At its core, a rolling mill uses the force of rotating cylinders, or "rolls," to process a material. The fundamental working principle involves passing a substance through the gap between these rolls to change its physical properties, but the specific mechanism depends entirely on the mill's design and its intended purpose. This can range from applying immense compressive force to flatten metal to generating high shear force to mix pastes.
The term "rolling mill" is broad and covers several distinct technologies. The working principle is not singular; it is defined by the primary goal, which could be shaping solids through compression, mixing pastes through shear, or grinding powders through attrition.
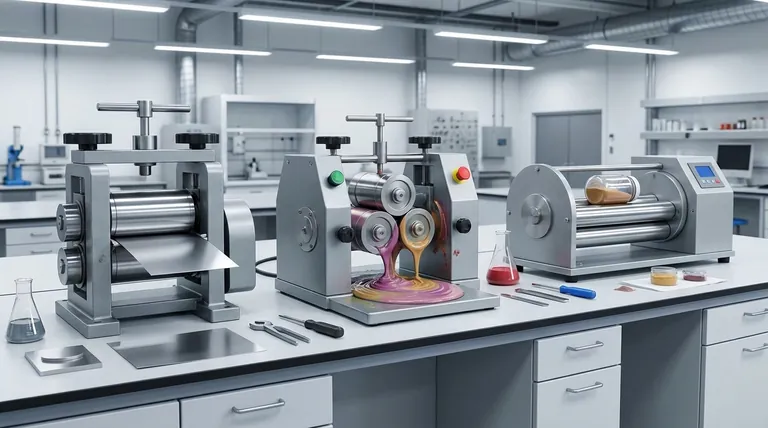

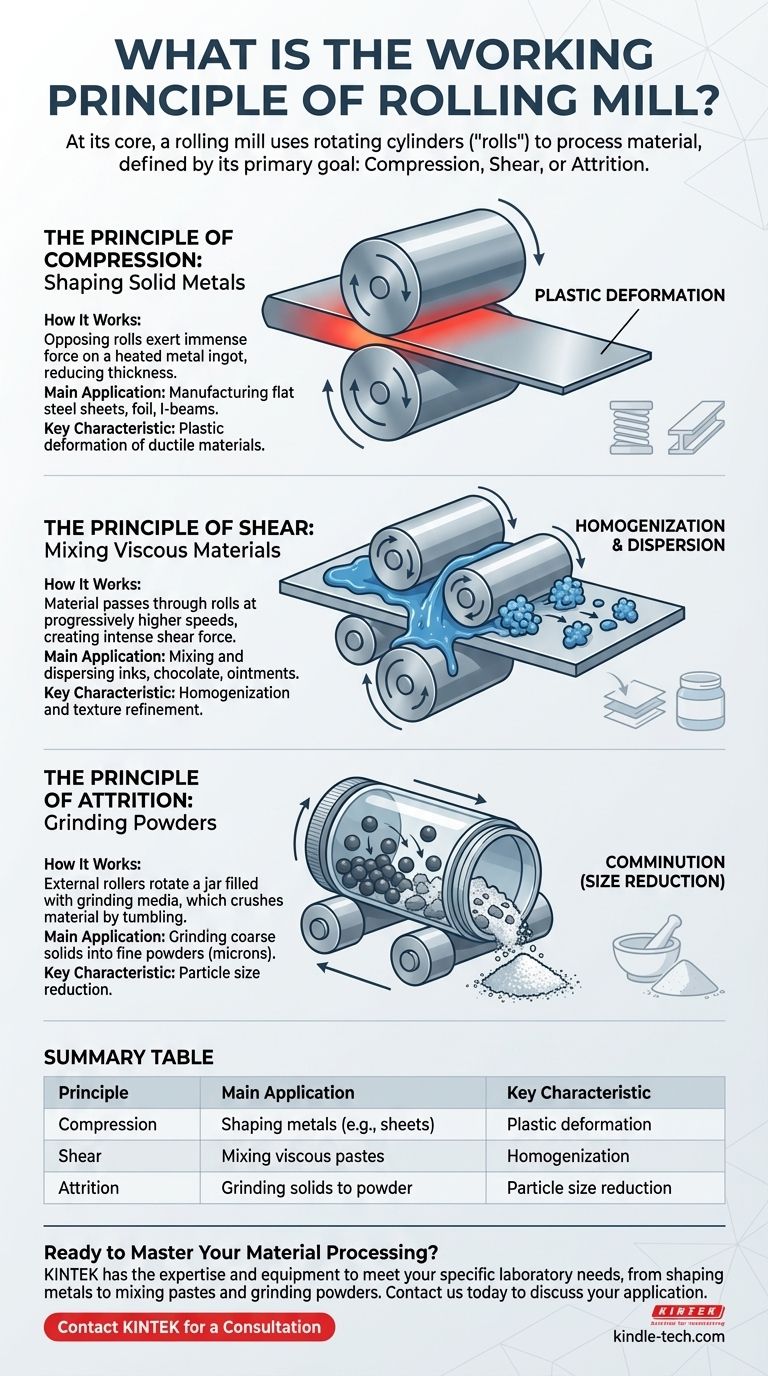
The Principle of Compression: Shaping Solid Metals
This is the classic and most common type of rolling mill, used extensively in metallurgy. Its function is to reduce the thickness of or impart a specific shape to a metal workpiece.
