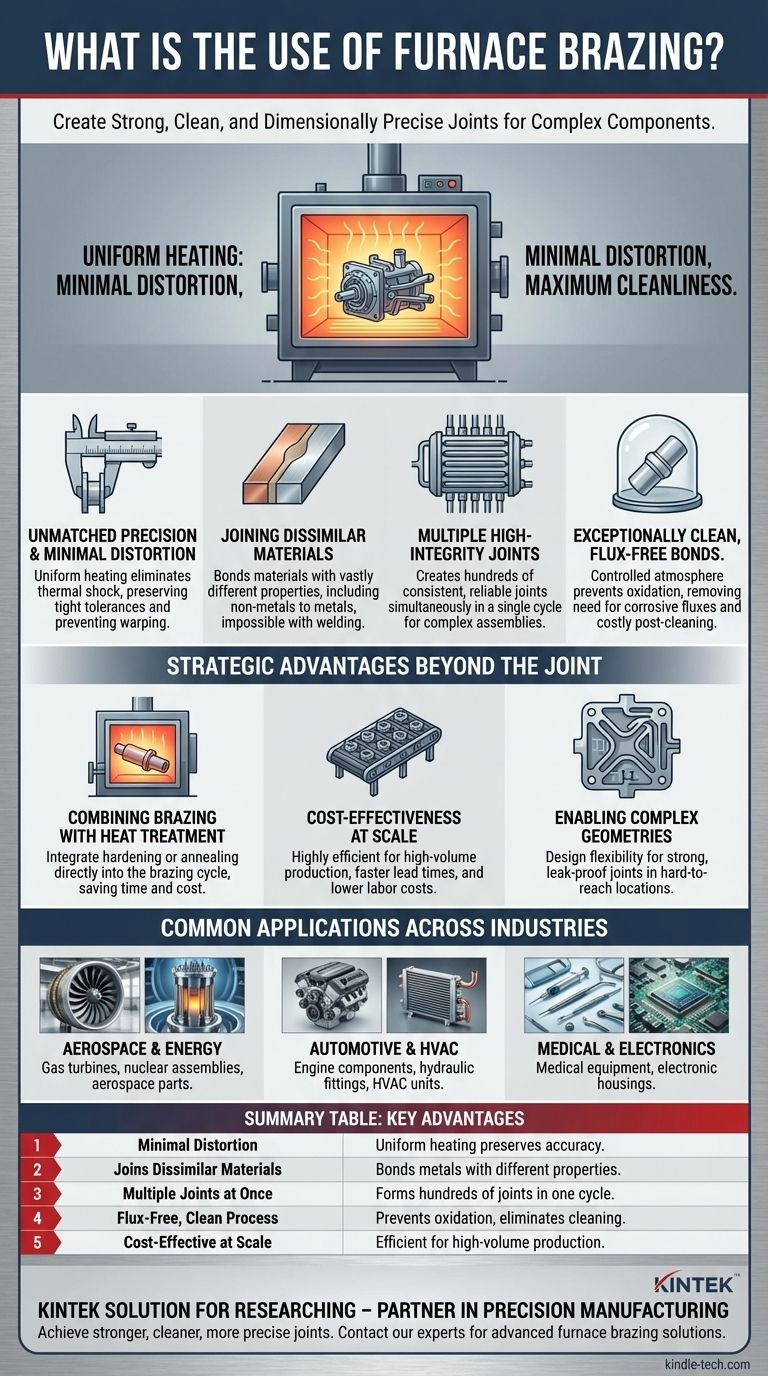
In short, furnace brazing is used to create strong, clean, and dimensionally precise joints for complex components, especially when joining dissimilar materials or creating multiple joints at once. It is a high-integrity metal joining process essential for manufacturing critical parts in industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to medical and electronics.
The core reason engineers choose furnace brazing is not just to join parts, but to do so with minimal thermal distortion and maximum cleanliness. It excels where welding would warp the material or where complex assemblies with hundreds of joints must be formed simultaneously with high reliability.
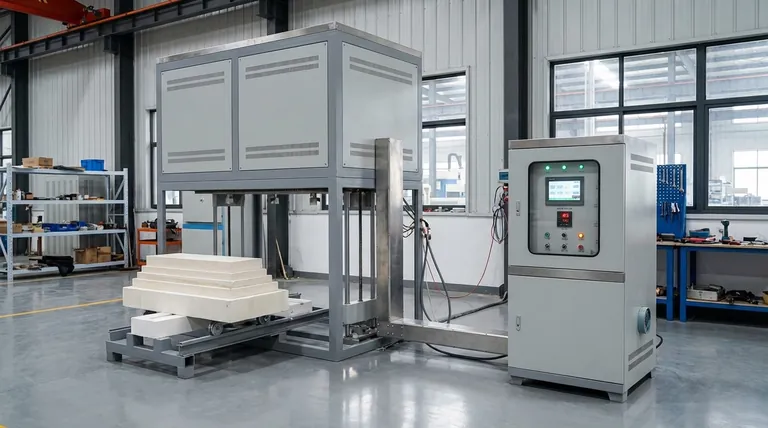

Why Furnace Brazing Excels for Complex Assemblies
Furnace brazing is selected when the limitations of other joining methods, like welding, become a barrier to design or performance. Its advantages stem from the controlled environment of the furnace itself.
