The fundamental purpose of a hydraulic press is to generate an immense compressive force using a very small initial effort. It achieves this by leveraging the properties of a confined liquid, allowing it to shape, deform, crush, or compact a wide variety of materials with exceptional control.
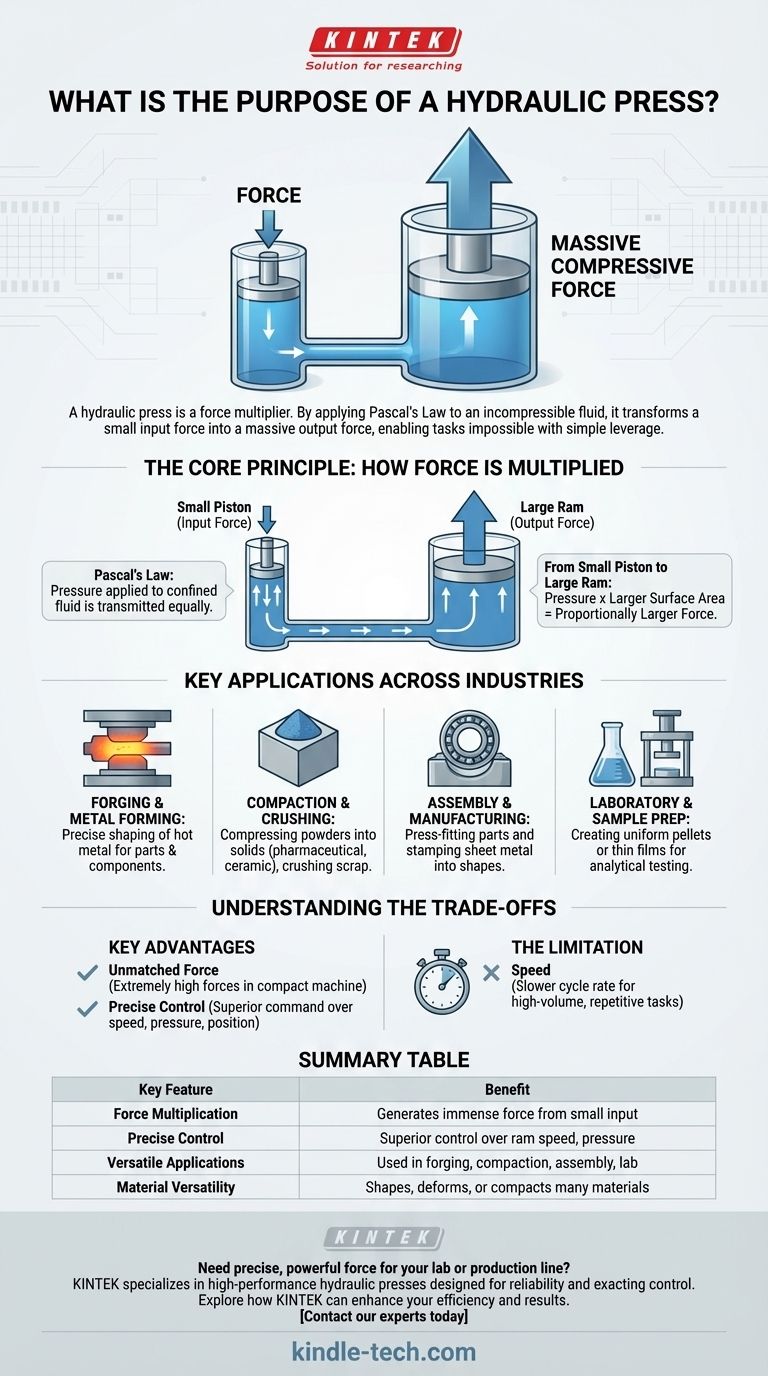
A hydraulic press is not just a machine; it is a force multiplier. By applying Pascal's Law to an incompressible fluid, it transforms a small input force on a small piston into a massive output force on a larger ram, enabling tasks that would be impossible with simple mechanical leverage.
