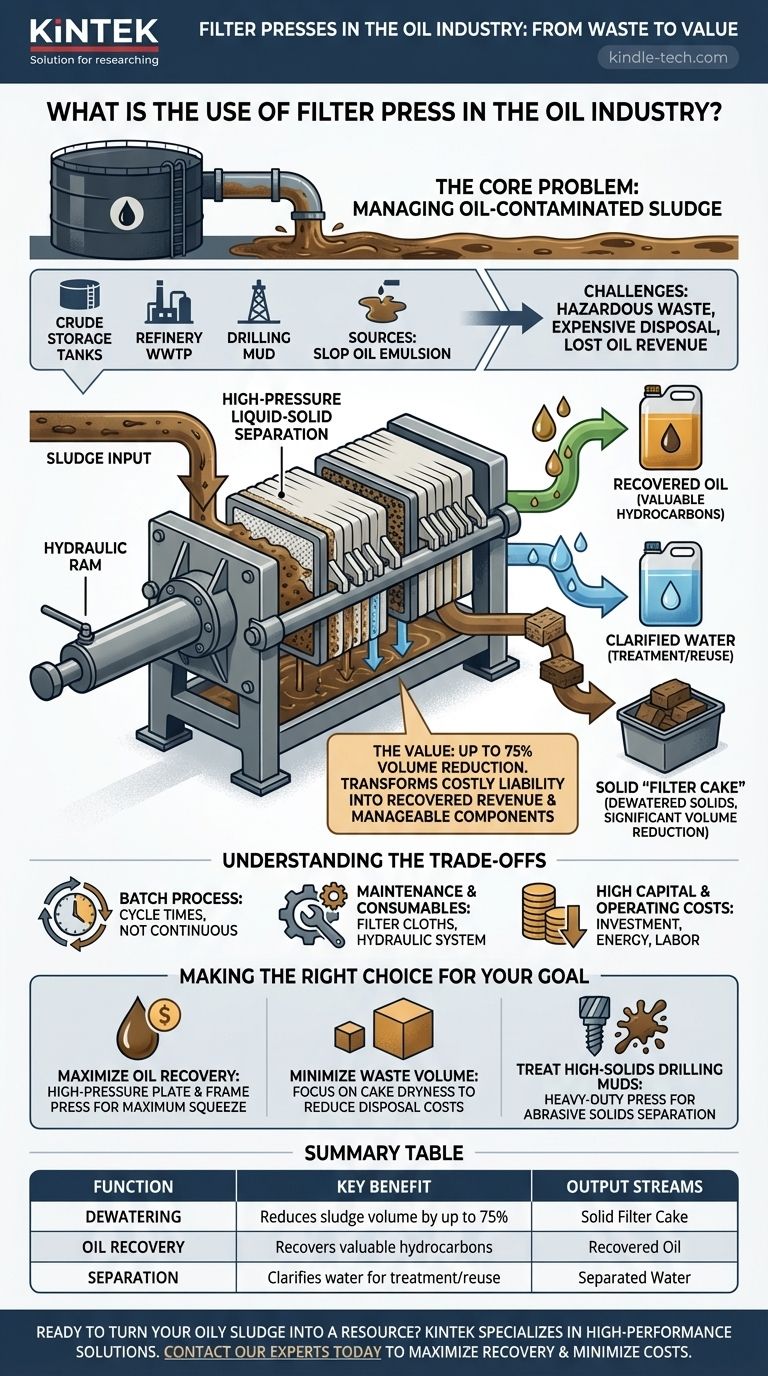
In the oil industry, a filter press is a critical piece of machinery used for high-pressure liquid-solid separation. Its primary function is to dewater sludges, recover valuable hydrocarbons from waste streams, and significantly reduce the volume of hazardous materials that require disposal. This process turns a costly environmental liability into a source of recovered revenue.
The core value of a filter press is not just waste treatment, but resource optimization. It transforms oil-contaminated sludge from a disposal problem into three manageable components: recovered oil, separated water, and a solid, semi-dry cake.
