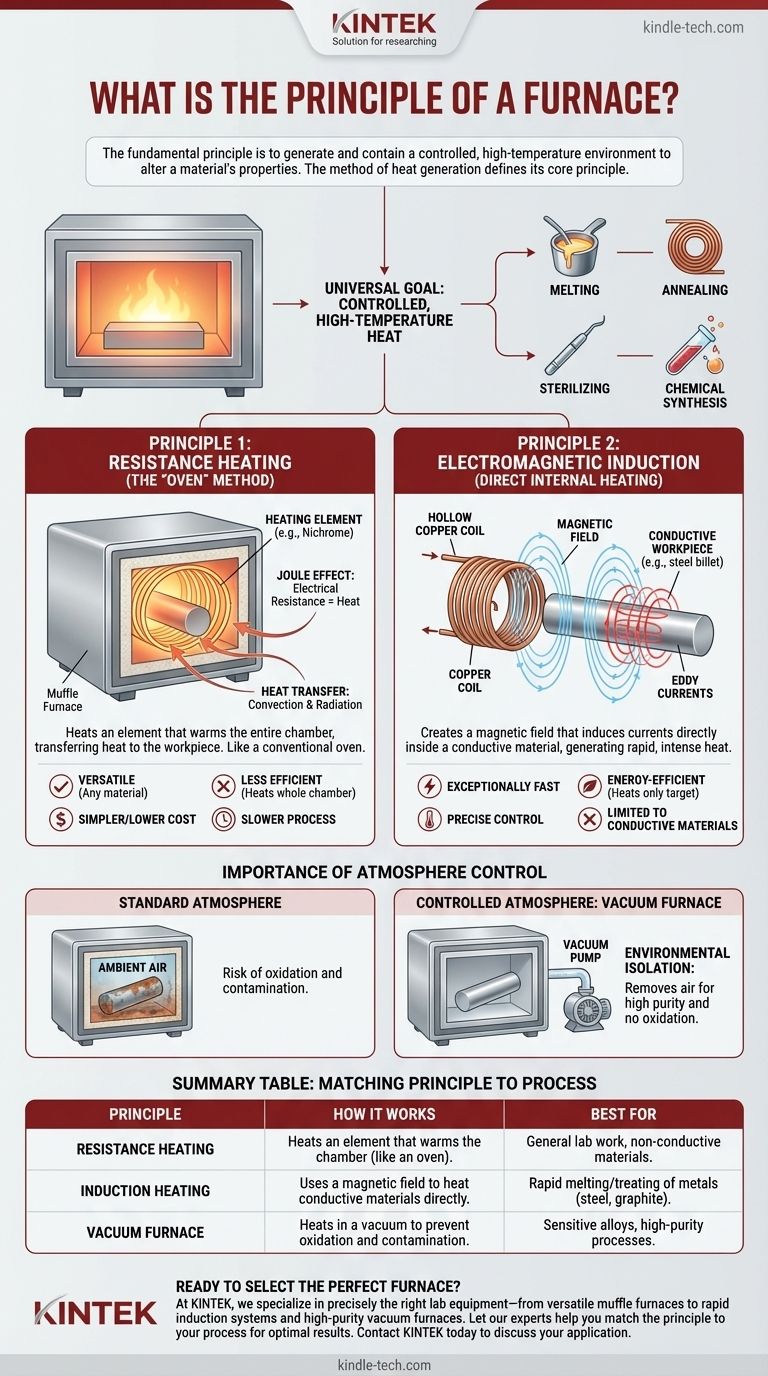
The fundamental principle of a furnace is to generate and contain a high-temperature environment to alter a material's physical or chemical properties. While the goal is universal, the method used to generate this heat defines the furnace's core principle, which primarily falls into two categories: passing electricity through a heating element (resistance) or using a magnetic field to heat the material directly (induction).
A furnace is not defined by a single principle. Instead, its design is dictated by the specific heating method required for the task, most commonly resistance heating for general applications and electromagnetic induction for rapidly melting conductive metals.

The Universal Goal: Controlled, High-Temperature Heat
Every furnace is designed to create a controlled thermal environment. The ultimate goal is to apply a precise amount of energy to a workpiece, initiating processes like melting, annealing, sterilizing, or chemical synthesis.
The "principle" of a furnace is simply the physical mechanism it employs to convert an energy source—typically electricity or fuel—into concentrated thermal energy within its chamber.
The Core Electrical Heating Principles
For modern industrial and laboratory furnaces, two electrical principles form the foundation of most designs. Understanding these two concepts clarifies how nearly every electric furnace operates.
