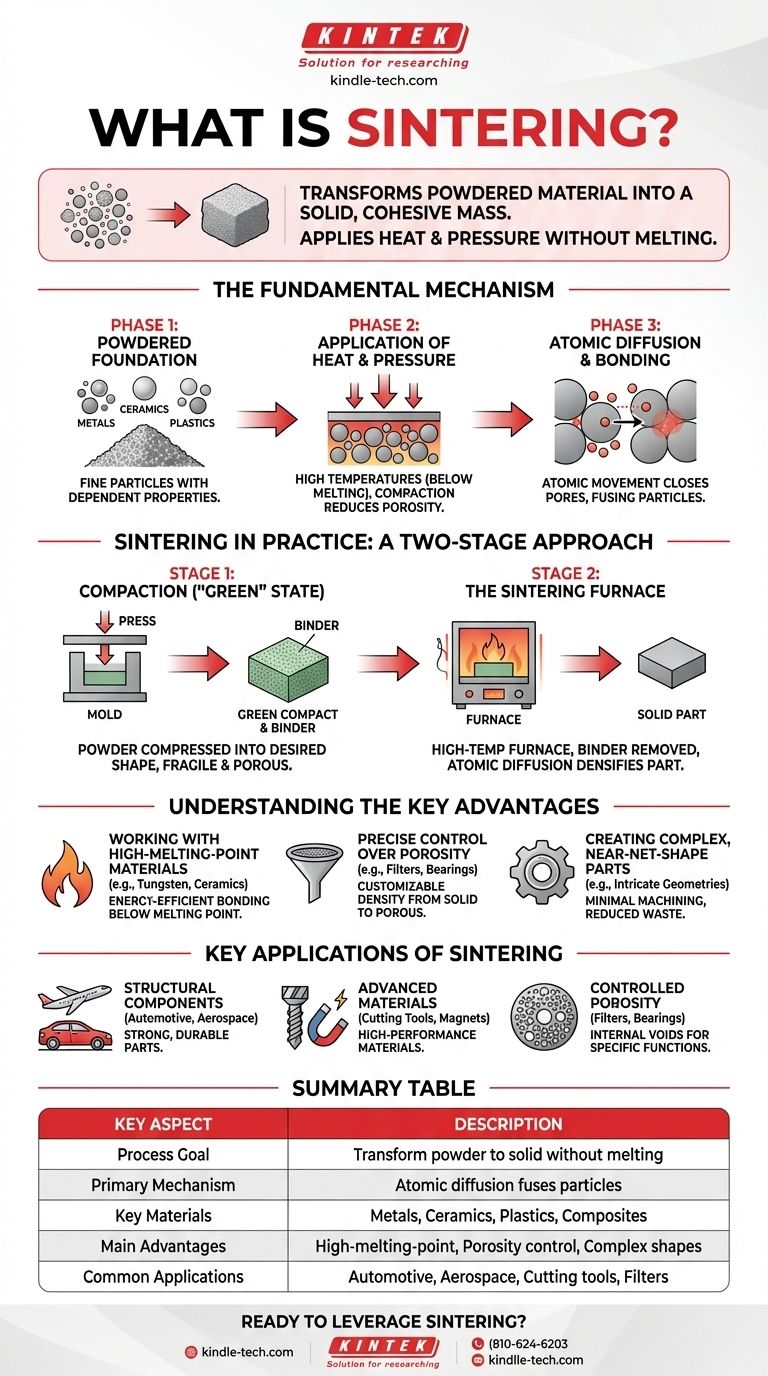
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a powdered material into a solid, cohesive mass. This is accomplished by applying heat and pressure, but crucially, without raising the temperature high enough to melt the material into a liquid state. Instead, sintering works by causing the atoms at the boundaries of individual powder particles to diffuse and fuse together, effectively "welding" them on a microscopic level.
The central challenge in advanced manufacturing is often how to form solid objects from materials with extremely high melting points, like ceramics or tungsten. Sintering solves this by providing a method to bond particles together at temperatures below their melting point, enabling the creation of strong, dense, and complex parts that would otherwise be impossible to shape.
