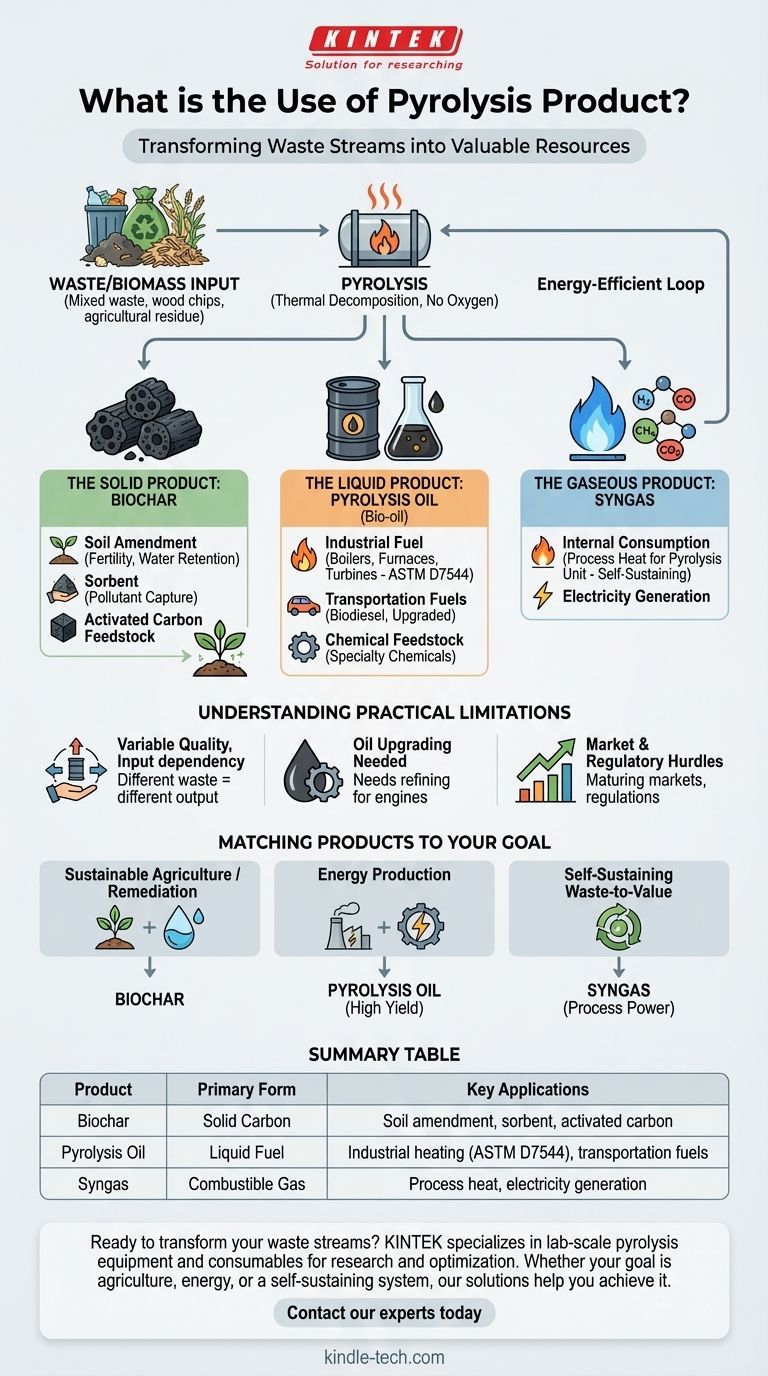
The primary use of pyrolysis products is to convert waste streams or biomass into three distinct and valuable outputs: a liquid fuel known as pyrolysis oil, a solid carbon-rich material called biochar, and a combustible synthesis gas (syngas). These products have direct applications in energy generation, agriculture, and chemical production, effectively transforming low-value materials into a portfolio of useful resources.
Pyrolysis should not be seen as a disposal method but as a versatile conversion technology. It refines a single input into three separate product streams, each with its own distinct market and application, ranging from renewable fuel to powerful soil amendments.
