IR-Transparent Matrix
To get a clean spectrum, the solid sample must be uniformly dispersed in a medium that is transparent to infrared light. This medium, or matrix, holds the sample particles in place and allows the IR beam to pass through for a clean transmission measurement. This is precisely the role KBr fulfills.
Why Potassium Bromide (KBr) is the Standard
KBr is the most common choice for this matrix material due to a specific combination of physical properties.
Property 1: Infrared Transparency
Potassium bromide is an alkali halide salt that has no molecular vibrations of its own in the mid-infrared region (approximately 4000 to 400 cm⁻¹). This means it does not absorb IR light in the region of interest for most analyses, ensuring that any absorption peaks detected in the spectrum belong only to the sample, not the KBr matrix.
Property 2: Plastic Deformation
Under high pressure (typically 8-10 tons), KBr powder exhibits plastic deformation or "cold flow." Instead of just compacting, the individual salt crystals fuse together to form a homogenous, glass-like, transparent disc. This property is critical for minimizing light scattering and creating a high-quality optical window.
Property 3: Chemical Inertness
For most organic and many inorganic compounds, KBr is a chemically inert host. It serves as a neutral diluent that holds the sample without reacting with it, preventing the sample's chemical structure from being altered during preparation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While KBr is the standard, proper technique is essential. Several common issues can compromise the quality of the analysis.
The Problem of Water Contamination
KBr is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Water has very strong, broad absorption bands in the IR spectrum which can easily mask important peaks from your sample. Therefore, spectroscopy-grade KBr must be kept perfectly dry, typically by storing it in a desiccator or drying it in an oven before use.
Poor Grinding Technique
The reference you provided correctly identifies that grinding is essential for a homogeneous mix. If the sample is not ground finely enough with the KBr, particles will remain large enough to scatter light. This leads to a severely sloping baseline in the spectrum, a phenomenon known as the Christiansen effect, and can make the resulting pellet appear cloudy instead of clear.
Incorrect Sample Concentration
The concentration of the sample in the KBr is critical. A typical mixture is only about 0.1% to 1% sample by weight.
- Too much sample causes total absorption, where the peaks are "flat-topped" because no light can get through at those frequencies.
- Too little sample results in a weak, noisy spectrum where the peaks are difficult to distinguish from the baseline.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles behind the KBr method allows you to troubleshoot issues and consider alternatives when necessary.
- If your primary focus is high-quality analysis of stable, solid compounds: The KBr pellet method is the gold standard for generating clean, sharp, and reproducible transmission spectra.
- If your sample is sensitive to moisture or cannot withstand high pressure: Consider alternative methods like preparing a Nujol mull or using Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR-FTIR), which analyzes the sample surface directly.
- If you are struggling with cloudy pellets or a sloping baseline: Your issue is almost certainly either moisture contamination or insufficient grinding. Ensure your KBr is bone-dry and grind the mixture until it is a fine, uniform, flour-like powder.
Ultimately, understanding KBr's role transforms it from a simple powder into a critical tool for revealing the molecular fingerprint of your sample.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as an IR-transparent matrix for solid samples in FTIR spectroscopy. |
| Key Properties | Infrared transparency, plastic deformation under pressure, chemical inertness. |
| Critical Ratio | Sample concentration typically 0.1% to 1% by weight in KBr. |
| Common Pitfalls | Moisture absorption (hygroscopic), insufficient grinding, incorrect sample concentration. |
Achieve superior FTIR results with KINTEK's high-purity KBr and expert support.
Struggling with cloudy pellets, sloping baselines, or moisture issues in your FTIR analysis? KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory-grade consumables and equipment tailored for analytical chemistry. Our spectroscopy-grade KBr is manufactured to ensure optimal transparency and minimal moisture content, helping you obtain clear, reliable spectra every time.
We serve laboratories like yours with:
- High-Purity KBr: Optimized for perfect pellet formation and minimal IR absorption.
- Technical Guidance: Expert advice on sample preparation techniques to avoid common pitfalls.
- Full Lab Support: From consumables to pressing equipment, we have your FTIR needs covered.
Enhance your analytical precision—contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right KBr solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System



















