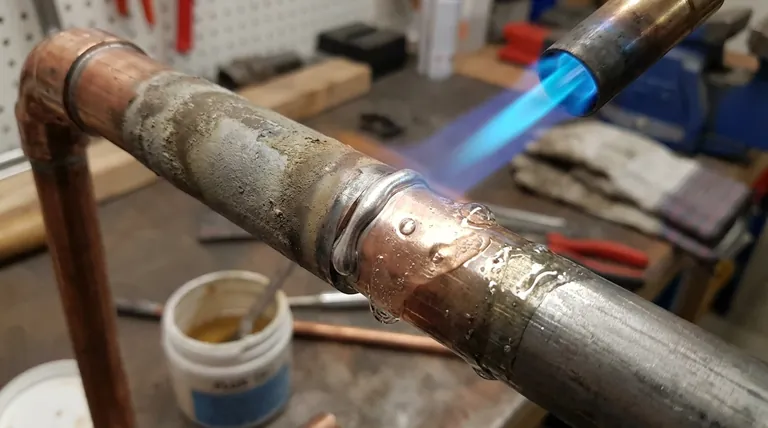
In brazing, flux is a chemical cleaning agent that prepares the base metal surfaces to be joined. Its primary purpose is to remove invisible but persistent metal oxides, prevent new oxides from forming during heating, and chemically assist the molten filler metal in wetting and flowing into the joint.
Brazing succeeds or fails based on the cleanliness of the metal surfaces. Flux is the agent that ensures this cleanliness at high temperatures, acting as a chemical solvent and a protective shield that allows the braze alloy to form a strong, continuous bond.

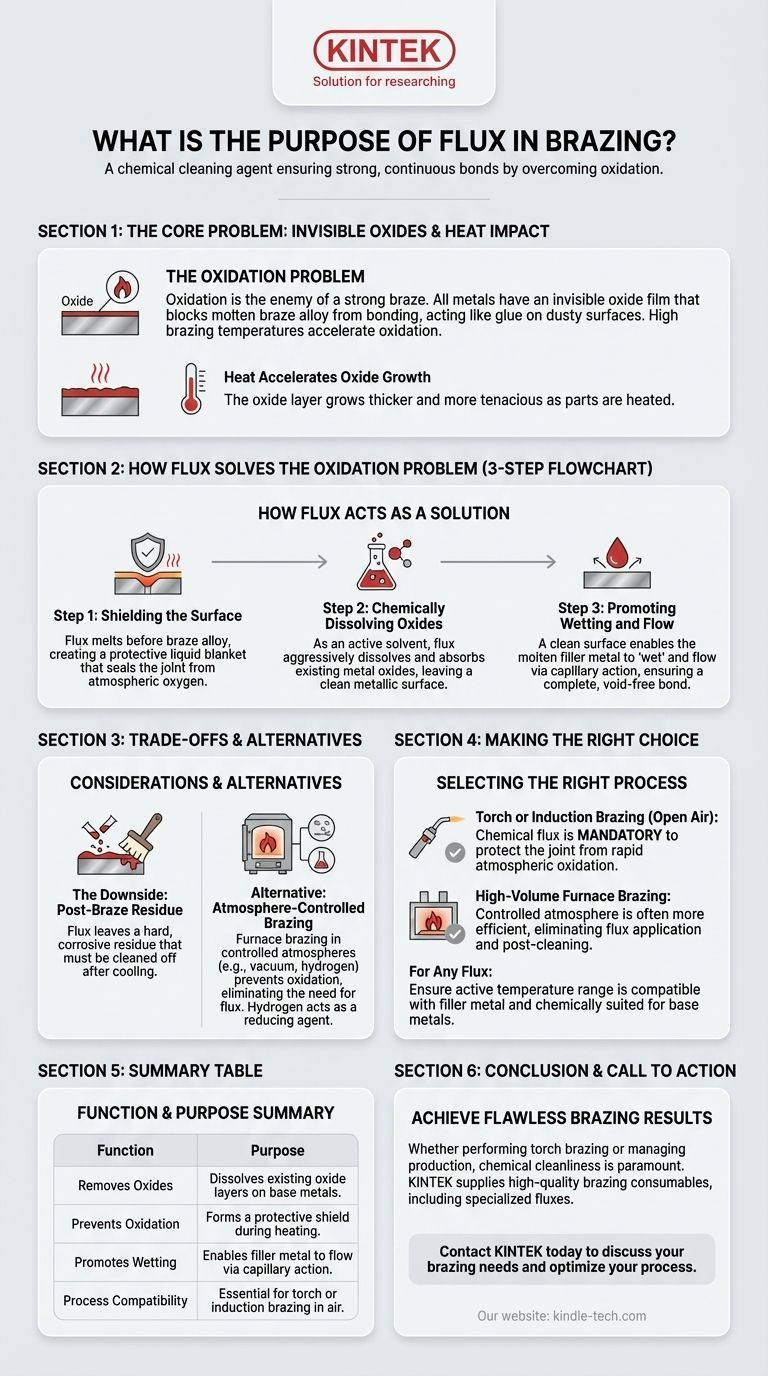
The Core Problem: Invisible Oxides
Why Oxidation is the Enemy of a Strong Braze
Nearly all metals are covered by a microscopic, invisible layer of oxide. This layer forms instantly when the metal is exposed to air.
