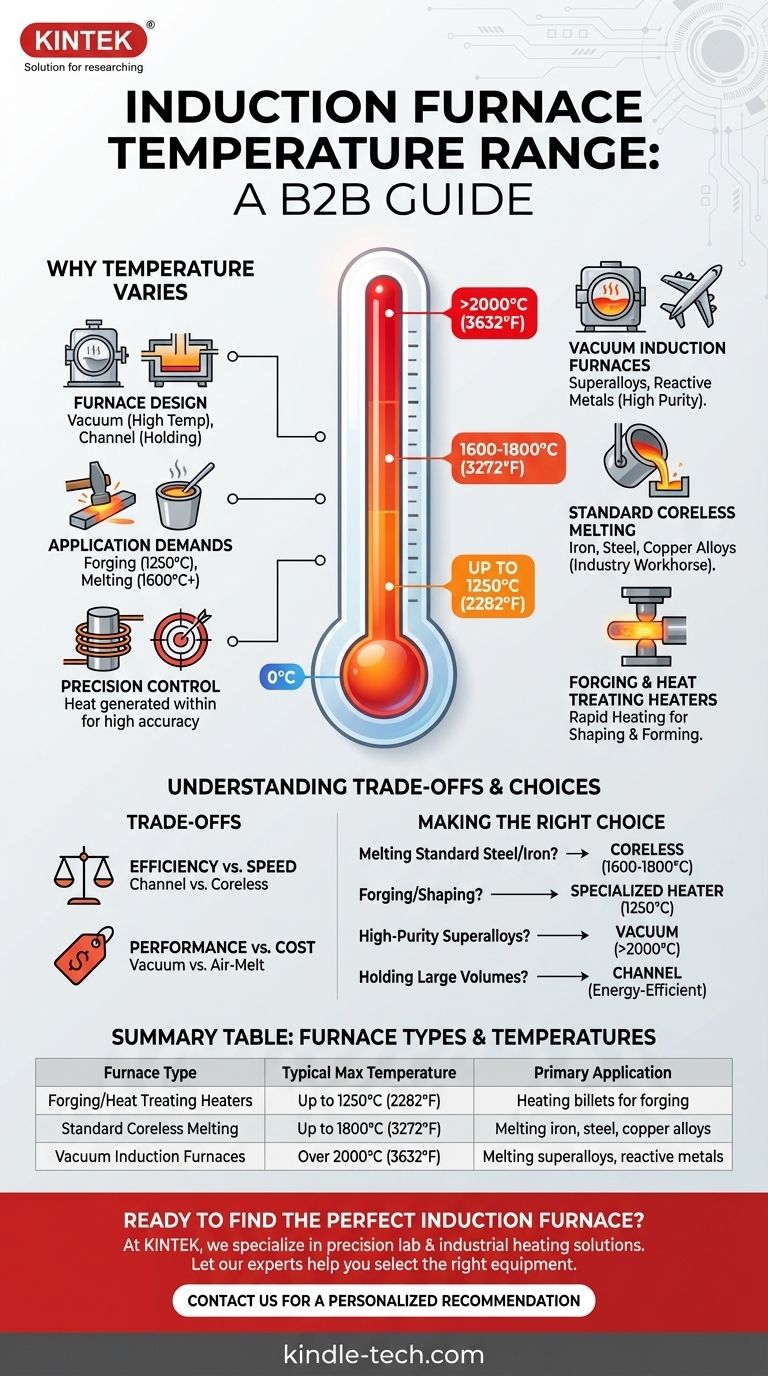
In short, an induction furnace can operate at temperatures ranging from 1250°C (2282°F) for forging applications to over 2000°C (3632°F) for melting specialty metals in a vacuum environment. The specific maximum temperature is not a single value but is determined by the furnace's design, the material being heated, and the intended industrial process.
The key takeaway is that an induction furnace's temperature capability is a function of its design and purpose. Instead of a fixed range, it's more accurate to think of different types of induction furnaces engineered for specific temperature targets, from forging and holding to melting high-performance alloys.
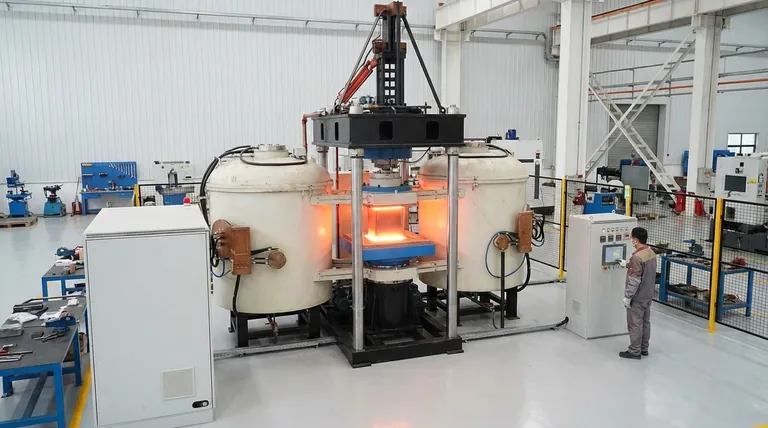

Why Temperature Varies by Furnace and Application
The term "induction furnace" covers a range of technologies, each optimized for a different task. The achievable temperature is a direct result of the furnace's construction and its intended use.
