At its core, heat treatment is the controlled process of heating and cooling a metal to change its internal microstructure. The purpose is to deliberately alter its physical and mechanical properties, making the material stronger, harder, and more wear-resistant, or, conversely, softer and more ductile to suit a specific engineering requirement.
Heat treatment is not about changing the metal itself, but about precisely manipulating its internal crystal structure. This allows engineers to transform a generic metal into a high-performance material optimized for a specific function, from being easily machined to withstanding extreme stress.

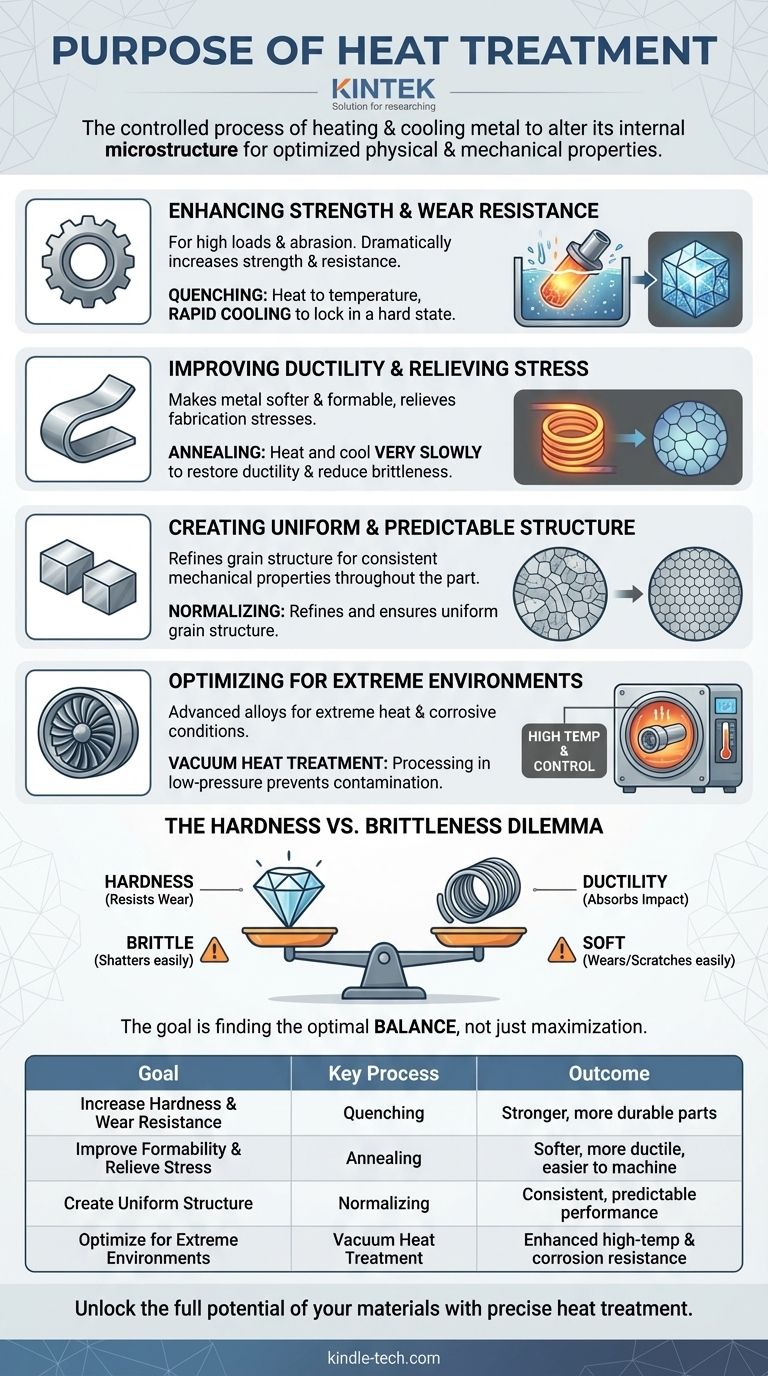
Why Heat Treatment is a Pillar of Manufacturing
A metal straight from the mill or foundry rarely possesses the ideal combination of properties for its final application. Processes like welding, forging, or casting can also introduce internal stresses and inconsistencies. Heat treatment is the critical step that resolves these issues and unlocks the material's full potential.
Enhancing Strength and Wear Resistance
For components that must endure high loads or abrasive forces, hardness is paramount. Heat treatment can dramatically increase a metal's strength and its resistance to wear and impact.
This is achieved by heating the metal to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling it (a process known as quenching). This change locks the material's internal structure into a very hard, strong state.
Improving Ductility and Relieving Stress
Conversely, sometimes the goal is to make a metal softer and more formable. A process called annealing involves heating a metal and then cooling it very slowly.
This process relieves internal stresses built up during fabrication, which makes the metal less brittle and easier to machine, bend, or stamp without cracking. It restores the material's ductility.
Creating a Uniform and Predictable Structure
Manufacturing processes can create an inconsistent, or non-homogenous, internal structure within a metal part. This leads to unpredictable performance, where one area of the part may be weaker than another.
A process called normalizing is used to refine the grain structure, making it uniform throughout the component. This ensures that the mechanical properties are consistent and reliable across the entire part.
Optimizing for Extreme Environments
For highly demanding sectors like aerospace, standard materials are not enough. Advanced alloys, such as those based on nickel, must perform reliably in the extreme heat of jet engines and exhausts.
Specialized techniques like vacuum heat treatment are used for these materials. Processing in a low-pressure vacuum prevents contamination and allows for precise control, enabling parts to better withstand high temperatures and intense operational stresses.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Hardness vs. Brittleness Dilemma
Heat treatment is not a magic bullet; it is a discipline of calculated compromises. The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and brittleness.
The Inevitable Compromise
As you make a metal harder, you almost always make it more brittle. A very hard material is excellent at resisting scratches and wear, but it may shatter like glass if subjected to a sudden, sharp impact.
Conversely, a softer, more ductile material can absorb impact by deforming, but it will wear down and scratch more easily.
The Goal is Balance, Not Maximization
The role of the engineer is not to simply maximize one property but to find the optimal balance for the job. A sword blade needs to be hard enough to hold a sharp edge but ductile enough not to shatter on impact. The steel in a car's safety cage must be strong but also able to crumple to absorb crash energy.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The specific heat treatment process is always chosen based on the desired final outcome for the component.
- If your primary focus is durability and wear resistance: You will likely use treatments like quenching and tempering to achieve a high hardness.
- If your primary focus is ease of manufacturing: You will use a process like annealing to soften the material and relieve stress, making it easier to machine or form.
- If your primary focus is predictable performance after welding or forging: You will use normalizing to create a uniform internal structure and ensure consistent properties.
- If your primary focus is performance in high-heat or corrosive environments: You will require specialized processes and alloys designed for those extreme conditions.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is what allows us to push materials to their limits and build a safer, more efficient world.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Wear Resistance | Quenching | Stronger, more durable parts |
| Improve Formability & Relieve Stress | Annealing | Softer, more ductile, easier to machine |
| Create Uniform Structure | Normalizing | Consistent, predictable performance |
| Optimize for Extreme Environments | Vacuum Heat Treatment | Enhanced high-temperature and corrosion resistance |
Ready to optimize your materials for peak performance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise and reliable heat treatment processes. Whether you are in R&D, quality control, or manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of hardness, strength, and ductility for your specific application.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs and discover the right equipment for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Trade-offs for Your Lab
- What is a laboratory furnace called? A Guide to Muffle and Tube Furnaces
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application



