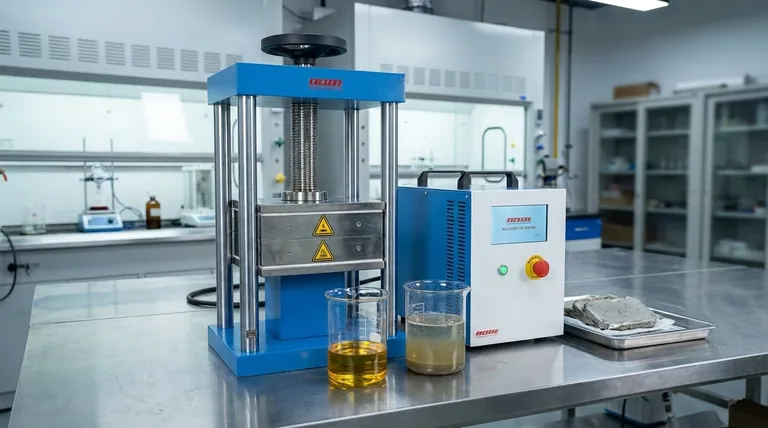

The Core Problem: Managing Oil-Contaminated Sludge
The exploration, production, and refining of crude oil inevitably generate large volumes of sludge. This is a stable, semi-solid emulsion of oil, water, and solid particles like sand, rust, and catalytic fines.
Where This Sludge Comes From
This waste stream originates from several key areas in the oil and gas lifecycle:
- Crude oil storage tank bottoms
- Refinery wastewater treatment plants (WWTP)
- Drilling mud and cuttings from exploration
- Slop oil emulsion from various refinery processes
The Dual Challenge: Cost and Environment
Untreated sludge presents two major problems. First, it is classified as hazardous waste, making its transportation and disposal extremely expensive and subject to strict environmental regulations. Second, it contains a significant amount of entrapped oil that, if not recovered, represents a direct financial loss.
How a Filter Press Solves the Problem
A filter press tackles these challenges by applying immense mechanical pressure to force the separation of the sludge's components. It is a more powerful and effective method than simple settling or centrifugation for many types of oily sludge.
The Principle of Dewatering
Sludge is pumped into a series of chambers lined with filter cloths. A powerful hydraulic system then presses the chambers together, squeezing the liquid components out through the cloths while retaining the solid particles.
Separating into Valuable Streams
The high pressure breaks the oil-water emulsion and forces a separation. The process typically yields three distinct output streams:
- Recovered Oil: The separated hydrocarbons can be reprocessed within the refinery.
- Clarified Water: The water (filtrate) can be sent for further treatment or reuse.
- Solid "Filter Cake": The dewatered solids form a compact, semi-dry cake.
The Value of the Filter Cake
The resulting filter cake has a drastically lower volume and weight compared to the original sludge, sometimes reducing the final disposal volume by over 75%. This directly cuts down on transportation and disposal costs. In some cases, the cake can be further processed or used as a low-grade fuel source.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the filter press is not a universal solution. Understanding its operational characteristics is key to its proper application.
Batch vs. Continuous Operation
A filter press is a batch process. A cycle involves filling the press, applying pressure, discharging the cake, and cleaning the cloths. This differs from continuous systems like centrifuges and can be a bottleneck if not sized correctly for the facility's waste generation rate.
Maintenance and Consumables
The filter cloths are the heart of the machine and require periodic cleaning and eventual replacement. The high-pressure hydraulic system also demands regular, specialized maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operation.
High Capital and Operating Costs
Filter presses, particularly large-scale hydraulic units, represent a significant capital investment. They also have high operating costs related to energy consumption for the hydraulic pumps and labor for operating the batch process and performing maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a filter press should be driven by a clear operational or financial objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing oil recovery: A high-pressure plate and frame filter press is ideal for squeezing the maximum amount of valuable oil from slop oil or tank bottom sludge.
- If your primary focus is minimizing waste disposal volume: The key metric is cake dryness. A press capable of achieving the highest pressure will produce the driest, most compact solid cake, drastically reducing disposal costs.
- If your primary focus is treating high-solids drilling muds: You need a heavy-duty press designed to handle abrasive solids and effectively separate the drilling fluid for reuse while minimizing the volume of cuttings for disposal.
Ultimately, the filter press allows an operator to take direct control over a challenging waste stream, turning it into a managed process that enhances both environmental compliance and operational profitability.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Output Streams |
|---|---|---|
| Dewatering | Reduces sludge volume by up to 75% | Solid Filter Cake |
| Oil Recovery | Recovers valuable hydrocarbons | Recovered Oil |
| Separation | Clarifies water for treatment/reuse | Separated Water |
Ready to turn your oily sludge from a cost into a resource? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables for optimizing industrial processes like yours. Our expertise can help you select the right filtration solution to maximize oil recovery, minimize disposal costs, and ensure regulatory compliance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover the value we can bring to your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System



















