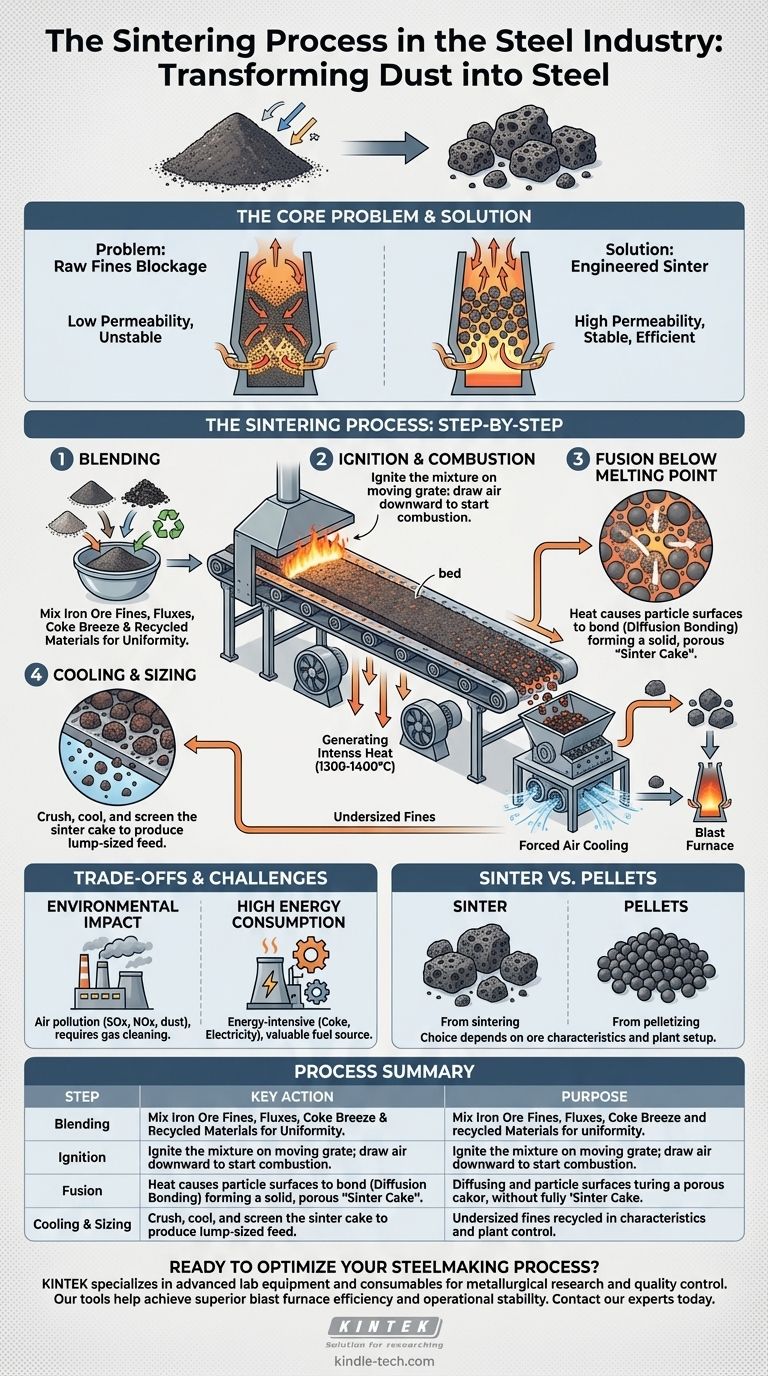
In the steel industry, sintering is a high-temperature process that transforms fine iron ore powder and other additives into a coarse, solid, and chemically consistent material called "sinter." This sinter is the ideal feed for a blast furnace, as its size and porosity allow for a more efficient and stable iron-making operation. The process involves blending raw materials, igniting them on a moving grate, and fusing the particles together at a temperature just below their melting point.
The core purpose of sintering is not merely to make big pieces out of small ones. It is an essential preparatory step that engineers a low-value byproduct—iron ore fines—into a high-performance raw material, fundamentally improving the efficiency, stability, and fuel consumption of the blast furnace.

The Core Problem: Why Sintering is Necessary
The Challenge of Raw Iron Ore Fines
Directly charging fine materials, like iron ore dust, into a blast furnace is highly problematic. These fine particles are too dense for hot gases to pass through.
This blockage, known as low permeability, would choke the furnace, prevent uniform heating, and cause massive operational instability. Furthermore, the intense upward draft of gases would simply blow the fine powder straight out of the furnace stack.
Creating an Engineered Solution
Sintering solves this by agglomerating—or clumping together—these fines into larger, porous chunks of a specific size range. This engineered product ensures a permeable column of material inside the blast furnace, allowing hot reducing gases to flow freely and react efficiently with the iron-bearing material.
The Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The industrial sintering process for blast furnace feed is distinct from the powder metallurgy used to create small metal parts. It is a continuous, large-scale operation.
Step 1: Raw Material Blending
The process begins by precisely mixing several key ingredients. The primary components are:
- Iron Ore Fines: The main iron-bearing material.
- Fluxes: Materials like limestone and dolomite, which will later help remove impurities in the blast furnace.
- Fuel: A fine carbon source, typically coke breeze, which provides the heat for the process.
- Recycled Materials: Dust and sludge collected from other parts of the steel plant, which contain valuable iron and carbon units.
Step 2: Ignition and Combustion
This carefully prepared mix is laid onto a long, continuously moving perforated grate, forming a "bed." As the grate moves along, the top surface of the bed passes under an ignition hood, which lights the coke fuel on the surface.
Powerful fans beneath the grate draw air down through the mixture. This pulls the combustion zone downward, layer by layer, through the entire depth of the bed.
Step 3: Fusing Below the Melting Point
The heat generated by the burning coke (reaching temperatures around 1300-1400°C) is intense but localized. It does not fully melt the iron ore.
Instead, the heat causes the surfaces of the individual particles to become "tacky" and diffuse into one another. This phenomenon, known as diffusion bonding, fuses the loose powder into a single, solid, but porous mass called a "sinter cake."
Step 4: Cooling and Sizing
At the end of the moving grate, the hot sinter cake falls off and is broken into smaller lumps by a crusher. This hot sinter is then cooled by forced air to prevent degradation.
Finally, the cooled sinter is screened. Lumps within the target size range are sent to the blast furnace, while any undersized fines are recycled back to the beginning of the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Environmental Impact
Sintering is one of the most significant sources of air pollution in an integrated steel mill. The combustion process releases pollutants like sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and dust. This necessitates extensive and costly gas cleaning and emission control systems to meet environmental regulations.
High Energy Consumption
While it improves the energy efficiency of the blast furnace, the sintering process itself is highly energy-intensive. The fuel required (coke breeze) is a valuable resource, and the large fans and machinery consume a significant amount of electricity.
Sinter vs. Pellets
Sintering is not the only method of agglomerating iron ore fines. Pelletizing is an alternative process where fines are rolled into small, uniform balls and fired in a kiln. The choice between sintering and pelletizing often depends on the specific characteristics of the available iron ore and the configuration of the steel plant.
Applying This to Your Goals
Your understanding of sintering should be framed by its strategic role in the steelmaking value chain.
- If your primary focus is blast furnace efficiency: Sintering is the key to creating a highly permeable and chemically uniform feed, which directly reduces fuel (coke) consumption and increases productivity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective material use: The process enables the use of low-cost iron ore fines and internal waste streams, turning potential waste products into valuable raw materials.
- If your primary focus is operational stability: The consistency of sinter in size and chemistry leads to a much more predictable and smoothly running blast furnace operation compared to using raw ore.
Ultimately, sintering is a transformative process that chemically and physically optimizes raw materials to unlock the full potential of the iron-making process.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Blending | Mix iron ore fines, fluxes, coke breeze, and recycled materials | Create a uniform raw material mix for consistent sintering |
| Ignition | Ignite the mixture on a moving grate; draw air downward | Initiate combustion to generate heat for particle fusion |
| Fusion | Heat particles to 1300-1400°C (below melting point) | Fuse particles via diffusion bonding into solid, porous sinter cake |
| Cooling & Sizing | Crush, cool, and screen the sinter cake | Produce lump-sized sinter for blast furnace use; recycle fines |
Ready to optimize your steelmaking process with high-performance sintering solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical research and quality control. Whether you're developing new sinter mixes or analyzing material properties, our tools help you achieve superior blast furnace efficiency and operational stability. Contact our experts today to discover how we can support your laboratory's critical role in the steel industry.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is plasma in the context of materials science? Understanding Its Role as a Versatile Material Processing Tool
- What does a layered film mean? Unpacking the Depths of Cinematic Storytelling
- How accurate is the XRF analysis? Achieve Lab-Quality Results with the Right Methodology
- What is the physics of sputtering? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition by Momentum Transfer
- What types of metals can be used in sintering? Expert Guide to Sintered Alloys and Non-Ferrous Metals
- What is flash sintering? Achieve Rapid, Energy-Efficient Ceramic Densification
- What is the pyrolysis method of waste management? Converting Waste into Energy and Resources
- What is the source of XRF radiation? Understanding X-ray Tubes vs. Radioisotopes for Analysis



