This oxide film acts as a barrier, preventing the molten braze alloy from making direct metallic contact with the base metals. Attempting to braze an oxidized surface is like trying to glue two dusty boards together—the adhesive will stick to the dust, not the wood.
The Impact of Heat
The high temperatures required for brazing dramatically accelerate the rate of oxidation. As you heat the parts, the oxide layer grows thicker and more tenacious, making a proper bond impossible without a protective agent.
How Flux Solves the Oxidation Problem
Step 1: Shielding the Surface
A key characteristic of a good flux is that its melting point is lower than that of the braze alloy. As the joint is heated, the flux melts first, flowing over the base metals.
This liquid flux creates a protective blanket, sealing the joint area from atmospheric oxygen and preventing further oxidation during the heating cycle.
Step 2: Chemically Dissolving Oxides
Flux is an active chemical solvent. As it melts, it aggressively dissolves and absorbs the metal oxides that were already present on the surface. This leaves behind a chemically clean metallic surface, ready for the filler metal.
Step 3: Promoting Wetting and Flow
With the oxides removed, the molten filler metal can now properly "wet" the base metals. Wetting is the ability of a liquid to spread out over a solid surface.
This clean, wetted surface is what enables capillary action, the force that pulls the molten filler alloy deep into the tight-fitting gap of the joint, ensuring a complete and void-free bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
The Downside: Post-Braze Residue
Flux does its job, but it doesn't disappear. After cooling, the flux and the oxides it has absorbed form a hard, glass-like residue on and around the joint.
This residue is often corrosive and must be thoroughly cleaned off, adding an extra step to the manufacturing process.
When Flux Isn't Needed: Atmosphere-Controlled Brazing
In some industrial processes like furnace brazing, a chemical flux is not necessary. Instead, the entire part is heated inside a chamber with a controlled atmosphere.
This atmosphere, often a vacuum or a specific blend of gases, prevents oxidation from occurring in the first place, thus serving the primary function of a flux.
The Role of Hydrogen as an Active Flux
A hydrogen atmosphere is a common example of an alternative. At brazing temperatures, hydrogen acts as a powerful reducing agent, actively stripping oxygen atoms from the metal oxides. The resulting water vapor is then flushed out of the furnace, leaving a perfectly clean surface for the braze alloy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use flux is dictated entirely by your brazing method and the environment in which you are working.
- If your primary focus is torch or induction brazing in open air: A chemical flux is mandatory to protect the joint from rapid atmospheric oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume furnace brazing: A controlled atmosphere (like a vacuum or hydrogen) is often more efficient as it eliminates the need for flux application and post-braze cleaning.
- When selecting a flux for any process: Always ensure its active temperature range is compatible with your filler metal and that it is chemically suited for the base metals you are joining.
Understanding the function of flux transforms it from a simple consumable into a critical tool for guaranteeing the chemical cleanliness required for a perfect brazed joint.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Removes Oxides | Dissolves existing oxide layers on base metals. |
| Prevents Oxidation | Forms a protective shield during heating. |
| Promotes Wetting | Enables filler metal to flow via capillary action. |
| Process Compatibility | Essential for torch or induction brazing in air. |
Achieve flawless brazing results with the right materials and expertise.
Whether you are performing torch brazing in your workshop or managing a high-volume production line, the chemical cleanliness of your metal surfaces is paramount for joint integrity. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality brazing consumables, including specialized fluxes designed for specific metals and temperature ranges.
Let our experts help you select the perfect flux for your application, ensuring strong, reliable bonds without the guesswork. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your brazing needs and optimize your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
People Also Ask
- What are 3 benefits of biomass energy? Turn Waste into Renewable Power
- What is the recommended cleaning procedure for a carbon fiber brush after use? Extend Brush Life and Maintain Performance
- Under what conditions should a carbon fiber brush be replaced? Identify Critical Failure to Ensure Performance
- What does the regular maintenance inspection of a carbon fiber brush entail? Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity
- Why is it important to prevent mechanical damage to a carbon fiber brush? Ensure Peak Performance & Longevity



















