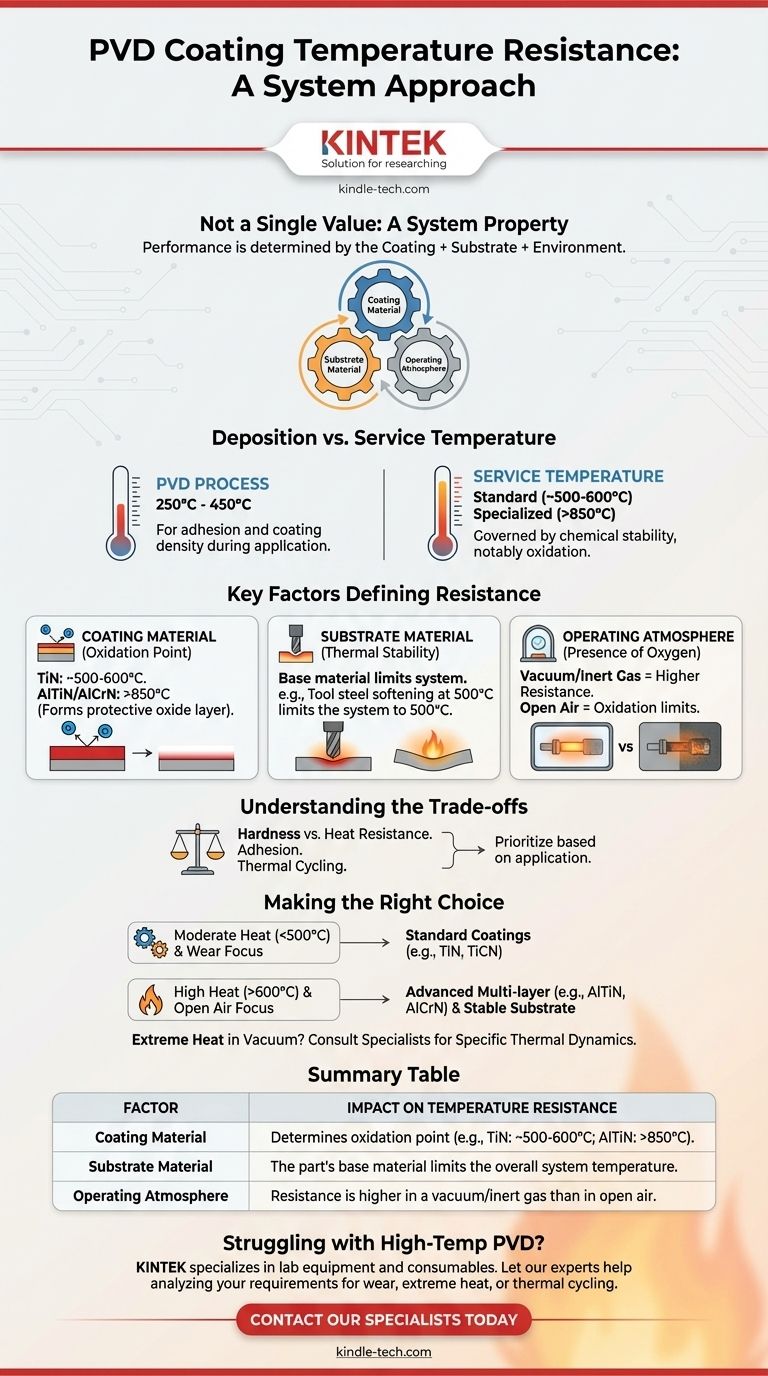
To be precise, the temperature resistance of a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is not a single value but is determined by the specific coating material, the substrate it is applied to, and the operating environment. While many standard PVD coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) begin to oxidize and break down around 500-600°C, specialized coatings are engineered to perform reliably at temperatures exceeding 850°C.
The crucial takeaway is that a PVD coating's performance at high temperatures is a property of the entire system. The coating's own oxidation point, the thermal stability of the underlying component, and the presence of oxygen all dictate its true temperature resistance in an application.

Clarifying Deposition vs. Service Temperature
A common point of confusion is the difference between the temperature of the PVD process and the temperature the final coated part can withstand.
