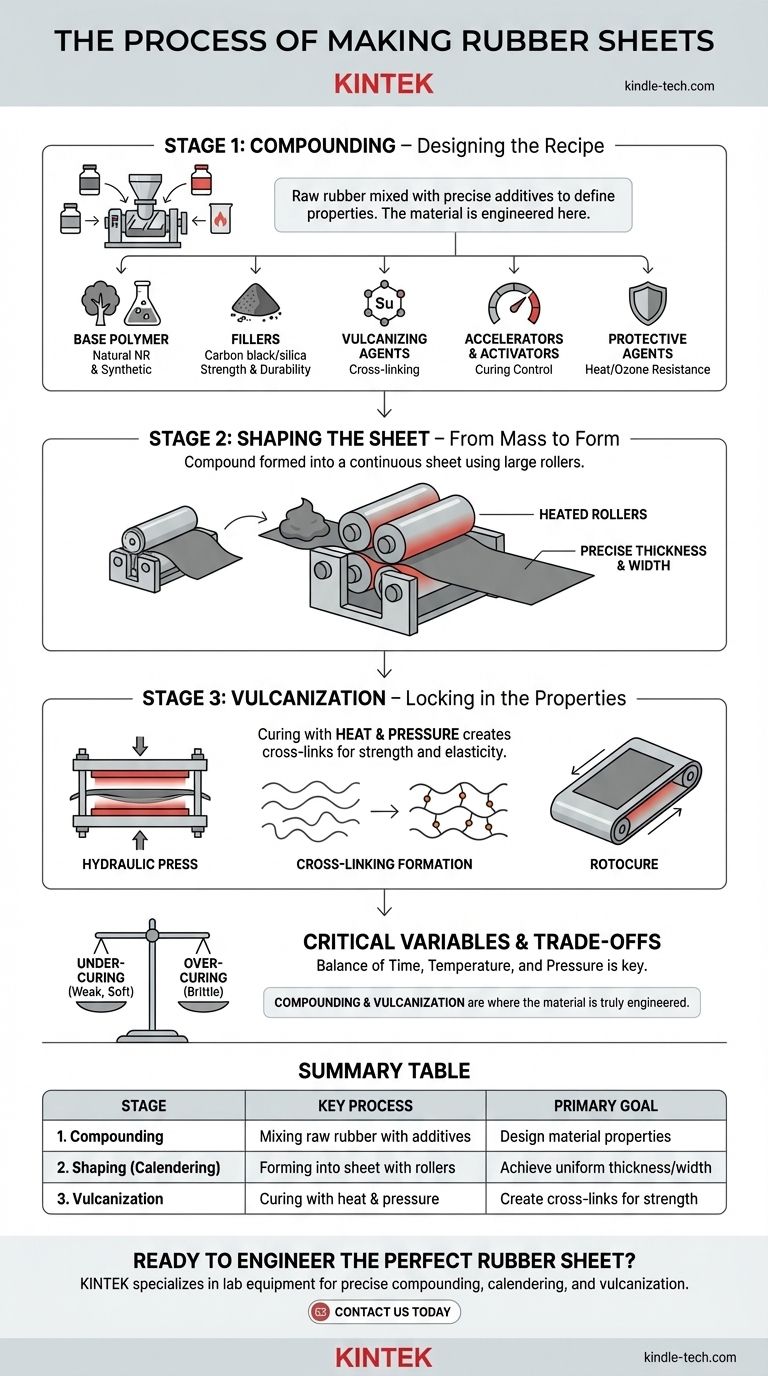
The core process for making rubber sheets involves transforming raw rubber into a finished product through three critical stages: compounding, shaping, and vulcanization. Raw natural or synthetic rubber is first mixed with a precise recipe of additives to define its future properties. This "compound" is then formed into a continuous sheet using large rollers in a process called calendering, and finally, it is cured with heat and pressure to lock in its strength and elasticity.
The key takeaway is not just the sequence of steps, but understanding that the compounding and vulcanization stages are where the material is truly engineered. The final sheet's strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability are all predetermined by the chemical "recipe" and the precise application of heat and time.

Stage 1: Compounding – Designing the Recipe
The properties of the final rubber sheet are not inherent in the raw rubber; they are built in during the compounding stage. This is where a base polymer is meticulously mixed with various additives to meet specific performance requirements.
The Base Polymer: Natural vs. Synthetic
The process begins with the selection of the base rubber. Natural Rubber (NR), harvested as latex from rubber trees, is known for its excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
Synthetic Rubbers are man-made polymers designed for specific tasks. Common examples include Neoprene for oil resistance, EPDM for weather and ozone resistance, or SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) as a general-purpose option.
The Art of the Compound
Think of compounding as creating a specific recipe. Each ingredient is added to achieve a desired outcome in the final product. The mixture is created in powerful machines like Banbury mixers, which ensure all ingredients are distributed perfectly evenly.