How It Works
Two or more heavy rolls are mounted opposite each other, rotating in opposite directions at the same speed. A metal ingot or slab, heated to be more malleable, is fed into the gap between them.
This gap is intentionally set to be smaller than the thickness of the incoming metal. The immense compressive force exerted by the rolls squeezes the material, reducing its thickness and elongating it. The friction between the rolls and the metal surface pulls the workpiece forward.
The Primary Goal
The objective is plastic deformation. This process is used to manufacture everything from flat steel sheets and aluminum foil to structural shapes like I-beams and rails.
The Principle of Shear: Mixing Viscous Materials
A different class of machine, often called a three-roll mill, uses a different principle for a completely different task: mixing and dispersing thick liquids or pastes.
How It Works
These mills consist of three parallel rolls positioned very close to each other. Critically, each roll rotates at a progressively higher speed than the one before it.
Material (like printing ink, chocolate, or ointment) is fed into the gap between the first two, slower-moving rolls. As it transfers to the gaps between the faster-moving rolls, the difference in surface speed creates intense shear force. This force tears apart clumps of particles, dispersing them uniformly throughout the paste.
The Primary Goal
The objective is homogenization and dispersion. This mill doesn't reduce the thickness of a solid; it refines the texture of a viscous mixture, ensuring a smooth, consistent product.
The Principle of Attrition: Grinding Powders
A third category, known as a jar or ball rolling mill, uses rollers in a supportive role to achieve fine grinding.
How It Works
In this setup, the material to be ground is placed inside a sealed cylinder or jar, along with hard grinding media like ceramic or steel balls. This jar is then placed on two rollers that spin it.
The external rollers do not process the material directly. Their only job is to rotate the jar. Inside, a tumbling, cascading motion lifts the grinding balls, which then fall and crush the material. This process of crushing and rubbing is known as attrition.
The Primary Goal
The objective is comminution, or size reduction. This method is used to turn coarse solids into a very fine powder, often down to a few microns in size.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single rolling mill principle is universally applicable. Each is designed for a specific task and comes with inherent limitations.
Compression Mills (Metal Rolling)
These machines are massive, require enormous amounts of energy, and are built for heavy-duty shaping. They are only suitable for ductile materials (like metals) that can be deformed without shattering.
Shear Mills (Three-Roll)
These are highly effective for pastes and thick liquids but are completely useless for processing dry solids or shaping metals. Achieving a very fine dispersion may require passing the material through the mill multiple times, which can be time-consuming.
Attrition Mills (Ball/Jar)
While excellent for creating fine powders from a wide range of brittle materials, this process can be slow. There is also a risk of minor contamination as the grinding media itself wears down over time.
Matching the Mill to the Material Goal
To select the right process, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is to shape and reduce the thickness of a solid metal: You need a compression-based rolling mill with opposing rolls.
- If your primary focus is to mix and create a smooth, homogeneous paste: You need a shear-based three-roll mill with differential roll speeds.
- If your primary focus is to grind a solid material into a fine powder: You need an attrition-based ball or jar mill that uses grinding media.
Understanding which force—compression, shear, or attrition—is required is the key to mastering your material processing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Primary Force | Main Application | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression | Squeezing force between opposing rolls | Shaping and thinning solid metals (e.g., sheets, beams) | Plastic deformation of ductile materials |
| Shear | High friction from rolls at different speeds | Mixing and dispersing viscous pastes (e.g., inks, chocolate) | Homogenization and texture refinement |
| Attrition | Crushing and rubbing using grinding media | Grinding brittle solids into fine powders | Particle size reduction (comminution) |
Ready to Master Your Material Processing?
Understanding the correct rolling mill principle—compression, shear, or attrition—is the first step to optimizing your lab's efficiency and product quality. Whether you need to shape metals, mix pastes, or grind powders, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Don't let the wrong process slow you down. Contact us today to discuss your application and let our specialists help you select the perfect lab equipment solution.
Contact KINTEK for a Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
People Also Ask
- What is the procedure of a ball mill experiment? Master Particle Size Reduction for Your Lab
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- What is the particle size of a ball mill? Control Your Grind from Microns to Nanometers
- What is a ball mill used for in ceramics? Achieve Ultimate Control Over Glaze and Clay Quality
- What is the particle size range of a ball mill? Achieve Precise Grinding from 10 mm to Sub-Micron



