The Impact of Furnace Design
Different designs are built to meet different thermal and metallurgical requirements. For example, a vacuum induction furnace is specifically designed to reach extremely high temperatures (up to 2000°C) while preventing the molten metal from reacting with air, which is critical for specialty alloys.
In contrast, a channel induction furnace operates more like a transformer, where the molten metal forms a secondary loop. This design is highly efficient for holding metal at a constant temperature or for melting lower-temperature alloys, rather than for reaching peak melting points rapidly.
The Demands of the Application
The process itself dictates the required temperature. Forging steel requires heating it to a malleable state, typically up to 1250°C, without melting it.
Melting common ferrous metals like iron and steel requires higher temperatures, often in the range of 1600°C to 1650°C. The powerful electromagnetic field not only generates this heat but also provides a continuous stirring action, ensuring a uniform temperature and chemical composition throughout the melt.
The Principle of Precise Control
A core advantage of induction is its precision. Unlike fuel-fired furnaces, the heat is generated directly within the metal itself. This results in a very small temperature difference between the surface and the core of the material, allowing for exceptionally high temperature control accuracy.
Common Furnace Types and Their Operating Temperatures
To select the right equipment, you must match the furnace type to your operational temperature needs.
Standard Coreless Melting Furnaces (Up to 1800°C)
These are the workhorses of the foundry industry. They are used for melting a wide variety of metals, including iron, steel, and copper alloys. They can efficiently reach temperatures of 1600°C to 1800°C for standard melting operations.
Vacuum Induction Furnaces (Up to 2000°C)
When metal purity and performance are paramount, vacuum furnaces are used. By removing the atmosphere, they prevent oxidation and contamination at extreme temperatures, making them essential for producing aerospace-grade superalloys and other reactive metals. Their maximum temperatures can exceed 2000°C.
Forging and Heat Treating Heaters (Up to 1250°C)
These systems are designed not for melting, but for rapidly and uniformly heating metal billets before forging or shaping. They prioritize speed and precise temperature control, typically operating up to 1250°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an induction furnace involves balancing temperature capabilities against other factors like efficiency and cost.
Temperature vs. Efficiency
A channel furnace is extremely energy-efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a steady temperature. However, it is not well-suited for rapidly melting cold scrap. A coreless furnace excels at rapid melting but may be less efficient for long-term holding.
Performance vs. Cost
The ability to reach higher temperatures and operate in a vacuum comes at a significant cost. A vacuum induction melting furnace is a far more complex and expensive piece of equipment than a standard air-melt furnace due to the need for a vacuum chamber, pumps, and sophisticated controls.
Induction vs. Fuel-Fired Furnaces
Traditional natural gas furnaces typically max out around 1100°C (2000°F). For any application requiring higher temperatures—such as melting steel—induction heating is not just an option, but a necessity. It provides higher temperatures, faster heating, and a cleaner operating environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective is the most important factor in determining the required temperature range.
- If your primary focus is melting standard steel and iron: A coreless induction furnace capable of reaching 1600-1800°C is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is forging or shaping metal: A specialized induction heater with precise controls for temperatures up to 1250°C is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity superalloys or reactive metals: A vacuum induction furnace that can achieve temperatures of 2000°C or more is required.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of molten metal: An energy-efficient channel furnace is the most economical and effective solution.
Understanding how an induction furnace's design aligns with its intended function empowers you to select the precise technology for your metallurgical goal.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Forging/Heat Treating Heaters | Up to 1250°C (2282°F) | Heating billets for forging |
| Standard Coreless Melting Furnaces | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) | Melting iron, steel, copper alloys |
| Vacuum Induction Furnaces | Over 2000°C (3632°F) | Melting superalloys, reactive metals |
Ready to find the perfect induction furnace for your temperature requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing precision lab equipment and industrial heating solutions. Whether you need a standard melting furnace for steel or a high-temperature vacuum system for superalloys, our experts will help you select the right equipment for your specific metallurgical process.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Get in touch with our heating specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What critical processing conditions does a Vacuum Hot-Press Sintering Furnace provide? Achieve High-Performance Composites
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- Why use vacuum in hot-press sintering for boron carbide? Achieve Superior Density and Material Purity
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production
- Why is a high-vacuum environment essential for sintering Cu-Ni-W alloys? Achieve Peak Thermal Conductivity



