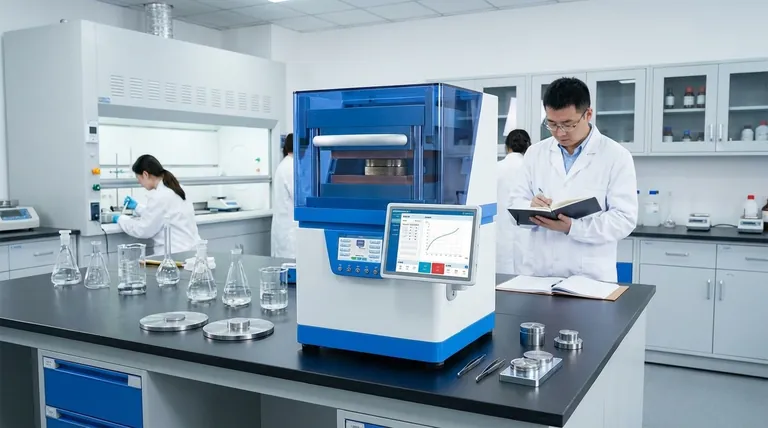

The Core Principle: How Force is Multiplied
A hydraulic press operates on a simple yet powerful principle of fluid mechanics discovered in the 17th century. Understanding this principle is key to understanding the machine's capabilities.
Pascal's Law in Action
The entire system is based on Pascal's Law. This law states that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, that pressure is transmitted equally and undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
From Small Piston to Large Ram
Imagine two connected cylinders, one narrow and one wide, both filled with hydraulic fluid and sealed with pistons. Pushing down on the small piston with a small force creates pressure in the fluid.
Because that pressure is transmitted equally throughout the fluid, it pushes up on the large piston. Since the surface area of the large piston is much greater, the resulting upward force is proportionally larger, effectively multiplying the initial force.
The Role of Hydraulic Fluid
This process works because liquids like oil are practically incompressible. The fluid does not get squeezed into a smaller volume; instead, it efficiently transfers the energy from the small piston directly to the large ram.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to generate and control massive force makes the hydraulic press a versatile and indispensable tool in nearly every industrial sector.
Forging and Metal Forming
In manufacturing, a hydraulic press is used to shape hot billets or ingots of metal. Operators can precisely control the speed and pressure of the ram, allowing for the creation of complex geometries required for automotive parts, aerospace components, and tools.
Compaction and Crushing
The immense force is ideal for high-pressure applications. This includes compressing powdered materials into solid forms, such as in the pharmaceutical or ceramic industries, and crushing large objects like scrap cars for recycling.
Assembly and Manufacturing
Hydraulic presses are often used to press-fit parts together, such as inserting bearings into housings. They are also used for stamping, where they press sheet metal into specific shapes to create car body panels or appliance casings.
Laboratory and Sample Preparation
On a smaller scale, hydraulic presses are crucial in scientific labs. They are used to press material samples into uniform pellets or thin films, which is a required step for many types of analytical testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, the hydraulic press is not the solution for every application. Its design comes with inherent advantages and limitations.
Key Advantage: Unmatched Force
The primary benefit is the ability to generate extremely high forces within a relatively compact machine. The force is limited only by the strength of the components and the pressure the system can handle.
Key Advantage: Precise Control
Unlike purely mechanical presses, hydraulic systems offer superior control over the ram's speed, pressure, and position throughout its stroke. This is critical for delicate operations or when working with unique alloys.
The Limitation: Speed
For high-volume, repetitive tasks like small-parts stamping, a hydraulic press can be slower than a mechanical press. The time it takes for the hydraulic fluid to flow and build pressure limits its cycle rate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right equipment depends entirely on the forces and control required for the task at hand.
- If your primary focus is massive force generation: A hydraulic press is the clear choice for heavy forging, large-scale compaction, and crushing operations.
- If your primary focus is precise process control: The fine-tuned command over speed and pressure makes hydraulics ideal for creating complex parts or working with sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is high-speed repetition: A mechanical press may be a more efficient solution for rapid, simple stamping or punching tasks.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press stands as a cornerstone of modern industry by providing a practical and controllable method for applying immense force.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Force Multiplication | Generates immense compressive force from a small input |
| Precise Control | Superior control over ram speed, pressure, and position |
| Versatile Applications | Used in forging, compaction, assembly, and lab work |
| Material Versatility | Shapes, deforms, or compacts a wide variety of materials |
Need precise, powerful force for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including hydraulic presses designed for reliability and exacting control. Whether you're compacting powder samples for analysis or require a robust press for R&D, our solutions are built to meet your specific needs.
Explore how a KINTEK hydraulic press can enhance your efficiency and results. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?



















