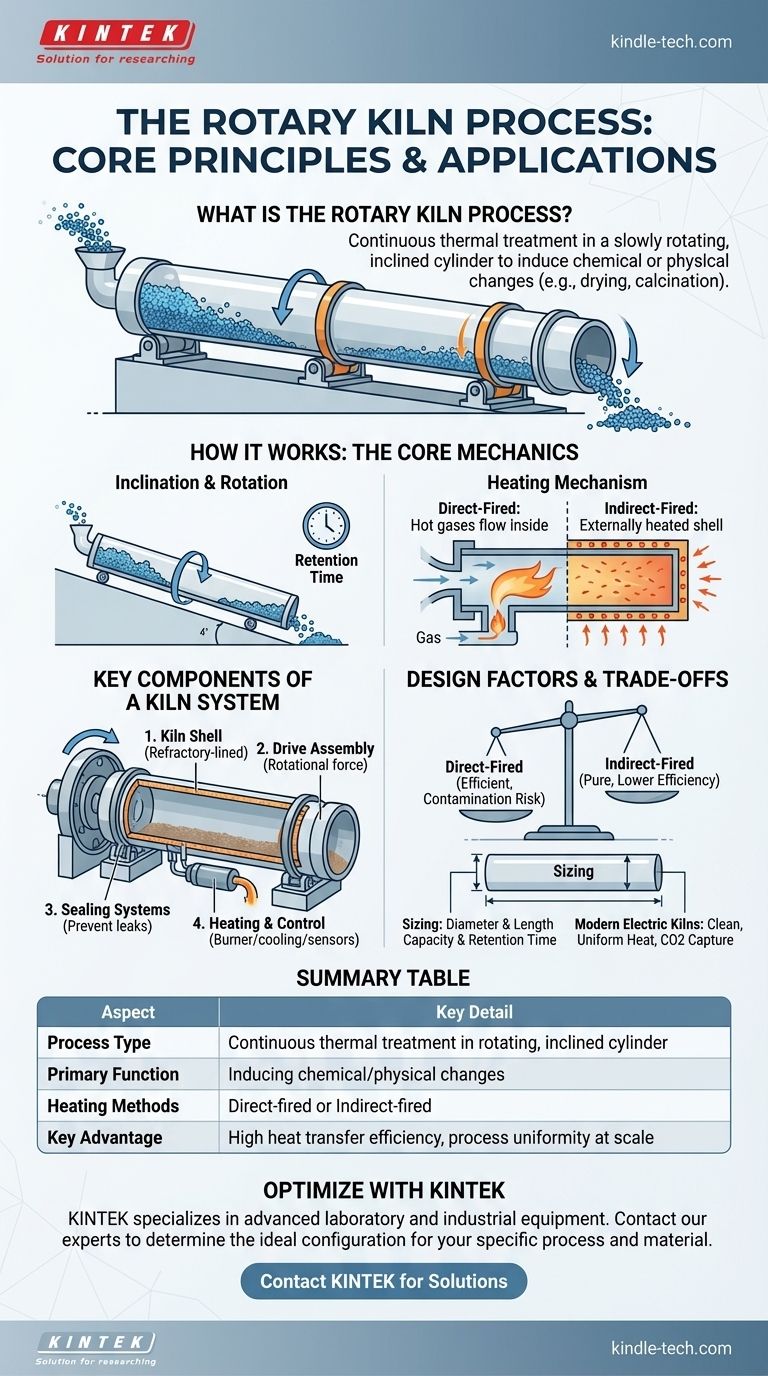
At its core, the rotary kiln process is a method for heating solid materials to extremely high temperatures within a slowly rotating, inclined cylinder. As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and gradually moves from the higher feed end to the lower discharge end, ensuring it is thoroughly mixed and uniformly heated by hot gases. This controlled thermal treatment is used to induce a specific chemical reaction or physical change, such as drying, calcination, or incineration.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary kiln lies in its continuous and dynamic operation. The combination of rotation and inclination creates a constantly agitated bed of material, which promotes unparalleled heat transfer efficiency and process uniformity for large-scale industrial applications.

How a Rotary Kiln Works: The Core Mechanics
A rotary kiln functions as a highly specialized heat exchanger, transforming raw feedstock through controlled thermal exposure. The process is a seamless integration of motion and heat.
The Principle of Inclination and Rotation
The entire kiln vessel is tilted at a slight angle from the horizontal, typically between 1 to 4 degrees. This inclination, combined with a slow, constant rotation, is what drives the process.