Unmatched Precision and Minimal Distortion
The entire assembly is heated and cooled slowly and uniformly within the furnace. This eliminates the localized thermal shock associated with welding, which drastically reduces the risk of warping or distortion.
This process ensures that assemblies with tight tolerances maintain their dimensional accuracy, which is critical for high-performance components.
Joining Dissimilar and "Unweldable" Materials
Furnace brazing uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base materials being joined.
This fundamental difference allows it to join materials with vastly different properties, such as copper to steel or even non-metals to metals—a task that is often impossible with traditional welding.
Creating Multiple, High-Integrity Joints at Once
A key advantage is its ability to create one joint or several hundred joints in a single cycle.
This makes it exceptionally efficient for complex designs like heat exchangers or tube assemblies, where each joint is formed simultaneously, ensuring consistent quality across the entire part.
Exceptionally Clean, Flux-Free Bonds
The process is typically conducted in a controlled atmosphere (like a vacuum or inert gas) which prevents oxidation.
This eliminates the need for corrosive chemical fluxes used in other brazing or soldering methods, resulting in cleaner joints and removing the need for costly post-process cleaning.
The Strategic Advantages Beyond the Joint
The benefits of furnace brazing often extend beyond the physical bond, influencing the entire manufacturing workflow and enabling new design possibilities.
Combining Brazing with Heat Treatment
The controlled thermal cycle of the furnace can be engineered to perform other tasks.
Processes like hardening or annealing can be integrated directly into the brazing cycle. This consolidation saves significant time, energy, and cost by eliminating separate manufacturing steps.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
While the initial equipment can be expensive, furnace brazing is highly cost-effective for high-volume production.
The process allows for batch processing of many parts at once and generally requires less specialized operator skill than manual welding, leading to faster lead times and lower labor costs.
Enabling Complex Geometries
Furnace brazing provides engineers with the flexibility to design intricate parts that would be impractical or impossible to assemble otherwise. The process supports the creation of strong, leak-proof joints in hard-to-reach internal locations.
Common Applications Across Industries
The unique benefits of furnace brazing make it the go-to solution for a wide range of demanding applications.
Aerospace and Energy
Furnace brazing is essential for creating components that must withstand extreme conditions, such as industrial gas turbine components, nuclear assemblies, and aerospace parts. Reliability and strength are paramount in these applications.
Automotive and HVAC
In high-volume manufacturing, it is used for parts like automotive engine components, hydraulic fittings, and HVAC heat exchangers. The process delivers strong, leak-proof joints repeatably and economically.
Medical and Electronics
The cleanliness and precision of furnace brazing are ideal for medical and scientific equipment. It is also used for electronic devices and housings where joining dissimilar materials without distortion is critical.
When to Choose Furnace Brazing
Your decision to use furnace brazing should be guided by the specific demands of your component and production goals.
- If your primary focus is precision and minimal distortion: Furnace brazing's uniform heating is superior for maintaining tight tolerances in delicate or complex assemblies.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials: This process provides unmatched flexibility to join materials that cannot be welded, such as steel to copper or metals to ceramics.
- If your primary focus is complex assemblies or high volume: Its ability to create hundreds of clean joints at once makes it highly efficient and cost-effective for intricate designs and mass production.
Ultimately, choosing furnace brazing is a strategic decision to prioritize joint integrity, dimensional accuracy, and manufacturing efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Minimal Distortion | Uniform heating preserves dimensional accuracy of complex parts. |
| Joins Dissimilar Materials | Bonds metals with vastly different properties (e.g., steel to copper). |
| Multiple Joints at Once | Forms hundreds of high-integrity joints simultaneously in a single cycle. |
| Flux-Free, Clean Process | Controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation, eliminating post-cleaning. |
| Cost-Effective at Scale | Highly efficient for high-volume production, reducing labor costs. |
Ready to achieve stronger, cleaner, and more precise joints for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced furnace brazing solutions and the high-quality lab equipment needed to support this precise process. Whether you are joining dissimilar materials for aerospace applications or producing high-volume automotive parts, our expertise ensures your assemblies meet the highest standards of integrity and performance.
Let KINTEK be your partner in precision manufacturing. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting the rate of melting process? Master Heat Transfer for Faster Results
- What hazard is involved when using a furnace? Protect Your Home from the Silent Killer
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What affects the melting point of a substance? Uncover the Key Factors & Forces
- Why do we need to use properly some of the laboratory apparatus in the laboratory? The Foundation of Safe and Accurate Science



