Key Ingredients and Their Roles
- Fillers: Materials like carbon black or silica are added to reinforce the rubber, dramatically increasing its strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion.
- Vulcanizing Agents: Sulfur is the most common agent. It is the critical ingredient that will later form cross-links between polymer chains during the curing process.
- Accelerators & Activators: These chemicals control the speed of the vulcanization process, ensuring it happens efficiently and completely without damaging the rubber.
- Protective Agents: Antioxidants and antiozonants are included to protect the final product from degradation due to heat, oxygen, and ozone exposure.
- Processing Aids: Oils and plasticizers can be added to make the rubber compound softer, more flexible, and easier to work with during the shaping stage.
Stage 2: Shaping the Sheet – From Mass to Form
Once the compound is thoroughly mixed, it must be formed into a flat sheet of a consistent, specified thickness. The primary method for this is calendering.
The Calendering Process
A calender is a machine with a series of large, heavy, heated rollers. The warm, pliable rubber compound is fed into the gap between these rollers.
As the compound passes through, it is squeezed into a continuous sheet. The distance between the final set of rollers determines the precise thickness of the rubber sheeting.
Controlling Thickness and Width
The calendering process is highly controlled to ensure uniformity. Any variation in thickness can create a weak point in the final product, so precision is paramount. The width of the sheet is determined by the width of the rollers.
Stage 3: Vulcanization – Locking in the Properties
This is the final, irreversible chemical transformation. The raw, shaped sheet is weak and plastic-like; vulcanization (or curing) converts it into the strong, elastic material we recognize as rubber.
The Chemical Transformation
During vulcanization, the sheet is heated under pressure. This heat activates the sulfur (or other vulcanizing agent) mixed in during compounding.
The sulfur creates strong chemical bonds, or cross-links, between the long polymer chains. This process transforms the material from a collection of individual strands into a single, interconnected molecular network, giving it strength, elasticity, and "memory."
How Curing is Achieved
The most common method involves placing the uncured sheet into a large hydraulic press with heated platens. The combination of high pressure and temperature is maintained for a specific duration to ensure a full cure.
For continuous production, a machine called a Rotocure may be used, which cures the sheet as it moves along a heated, rotating steel belt under pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Variables
Achieving a high-quality rubber sheet requires a deep understanding of how each variable interacts. Missteps in any stage can lead to product failure.
Compounding: The Recipe is Everything
An incorrect proportion of any ingredient can have a drastic effect. Too much filler can make the rubber brittle, while not enough accelerator can lead to an incomplete cure. The compound recipe is the foundation of the product's performance.
Curing: A Delicate Balance
The combination of time, temperature, and pressure during vulcanization is critical.
- Under-curing results in a weak, soft, and sometimes sticky product that will not perform as intended.
- Over-curing can cause the rubber to become brittle, lose its flexibility, and degrade its physical properties.
Process Control: Consistency is Key
Maintaining tight control over the mixing energy, roller temperatures, and curing conditions is essential for producing a consistent product. Any deviation can result in variations from one batch to the next.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The manufacturing process is tailored to the intended application of the rubber sheet.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and abrasion resistance: The compounding stage, specifically the type and amount of reinforcing filler like carbon black, is the most critical variable.
- If your primary focus is environmental resistance (oil, chemicals, or weather): Your choice of base polymer (e.g., Neoprene for oil, EPDM for weather) is the most important decision you will make.
- If your primary focus is dimensional precision and uniformity: You must ensure the highest level of control over the calendering and curing stages to guarantee consistent thickness and a complete cure.
Ultimately, understanding this process transforms your perspective from simply buying a product to specifying a material engineered for a precise purpose.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Compounding | Mixing raw rubber with additives (fillers, sulfur, etc.) | Design the material's properties (strength, resistance, etc.) |
| 2. Shaping (Calendering) | Forming the compound into a sheet using heated rollers | Achieve a uniform sheet of precise thickness and width |
| 3. Vulcanization | Curing the sheet with heat and pressure | Create cross-links for final strength, elasticity, and durability |
Ready to engineer the perfect rubber sheet for your application? The right equipment is critical for precise compounding, calendering, and vulcanization. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for material testing and development. Our experts can help you select the right tools to ensure quality and consistency in your process.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the process of rubber by pyrolysis? A Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Waste Rubber into Valuable Resources
- How do you recycle rubber waste? Unlock the 3 Key Methods for Tire & Rubber Recycling
- How to mix rubber compounds? Choosing Between Open Mill and Internal Mixer
- What is the process of mixing rubber compounds? A Guide to Creating Uniform, High-Performance Materials
- What is a two-roll differential speed mill? Achieve Superior Polymer Mixing & Dispersion



