The PVD Process Temperature
The PVD process itself is typically conducted at elevated temperatures, usually between 250°C and 450°C.
This heat is critical during deposition. It ensures high coating density and promotes strong molecular adhesion between the coating and the substrate material.
The Application Service Temperature
This is the actual temperature the part will experience during use, and it is unrelated to the deposition temperature. The service temperature limit is governed by the chemical stability of the specific coating material, most notably its resistance to oxidation.
Key Factors Defining Temperature Resistance
You cannot evaluate a coating in isolation. Three elements work together to determine the thermal limits of the final component.
1. The Coating Material
Different PVD materials have vastly different thermal limits. The primary failure mode at high temperatures is oxidation, where the coating reacts with oxygen in the air, becomes brittle, and loses its beneficial properties.
For example, a common Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) coating, known for its hardness, has a different thermal profile than a coating designed specifically for high heat. Coatings like Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) or Aluminum Chromium Nitride (AlCrN) are specifically formulated to form a protective aluminum oxide layer at high temperatures, pushing their effective service limits much higher.
2. The Substrate Material
The PVD coating relies entirely on the stability of the material it covers. The properties of the final part are always determined by the underlying substrate.
If you apply a coating rated for 900°C onto a tool steel that begins to soften or lose its temper at 500°C, the system's maximum service temperature is limited to 500°C. The component will fail long before the coating does.
3. The Operating Atmosphere
The environment plays a decisive role. A coating's temperature resistance is significantly higher in a vacuum or an inert gas environment than it is in open air.
Without the presence of oxygen, the primary failure mechanism (oxidation) is removed. In this case, the limiting factor may become the temperature at which the coating itself begins to soften or diffuse into the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a PVD coating involves balancing competing properties. The best choice for one application may be unsuitable for another.
Hardness vs. Heat Resistance
The hardest coatings are not always the most heat-resistant. You must choose a material formulated for your specific priority, whether that is wear resistance at ambient temperature or stability in a high-heat environment.
Coating Adhesion
A coating's thermal stability is meaningless if it doesn't adhere properly to the part. The deposition process parameters, including temperature and surface preparation, are critical for ensuring a strong bond that won't flake or delaminate under thermal stress.
Thermal Cycling
Components that experience rapid heating and cooling face unique challenges. Mismatches in the thermal expansion rates between the coating (which is typically a ceramic) and the metal substrate can create immense internal stress, leading to cracking and premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate coating, you must first define your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is general wear resistance at moderate temperatures (< 500°C): Standard coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) offer a proven balance of hardness and reliability.
- If your primary focus is performance in high-heat, open-air environments (> 600°C): You must select advanced, multi-layer coatings like AlTiN or AlCrN and ensure your substrate material can maintain its structural integrity at those temperatures.
- If your primary focus is an extreme-heat application in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Your limits will be higher, but you must consult with a coating specialist to analyze the specific thermal dynamics between the coating and your chosen substrate.
Ultimately, treating temperature resistance as a system property—not just a coating specification—is the key to achieving reliable performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Temperature Resistance |
|---|---|
| Coating Material | Determines oxidation point (e.g., TiN: ~500-600°C; AlTiN: >850°C). |
| Substrate Material | The part's base material limits the overall system temperature. |
| Operating Atmosphere | Resistance is higher in a vacuum/inert gas than in open air. |
Struggling to select the right PVD coating for your high-temperature application?
You don't have to navigate the trade-offs between hardness, heat resistance, and substrate compatibility alone. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving precise laboratory needs. Our experts can help you analyze your specific requirements—whether for wear resistance, extreme heat, or thermal cycling—to ensure your coated components perform reliably.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your project and discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal CVD technique? The High-Temperature Secret to Superior Coatings
- Why is CVD better than PVD? Achieve Superior, Uniform Coatings on Complex Geometries
- What is the apparatus of chemical vapor deposition? The Essential Components for Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum deposition? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision Coatings
- What is the CVD method for synthetic diamonds? Grow Lab Diamonds from Gas with Precision



















