At its core, vacuum hardening is a high-precision heat treatment process used to increase the strength and hardness of steel and alloy components without damaging their surface. It achieves this by heating the metal in a controlled, oxygen-free environment, which prevents the oxidation and scaling that plague traditional hardening methods. This results in a superior final product that is both strong and clean.
The primary use of vacuum hardening is not just to make metal harder, but to do so while producing a clean, bright, and dimensionally stable part directly out of the furnace. This eliminates the need for costly secondary cleaning or grinding, making it the superior choice for high-value and precision components.

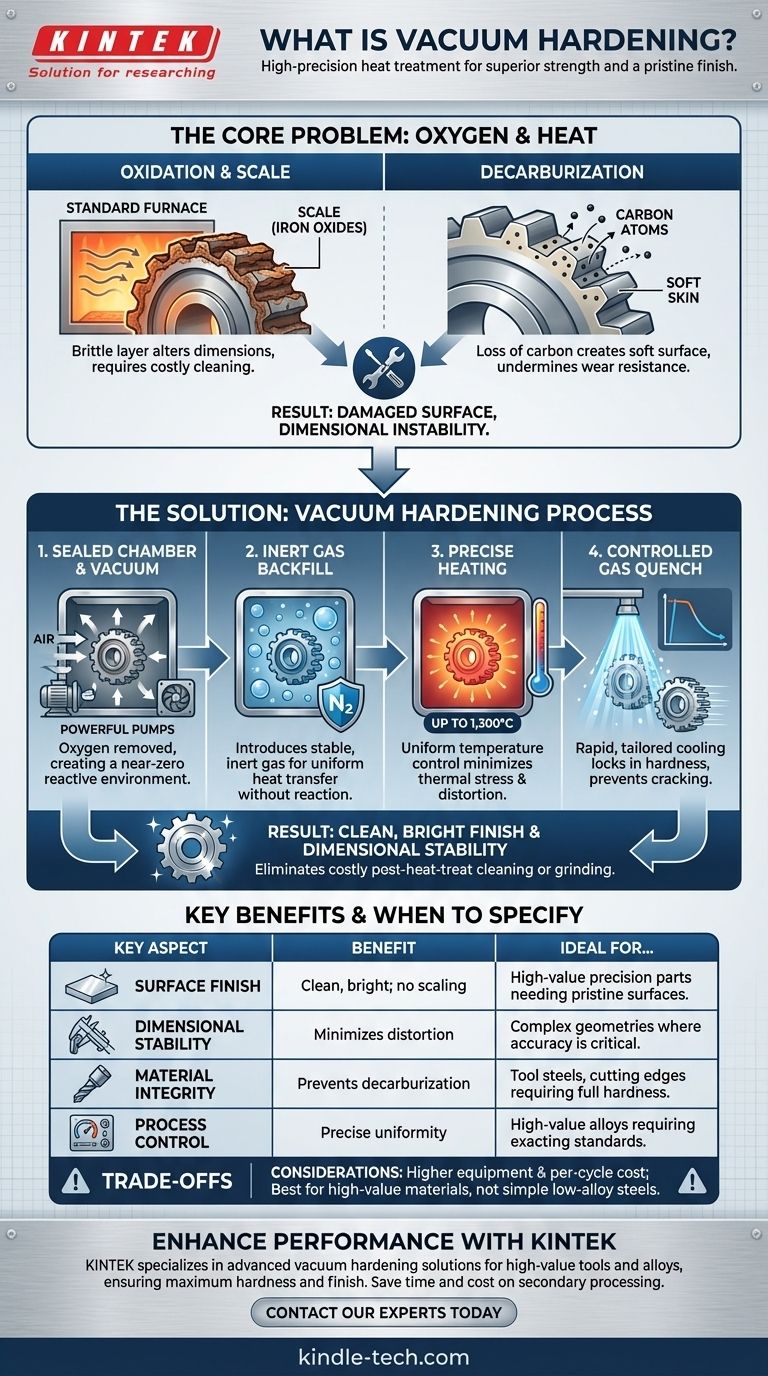
The Core Problem: Why Oxygen is the Enemy in Hardening
To understand the value of vacuum hardening, you must first understand the problems it solves. When steel is heated to high temperatures in the presence of air, two destructive chemical reactions occur.