Material fed into the upper end is gently lifted by the kiln's rotation and then tumbles back down. This repeated motion simultaneously mixes the material and causes it to gradually advance toward the lower discharge end.
The Heating Mechanism
Heat is the catalyst for the entire process, and it can be applied in two primary ways.
A direct-fired kiln is the most common type. Hot gases from a flame inside the kiln or an external furnace flow directly over and through the material. This flow can be counter-current (gases move opposite the material) for maximum heat efficiency or co-current (gases move with the material).
An indirect-fired kiln, often called a calciner, works differently. The kiln's outer shell is heated externally, and this heat radiates inward to the material inside. This method is used when the material cannot come into direct contact with combustion gases to prevent contamination.
The Material's Journey
The feedstock is introduced at the upper end, often using a quantitative system like a screw feeder to ensure a consistent rate. As it travels the length of the kiln, it passes through different temperature zones, undergoing its intended transformation. The total time the material spends inside is known as retention time, a critical process parameter.
Key Components of a Rotary Kiln System
While the rotating cylinder is the heart of the system, several other components are essential for its operation.
The Kiln Shell
This is the main cylindrical body, typically made of steel and lined with refractory bricks to withstand extreme internal temperatures. It is engineered to handle significant thermal and mechanical stress.
The Drive Assembly
The drive assembly provides the rotational force. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, including a large gear and pinion system, a chain and sprocket drive, or modern direct-drive systems.
Sealing Systems
Effective seals at both the feed and discharge ends are crucial. They prevent cold air from entering the kiln (which would disrupt thermal efficiency) and stop hot gases and material dust from escaping into the environment.
The Heating and Control System
For direct-fired kilns, this includes the burner pipe that projects the flame. For all kilns, it involves sophisticated temperature monitoring and air cooling mechanisms to maintain a stable and precise heat pattern throughout the vessel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Factors
Sizing and designing a rotary kiln is a complex engineering task that balances multiple variables. Getting this balance wrong leads to inefficiency and poor product quality.
Sizing and Capacity
The diameter and length of the kiln are not arbitrary. They are determined by the required production capacity, the specific heat requirements of the material's reaction, and the desired retention time.
Retention Time vs. Throughput
A longer retention time ensures a complete reaction but reduces the overall throughput (the amount of material processed per hour). Engineers must carefully calculate the kiln's length, incline, and rotation speed to achieve the target retention time at the desired production rate.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The choice between direct and indirect firing presents a clear trade-off. Direct firing is more thermally efficient but introduces combustion byproducts. Indirect firing offers high purity but is generally less efficient and operates at lower temperature ceilings.
The Rise of Electric Kilns
Modern electric rotary kilns offer a clean alternative to traditional fossil-fuel-fired systems. They provide exceptionally uniform heat and eliminate product contamination from combustion gases. Critically, they also enable the capture of pure CO2 produced by the process itself, which can then be sold or reused.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal rotary kiln configuration depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency for bulk materials: A counter-current, direct-fired kiln is the industry standard for processes like cement manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is process purity or avoiding gas contact: An indirect-fired kiln (calciner) is the correct choice to protect sensitive materials from contamination.
- If your primary focus is environmental control and high-purity output: An electric rotary kiln offers a fossil-fuel-free path with precise temperature control and the ability to capture process gases.
Ultimately, mastering the rotary kiln process means understanding how to manipulate its core variables—rotation, temperature, and time—to achieve a specific material transformation reliably and efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Continuous thermal treatment in a rotating, inclined cylinder |
| Primary Function | Inducing chemical/physical changes (e.g., drying, calcination) |
| Heating Methods | Direct-fired (common) or Indirect-fired (for purity) |
| Key Advantage | High heat transfer efficiency and process uniformity at scale |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Whether you are processing minerals, chemicals, or waste materials, selecting the right rotary kiln is critical to your operation's efficiency, purity, and environmental footprint. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory and industrial equipment, offering solutions tailored to your specific material and process requirements.
Our experts can help you determine the ideal configuration—direct-fired, indirect-fired, or modern electric—to achieve superior product quality and operational control.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our rotary kiln solutions can enhance your process efficiency and output.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the future of pyrolysis oil? A Key to Circular Economy & Renewable Fuels
- What is the temperature range for calcination? Master the 800°C to 1300°C Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is modified chemical vapour deposition method? The Inside-Out Process for Ultra-Pure Optical Fibers



















