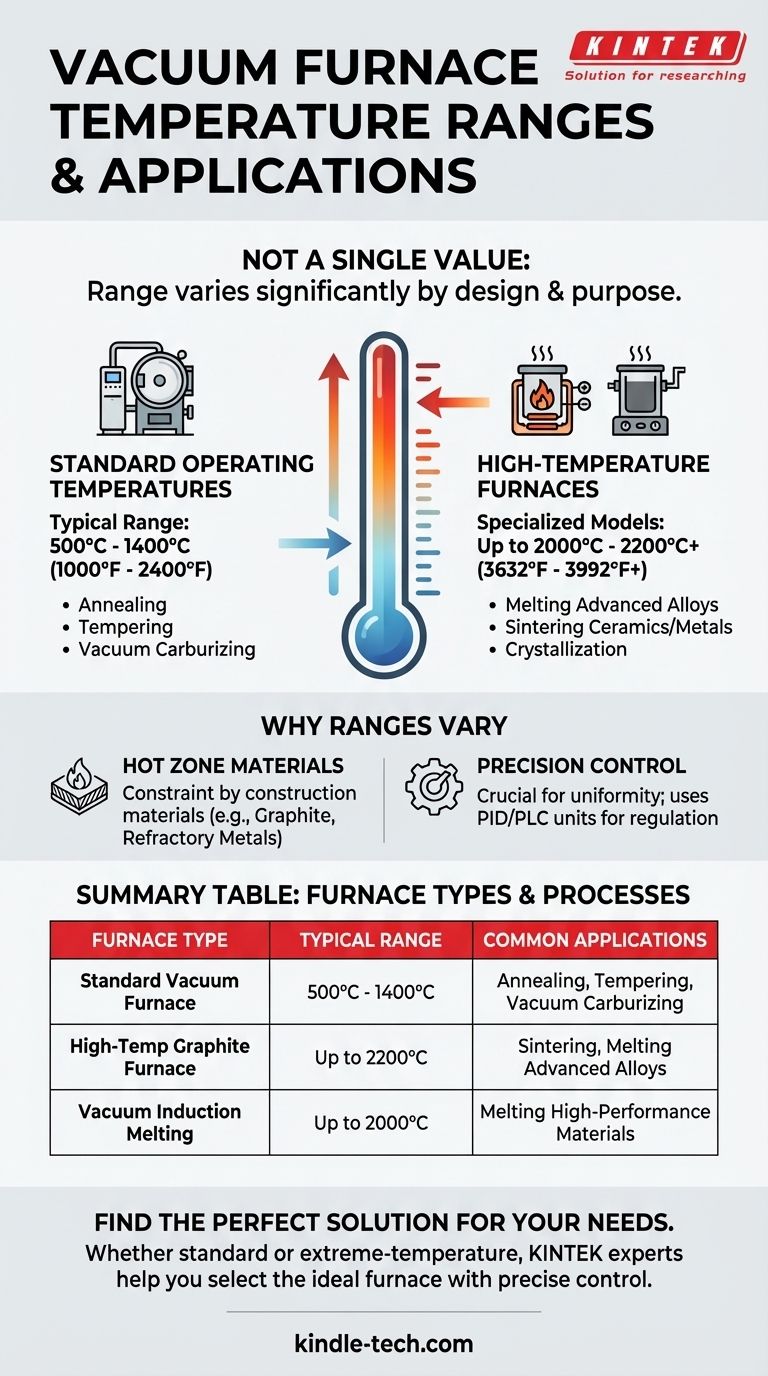
The temperature range of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but varies significantly based on its design and intended purpose. While a standard furnace typically operates between 500°C and 1400°C (about 1000°F to 2400°F), specialized high-temperature models, such as induction or graphite furnaces, can reach maximum temperatures of 2000°C to 2200°C (3632°F to 3992°F) or even higher.
The specific temperature capability of a vacuum furnace is dictated by its construction and the material processing task it is designed for. The question is not just "how hot can it get," but "what thermal process needs to be accomplished in a controlled, oxygen-free environment."