The Issue of Oxidation and Scale
At hardening temperatures, oxygen in the air aggressively reacts with the iron on the surface of a component. This reaction forms a layer of brittle iron oxides, known as scale or mill scale.
This scale alters the part's dimensions, creates a rough surface finish, and must be removed through costly and labor-intensive processes like sandblasting, chemical pickling, or grinding.
The Risk of Decarburization
Simultaneously, oxygen can pull carbon atoms out of the steel's surface layer. This loss of carbon, known as decarburization, creates a soft "skin" on the component.
For tools that rely on a hard surface for wear resistance and cutting edges, decarburization is catastrophic, as it directly undermines the purpose of the hardening process itself.
How Vacuum Hardening Solves the Problem
Vacuum hardening systematically eliminates oxygen from the process, thereby preventing the negative effects of oxidation and decarburization.
Creating an Oxygen-Free Environment
The process begins by placing components in a sealed furnace chamber and using powerful pumps to remove the atmosphere. By creating a vacuum, the density of oxygen and other reactive particles is reduced to near zero.
Often, the chamber is then backfilled with a high-purity, inert gas like nitrogen. This controlled atmosphere provides a stable medium for uniform heat transfer without any risk of chemical reaction.
Achieving a "Bright" Finish
Because no oxidation occurs, parts emerge from the furnace with the same clean, bright metallic surface they had going in. This is a key advantage, as it often eliminates the need for any post-heat-treat finishing operations, saving time and money.
Precise Temperature Control
Vacuum furnaces offer exceptionally uniform temperature control, often up to 1,300°C. The combination of radiant heating in a vacuum and convection heating in the inert gas ensures that the entire part, including complex geometries, reaches the target temperature evenly. This reduces thermal stress and minimizes distortion.
Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
After heating, the components are cooled rapidly (quenched) to lock in the hard structure. In a vacuum furnace, this is achieved by flooding the chamber with a high-pressure stream of inert gas, typically nitrogen.
The pressure and flow rate of this gas quench can be precisely controlled, allowing the cooling rate to be tailored to the specific steel alloy and part geometry, further minimizing the risk of distortion or cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, vacuum hardening is not the solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Equipment and Process Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems that represent a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. The process itself can be more expensive per cycle due to energy consumption and longer cycle times.
Not Ideal for All Steels
The benefits of vacuum hardening are most pronounced on higher-value materials. For simple, low-alloy carbon steels where surface finish is not a primary concern, a less expensive conventional hardening process may be sufficient. The added cost is justified when working with tool steels, high-speed steels, and stainless steels.
When to Specify Vacuum Hardening
Deciding whether to use vacuum hardening depends entirely on the requirements for the finished component.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and dimensional accuracy: Specify vacuum hardening to eliminate post-heat-treat grinding and ensure parts are delivered clean and dimensionally stable.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the performance of tool steels: Use vacuum hardening to prevent decarburization, preserving the full hardness and wear resistance required for cutting tools, dies, and molds.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in complex parts: Leverage the precise temperature uniformity and controlled gas quenching of a vacuum process to reduce internal stresses and prevent cracking.
Ultimately, vacuum hardening is the choice when the metallurgical integrity and surface quality of the final part cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit of Vacuum Hardening |
|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Clean, bright finish; eliminates need for post-process cleaning/grinding. |
| Dimensional Stability | Minimizes distortion and scaling, preserving part accuracy. |
| Material Integrity | Prevents decarburization, ensuring full hardness and wear resistance. |
| Process Control | Precise temperature uniformity and controlled gas quenching. |
Ready to enhance the performance and quality of your precision components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum hardening solutions, to meet the stringent demands of high-value tool steels and alloys. Our expertise ensures your parts achieve maximum hardness and a pristine finish, saving you time and cost on secondary processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum hardening technology can benefit your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability



















