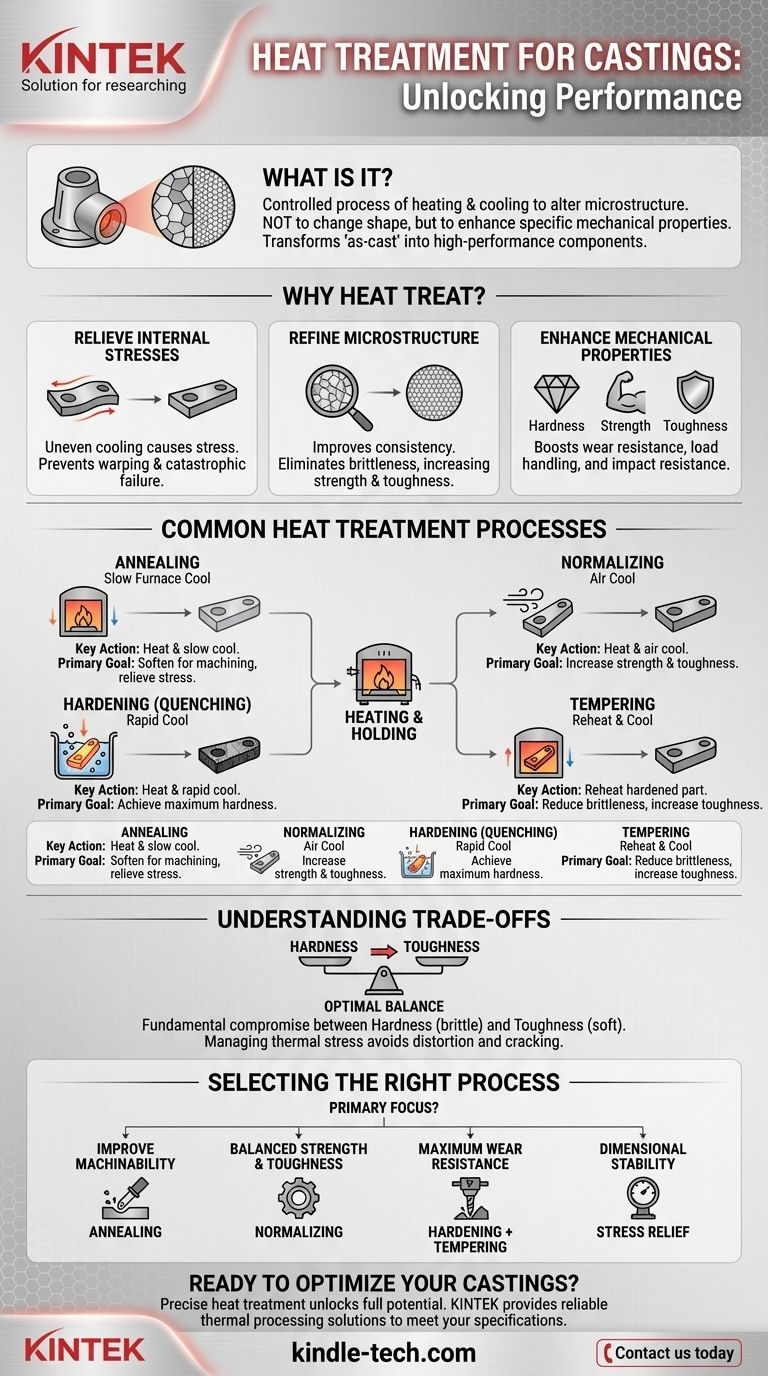
At its core, heat treatment for castings is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling a metal part to deliberately alter its internal microstructure. This is not done to change the casting's shape, but to unlock or enhance specific mechanical properties that are not present in its "as-cast" state. The goal is to transform a standard casting into a high-performance component tailored for a specific engineering demand.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a family of thermal processes. The choice of process—from softening to hardening—depends entirely on the final performance requirement, whether that is extreme hardness for wear resistance, ductility for forming, or internal stability to prevent distortion.

Why Heat Treat a Casting?