Why Temperature Ranges Vary by Furnace Type
The maximum operating temperature of a vacuum furnace is fundamentally limited by the materials used in its construction, particularly within the heating chamber or "hot zone."
Standard Operating Temperatures
A typical general-purpose vacuum furnace provides a wide operating range, often from around 538°C to 1315°C (1000°F to 2400°F).
This range is sufficient for a majority of common industrial heat-treating processes, including annealing, tempering, and vacuum carburizing for many standard metals and alloys.
High-Temperature Furnaces
For more demanding applications, specialized furnaces are required. These are designed with materials that can withstand extreme heat without degrading.
A vacuum induction melting furnace, for instance, can reach temperatures up to 2000°C. A vacuum graphite furnace, which uses graphite for its heating elements and insulation, can achieve even higher temperatures, often up to 2200°C.
The Role of the Hot Zone
The hot zone contains the heating elements and the insulation that reflects heat back onto the workpiece. The materials used here are the primary constraint on temperature.
Graphite and certain refractory metals are common choices for high-temperature hot zones due to their high melting points and stability under vacuum conditions.
How Temperature Enables Specific Processes
Different metallurgical and material processes are activated at specific temperatures. The ability to precisely control the temperature profile—including ramp rates and hold times—is what makes a vacuum furnace so versatile.
Lower-Temperature Processes (~500°C to 900°C)
Processes like workload outgassing and tempering occur at the lower end of the furnace's capability. A typical program might hold a part at 800°C to allow trapped gases to escape before proceeding to higher temperatures.
Mid-Range Processes (~900°C to 1200°C)
This range is critical for processes like annealing, normalizing, and vacuum carburizing. A treatment cycle might involve slowly warming a component to 1100°C and holding it there to alter its microstructure for improved ductility or hardness.
High-Temperature Applications (>1400°C)
The highest temperatures are reserved for advanced processes. This includes the melting of high-performance alloys, sintering of ceramics or powdered metals, and the crystallization of composite materials to create high-strength components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controls
Achieving a high maximum temperature is only one part of the equation. The quality of the final product depends heavily on the precision and environment of the furnace.
Precision Over Peak Temperature
For many applications, the ability to maintain a uniform and stable temperature is more critical than reaching an extreme peak. The temperature control system is therefore a crucial component.
These systems use thermocouples for measurement and sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) units to precisely regulate power to the heating elements.
The Purpose of the Vacuum
The primary benefit of a vacuum furnace is the oxygen-free environment. This prevents oxidation, scaling, and surface discoloration, which would otherwise occur when heating materials to high temperatures in air, as in a traditional muffle furnace.
This ensures the workpiece maintains its dimensional accuracy and surface integrity, which is a critical requirement in aerospace, medical, and high-tech industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires matching its capabilities to the specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treatment (annealing, tempering): A furnace with a maximum temperature around 1400°C will meet the vast majority of your needs.
- If your primary focus is melting or sintering advanced materials: You must invest in a specialized high-temperature furnace capable of reaching 2000°C or more.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and final part quality: Prioritize the furnace's temperature control system and its ability to maintain uniform heat, not just its peak temperature rating.
Ultimately, the ideal vacuum furnace is one whose thermal capabilities are precisely aligned with your material processing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Temperature Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Vacuum Furnace | 500°C - 1400°C | Annealing, Tempering, Vacuum Carburizing |
| High-Temperature Graphite Furnace | Up to 2200°C | Sintering, Melting Advanced Alloys |
| Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace | Up to 2000°C | Melting High-Performance Materials |
Ready to find the perfect vacuum furnace for your specific temperature requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing precision lab equipment tailored to your unique material processing needs. Whether you require standard heat treatment capabilities or extreme-temperature solutions for advanced materials, our experts will help you select the ideal vacuum furnace with the precise temperature range and control system your laboratory demands.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your application and receive a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your partner in achieving superior results with the right laboratory equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits
- What is the temperature of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Material Properties & Pristine Finishes



