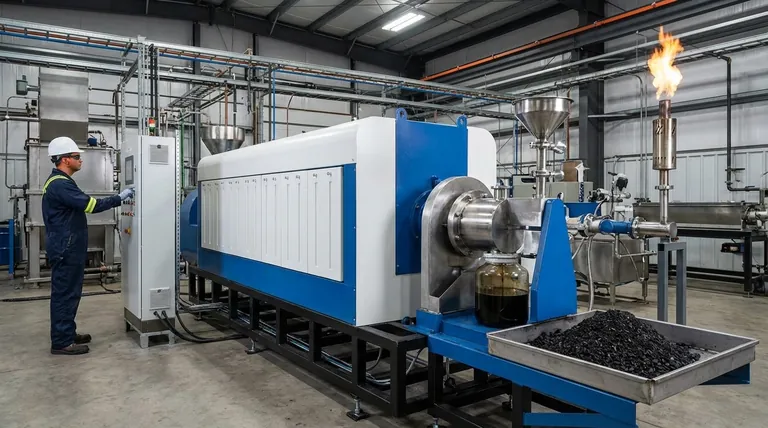

The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. This controlled heating breaks down complex materials into simpler, more stable components, which are then separated into solid, liquid, and gaseous phases.
The Solid Product: Biochar
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. It is analogous to charcoal.
Its primary applications are centered on its porous structure and high carbon content. It is widely used as a soil amendment to improve soil fertility, water retention, and microbial activity in agriculture. It can also function as a sorbent to capture pollutants or be used as a feedstock for producing activated carbon.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil
Often called bio-oil, this liquid is condensed from the pyrolysis gas during cooling. It is a complex mixture of organic compounds and is the most sought-after product for energy applications.
Its most direct use is as a substitute for conventional fuel oil in stationary applications like industrial boilers, furnaces, and turbines to generate heat or electricity. This application is regulated by standards such as ASTM D7544. With further refining, pyrolysis oil can be upgraded into transportation fuels like biodiesel or serve as a chemical feedstock for producing specialty chemicals and materials.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
This stream consists of non-condensable gases, including hydrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, and carbon dioxide. This mixture is combustible and has a significant energy value.
The most common use for syngas is internal consumption. The gas is often looped back to the pyrolysis furnace to provide the heat needed to run the process itself, making the entire operation more energy-efficient and self-sustaining. If produced in excess, it can be used to generate electricity.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While the applications are promising, it's critical to understand the real-world constraints associated with pyrolysis products.
Product Quality is Highly Variable
The composition and quality of the biochar, oil, and gas are directly dependent on the input feedstock. Pyrolysis of wood chips will produce very different outputs compared to the pyrolysis of waste plastic or tires, impacting their suitability for specific applications.
Pyrolysis Oil Requires Upgrading
Bio-oil is not a direct, drop-in replacement for diesel or gasoline. It is typically more acidic, less stable, and has a lower energy density than conventional petroleum fuels. For use in advanced engines or as a chemical feedstock, it requires significant secondary processing and upgrading.
Market and Regulatory Hurdles
The markets for pyrolysis products are still maturing. While biochar has established agricultural uses and bio-oil has industrial fuel standards, scaling these markets and navigating environmental regulations can present significant commercial challenges.
Matching Pyrolysis Products to Your Goal
The optimal use of pyrolysis outputs depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is sustainable agriculture or remediation: You should optimize your process for high-quality biochar to be used as a soil conditioner or pollutant sorbent.
- If your primary focus is energy production: You should aim for a high yield of pyrolysis oil, which can be used directly as an industrial fuel substitute in boilers and furnaces.
- If your primary focus is a self-sustaining waste-to-value system: You should leverage the syngas produced to power the pyrolysis unit, dramatically reducing operational energy costs and improving overall efficiency.
By treating pyrolysis as a refinery process, you can strategically convert inputs into a portfolio of outputs that best align with your specific economic or environmental goals.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Primary Form | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Solid Carbon | Soil amendment, sorbent, activated carbon feedstock |
| Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil) | Liquid Fuel | Industrial heating fuel (ASTM D7544), upgraded transportation fuels |
| Syngas | Combustible Gas | Process heat for the pyrolysis unit, electricity generation |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in lab-scale pyrolysis equipment and consumables, helping you research and optimize the conversion of biomass and waste materials. Whether your goal is sustainable agriculture, energy production, or creating a self-sustaining system, our solutions can help you achieve it. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