The decision to heat treat a casting is driven by the need to overcome the limitations of its raw, as-cast condition. The process addresses three fundamental engineering challenges.
To Relieve Internal Stresses
As molten metal cools and solidifies in a mold, different sections cool at different rates. This uneven cooling creates internal stresses within the casting, which can lead to warping over time or catastrophic failure under load.
To Refine the Microstructure
The "as-cast" grain structure of the metal can be coarse and non-uniform, which often leads to poor mechanical properties like brittleness. Heat treatment refines this grain structure, making it finer and more consistent, which directly improves strength and toughness.
To Enhance Mechanical Properties
The primary goal is often to significantly improve performance characteristics. This includes increasing hardness for wear resistance, improving strength to handle higher loads, and increasing toughness to resist impact without fracturing.
Common Heat Treatment Processes
Each process involves a unique cycle of heating, holding at a specific temperature (soaking), and cooling at a controlled rate. The combination of these three variables determines the final properties.
Annealing: Maximum Softness and Machinability
Annealing involves heating the casting to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it in the turned-off furnace.
This slow cooling process produces a soft, ductile, and stress-free material. The primary purpose of annealing is to make a hard or brittle casting easier to machine.
Normalizing: Strength and Structural Uniformity
Normalizing involves heating the casting above its upper critical temperature and then letting it cool in open air.
This air cooling is faster than the furnace cooling used in annealing. It results in a finer, more uniform grain structure, which increases both strength and toughness compared to an annealed part.
Hardening (Quenching): Maximum Hardness
To achieve maximum hardness, a casting is heated to a high temperature and then cooled rapidly by submerging it in a quenching medium like oil, water, or brine.
This process, known as quenching, locks the material into a very hard but also very brittle microstructural state. This is ideal for applications requiring high wear and abrasion resistance.
Tempering: Increasing Toughness in Hardened Parts
A part that has been hardened is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary process performed after quenching to reduce this brittleness.
The casting is reheated to a much lower temperature, held for a specific time, and then cooled. This process sacrifices a small amount of hardness to gain a significant improvement in toughness and ductility, making the part more durable and resistant to shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it is not without compromises and risks. Understanding these is critical for making sound engineering decisions.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Compromise
The most fundamental trade-off in heat treatment is between hardness and toughness. A very hard material is typically very brittle, while a very tough material is typically softer. The goal of processes like quenching and tempering is to find the optimal balance for the application.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid temperature changes involved in processes like quenching introduce significant thermal stress. If not managed correctly, this can cause the casting to warp, distort, or even crack, rendering it useless.
Cost and Time Considerations
Heat treatment is an additional manufacturing step that adds both cost and lead time to a project. It requires specialized furnace equipment, energy, and skilled labor. Therefore, it should only be specified when the performance benefits are essential and justify the added expense.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Application
The correct heat treatment cycle is dictated by the end-use of the component. Always begin with the required mechanical properties in mind.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Annealing is the most effective process for softening the material and relieving internal stress.
- If your primary focus is a balanced increase in strength and toughness: Normalizing provides a good combination of properties and a uniform microstructure.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance: Hardening (quenching) followed by a carefully selected tempering cycle will deliver high hardness with sufficient toughness.
- If your primary focus is ensuring dimensional stability after machining: A low-temperature stress relief cycle is the best choice to remove internal stresses without significantly altering hardness.
Ultimately, viewing heat treatment as a precise engineering tool allows you to transform a generic casting into a component optimized for its specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Heat & slow cool | Soften for machining, relieve stress |
| Normalizing | Heat & air cool | Increase strength and toughness |
| Hardening (Quenching) | Heat & rapid cool | Achieve maximum hardness |
| Tempering | Reheat hardened part | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness |
Ready to Optimize Your Castings?
Precise heat treatment is key to unlocking the full potential of your metal components. The right furnace and process control are critical for achieving the desired balance of hardness, strength, and toughness while minimizing distortion.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the reliable thermal processing solutions you need to ensure your castings meet demanding specifications. Our expertise helps you select the right equipment for processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your heat treatment applications and help you produce higher-performing, more reliable components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















