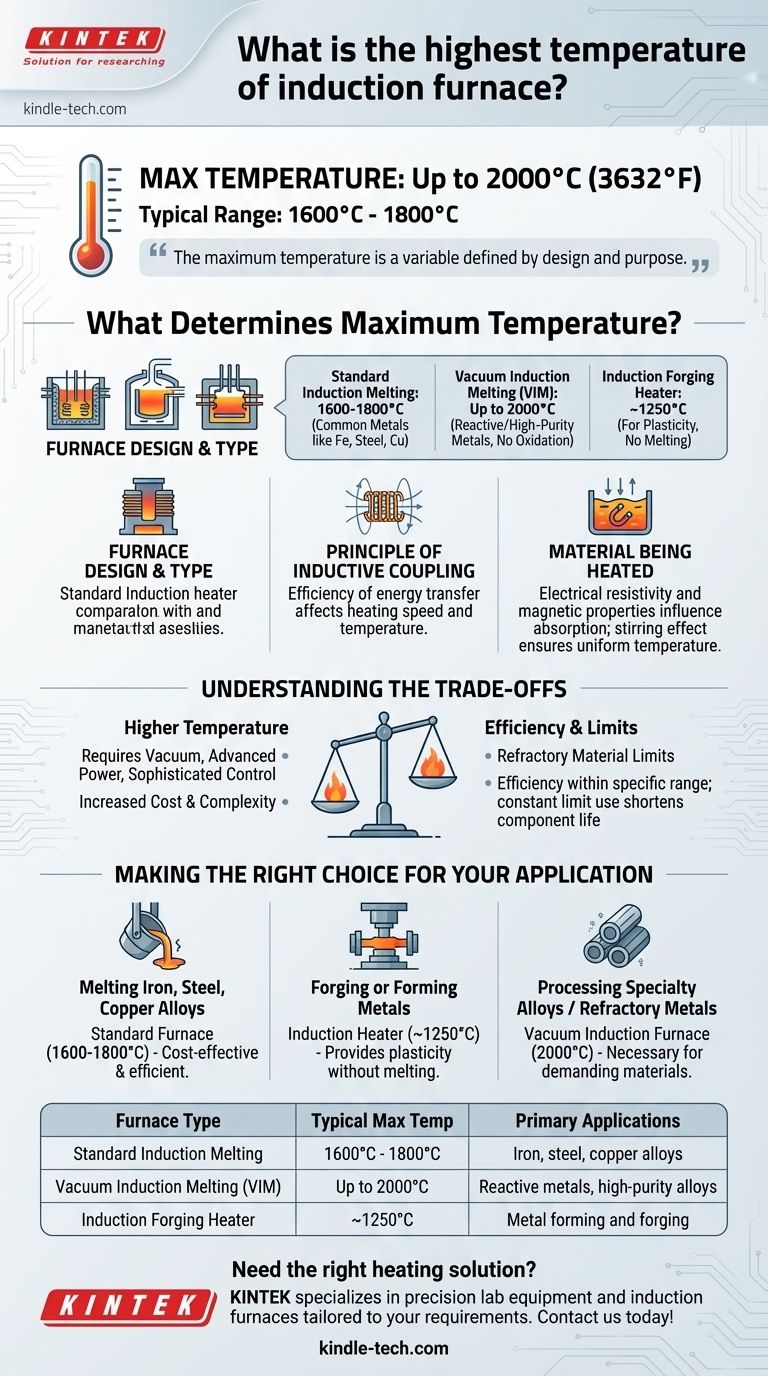
While typical induction furnaces operate up to 1800°C, the absolute maximum temperature depends heavily on the specific design and application. Specialized vacuum induction melting furnaces are capable of reaching temperatures as high as 2000°C (3632°F) for processing high-purity or reactive metals.
The maximum temperature of an induction furnace is not a single value but a variable defined by its design and purpose. While standard furnaces handle temperatures for common metals, specialized systems are required to push the limits for advanced materials.

What Determines an Induction Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The temperature an induction furnace can achieve is a result of its engineering, not a fixed physical law. Several key factors dictate its thermal performance and practical limits.
Furnace Design and Type
The single most important factor is the furnace's intended purpose, which dictates its construction.
A standard induction melting furnace is typically designed to reach temperatures around 1600°C to 1800°C. This range is sufficient for melting most common metals like iron, steel, and copper.
A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is a specialized system that operates in a vacuum. This prevents oxidation and allows for the processing of reactive or high-purity metals, enabling it to reach extreme temperatures of 2000°C.
An induction forging heater has a different goal. It heats metal to a plastic, malleable state without melting it, typically operating at temperatures around 1250°C.
The Principle of Inductive Coupling
Induction heating works by inducing an electric current directly within the material to be heated (the charge).
The efficiency of this energy transfer is known as inductive coupling. A furnace with better coupling between the power coil and the charge material will heat more effectively and can achieve higher temperatures more rapidly.
The Material Being Heated
The properties of the metal itself influence the heating process. Different materials have varying electrical resistivity and magnetic properties, which affect how efficiently they absorb energy from the magnetic field.
The famous stirring effect of induction furnaces, caused by the alternating magnetic field, ensures a uniform temperature throughout the molten bath, which is critical for consistent metallurgy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pursuing the highest possible temperature introduces significant engineering and operational compromises. It is rarely the primary design goal in itself.
Higher Temperature vs. Cost & Complexity
Reaching extreme temperatures of 2000°C is not a simple task. It requires a vacuum environment, advanced power supplies, and sophisticated control systems. This dramatically increases the initial cost and operational complexity of the furnace.
The Limit of Refractory Materials
Every furnace is lined with refractory materials (heat-resistant ceramics) that contain the molten metal. These linings have their own maximum temperature limits. Pushing a furnace beyond the rating of its refractory can lead to catastrophic failure.
Efficiency vs. Temperature Range
Furnaces are engineered to be most energy-efficient within a specific operating range. While a furnace might be technically capable of reaching a higher peak temperature, running it constantly at its absolute limit is often inefficient and can shorten the life of its components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The "best" furnace is the one that meets your specific process requirements safely and efficiently. The maximum temperature is a specification, not a goal.
- If your primary focus is melting iron, steel, or copper alloys: A standard furnace capable of 1600°C to 1800°C is the correct and most cost-effective tool.
- If your primary focus is forging or forming metals: An induction heater designed for a controlled 1250°C provides the necessary plasticity without the risk of melting.
- If your primary focus is processing specialty alloys or refractory metals: A vacuum induction furnace capable of reaching 2000°C is necessary to handle these demanding materials.
Ultimately, understanding your material and process goal is the key to selecting the appropriate heating technology.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Induction Melting | 1600°C - 1800°C | Iron, steel, copper alloys |
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Up to 2000°C | Reactive metals, high-purity alloys |
| Induction Forging Heater | ~1250°C | Metal forming and forging |
Need the right heating solution for your lab or production process? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, offering induction furnaces tailored to your specific material and temperature requirements. Whether you're working with common alloys or specialty metals, our experts can help you select the optimal system for efficient, safe, and cost-effective operation. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the theory of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnace? Achieve Absolute Purity and Control in Your Lab
- How did the design of muffle furnaces change with the advent of electric heating elements? The Evolution to Precision and Purity



