Principle 1: Resistance Heating (The "Oven" Method)
The most common principle is resistance heating. This works by passing a strong electrical current through a specialized material, known as a heating element.
These elements, often made of materials like Nichrome, are designed to have high electrical resistance. This resistance converts electrical energy directly into heat, following the Joule effect.
A muffle furnace is a classic example of this principle. The heating elements heat the walls of an insulated chamber (the "muffle"), which then transfers heat to the workpiece inside through convection and radiation. This method heats the entire chamber, much like a conventional oven.
Principle 2: Electromagnetic Induction (Direct Internal Heating)
Electromagnetic induction is a more direct and efficient heating principle. It works by creating a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field around the material to be heated.
A hollow copper coil, carrying a high-frequency alternating current, generates this field. The magnetic field passes through the conductive material (like steel or graphite) and induces powerful electrical currents within it, called eddy currents.
The material's own internal resistance fights against these eddy currents, generating rapid and intense heat directly inside the workpiece itself. The furnace chamber and coils remain relatively cool because the heat is generated only in the target material.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Beyond the heating method, a critical operating principle is the control of the internal atmosphere. The environment inside the furnace can dramatically affect the outcome of the process.
Standard Atmosphere Furnaces
Many furnaces, like a basic muffle furnace, operate in ambient air. This is suitable for many applications, but the presence of oxygen and other gases can cause unwanted reactions like oxidation (scaling or rust) on the material's surface at high temperatures.
Controlled Atmosphere: The Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum furnace operates on the principle of environmental isolation. Its primary function is to remove air and other reactive gases from the heating chamber before and during the process.
By creating a vacuum, it eliminates the risk of oxidation and contamination. This allows for extremely pure and precise heat treatment of sensitive metals and advanced materials. The heating inside a vacuum furnace can still be accomplished via resistance elements or induction, but its defining principle is the controlled, inert environment it creates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each heating principle comes with distinct advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for different applications.
Resistance Heating (Muffle Furnace)
Resistance furnaces are highly versatile because they can heat any type of material, whether it's conductive or not. They are generally simpler and less expensive. However, they are less energy-efficient as the entire chamber must be heated, and the process is typically slower.
Induction Heating
Induction heating is exceptionally fast and energy-efficient because it only heats the target material. This provides for very clean processing and precise temperature control. Its main limitation is that it can only be used on materials that are electrically conductive.
Vacuum Furnaces
The benefit of a vacuum furnace is unparalleled process purity and control over the final properties of the material. The trade-off is significantly higher equipment cost, complexity, and longer overall cycle times due to the need to pump down the chamber to a vacuum.
Matching the Principle to the Process
Choosing the right furnace means matching its operating principle to your specific technical requirements.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating or processing non-conductive materials: A resistance-based furnace (like a muffle furnace) provides the most straightforward and versatile solution.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting or treating conductive metals with high efficiency: Electromagnetic induction is the superior principle for speed, precision, and energy savings.
- If your primary focus is treating sensitive alloys without any surface oxidation or contamination: A vacuum furnace is essential for the atmospheric control it provides, regardless of the specific heating method used inside.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles allows you to select not just a furnace, but the right thermal process for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Principle | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Heating | Heats an element that warms the chamber (like an oven). | General lab work, non-conductive materials. |
| Induction Heating | Uses a magnetic field to heat conductive materials directly. | Rapid melting/treating of metals (steel, graphite). |
| Vacuum Furnace | Heats in a vacuum to prevent oxidation and contamination. | Sensitive alloys, high-purity processes. |
Ready to Select the Perfect Furnace for Your Lab?
Understanding the principle is the first step. Implementing the right solution is what drives your research and production forward. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing precisely the right lab equipment—from versatile muffle furnaces to rapid induction systems and high-purity vacuum furnaces—to meet your specific thermal processing needs.
Let our experts help you match the principle to your process for optimal results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover how our equipment can enhance your lab's efficiency, precision, and capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a constant temperature laboratory oven play in preparing waste eggshell catalysts? Ensure Peak Efficiency
- What is an example of a continuous furnace? Discover the Conveyor Belt Furnace for High-Volume Production
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is the theory of thin film evaporator? Master Efficient, Gentle Separation
- Which is the most applied area for additive manufacturing? From Prototyping to High-Value Production
- How does heat treatment affect microstructure? Mastering the Balance Between Hardness and Toughness
- What are the advantages of a wiped film evaporator? Purify Heat-Sensitive Materials Efficiently
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes



