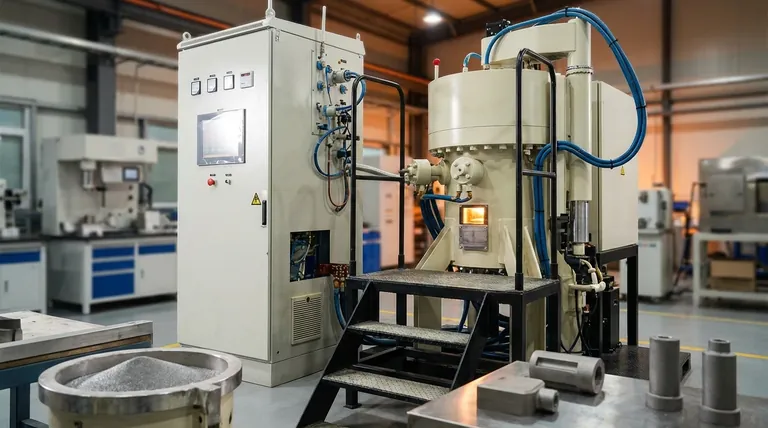

The Fundamental Mechanism: How Sintering Works
Sintering is not a simple melting and re-solidifying process. It relies on a more subtle thermodynamic principle called atomic diffusion, which happens in three distinct phases.
Phase 1: The Powdered Foundation
The process begins with a mass of fine particles. These can be made of a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, plastics, or a combination of different powders. The properties of the final object are heavily dependent on the size and shape of these initial particles.
Phase 2: The Application of Heat and Pressure
The powdered material is then subjected to high temperatures in a furnace. This temperature is carefully controlled to remain below the material’s melting point. The heat provides the thermal energy necessary to make the atoms within the particles highly mobile.
Simultaneously, pressure is often applied to compact the powder. This forces the particles into intimate contact, reducing the empty space (porosity) between them and creating more surface area for bonding to occur.
Phase 3: Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
This is the heart of the sintering process. With elevated energy from the heat and close contact from the pressure, atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries where the individual particles touch. This atomic movement closes up the pores between particles, fusing them together into a dense, solid piece.
Sintering in Practice: A Two-Stage Approach
While the physics involves heat, pressure, and diffusion, the industrial application is often a more structured, two-stage process.
Stage 1: Compaction ("Green" State)
First, the powder is compressed into a desired shape, often using a die or mold. This initial, fragile component is known as a "green compact." It has the basic geometry of the final part but lacks strength and is still porous. A temporary binder is sometimes mixed with the powder to help it hold this shape.
Stage 2: The Sintering Furnace
The green compact is then carefully placed into a high-temperature furnace. As the temperature rises, any temporary binder material is burned away. Then, as the part reaches its target sintering temperature, the atomic diffusion process takes over, densifying the component and transforming it into a strong, integrated part.
Understanding the Key Advantages
Sintering is not chosen by accident; it provides unique capabilities that traditional melting and casting cannot match.
Advantage: Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is the go-to method for materials like tungsten (melting point 3,422°C) and technical ceramics. It is far more energy-efficient and practical to bond these materials below their melting point than to attempt to melt and cast them.
Advantage: Precise Control Over Porosity
Because the process starts with a powder, engineers can precisely control the final density. Sintering can create fully solid, non-porous parts or be intentionally stopped short to produce objects with a specific level of porosity, which is ideal for filters or self-lubricating bearings.
Advantage: Creating Complex, Near-Net-Shape Parts
Sintering allows for the production of intricate and complex geometries directly from a mold. This creates "near-net-shape" parts that require minimal secondary machining, reducing waste and manufacturing costs. The primary challenge is accurately predicting and controlling the shrinkage that occurs as the part densifies.
Key Applications of Sintering
The right manufacturing process depends entirely on the desired outcome. Sintering is uniquely suited for several distinct goals.
- If your primary focus is structural components: Sintering is used to create strong, durable steel and alloy parts for the automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery sectors.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials: It is essential for producing high-performance ceramics, hard metals for cutting tools, and specialized magnetic materials.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity: The process is ideal for manufacturing metallic filters, porous bearings, and other components where internal voids are a critical design feature.
Ultimately, sintering is a foundational technology that unlocks the potential of advanced materials by building solid objects from the particle level up.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Transform powdered material into a solid mass without full melting. |
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion fuses particles together at high temperatures. |
| Key Materials | Metals, Ceramics, Plastics, Composites. |
| Main Advantages | Works with high-melting-point materials; Controls porosity; Creates complex shapes. |
| Common Applications | Automotive/Aerospace parts, Cutting tools, Filters, Porous bearings. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your advanced materials or complex part designs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for research and development in sintering processes. Whether you are working with high-performance ceramics, metal alloys, or developing new porous materials, our expertise can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your laboratory's sintering applications and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What temperature does tungsten carbide sinter at? Master the 1350°C-1500°C Liquid-Phase Sintering Process



















