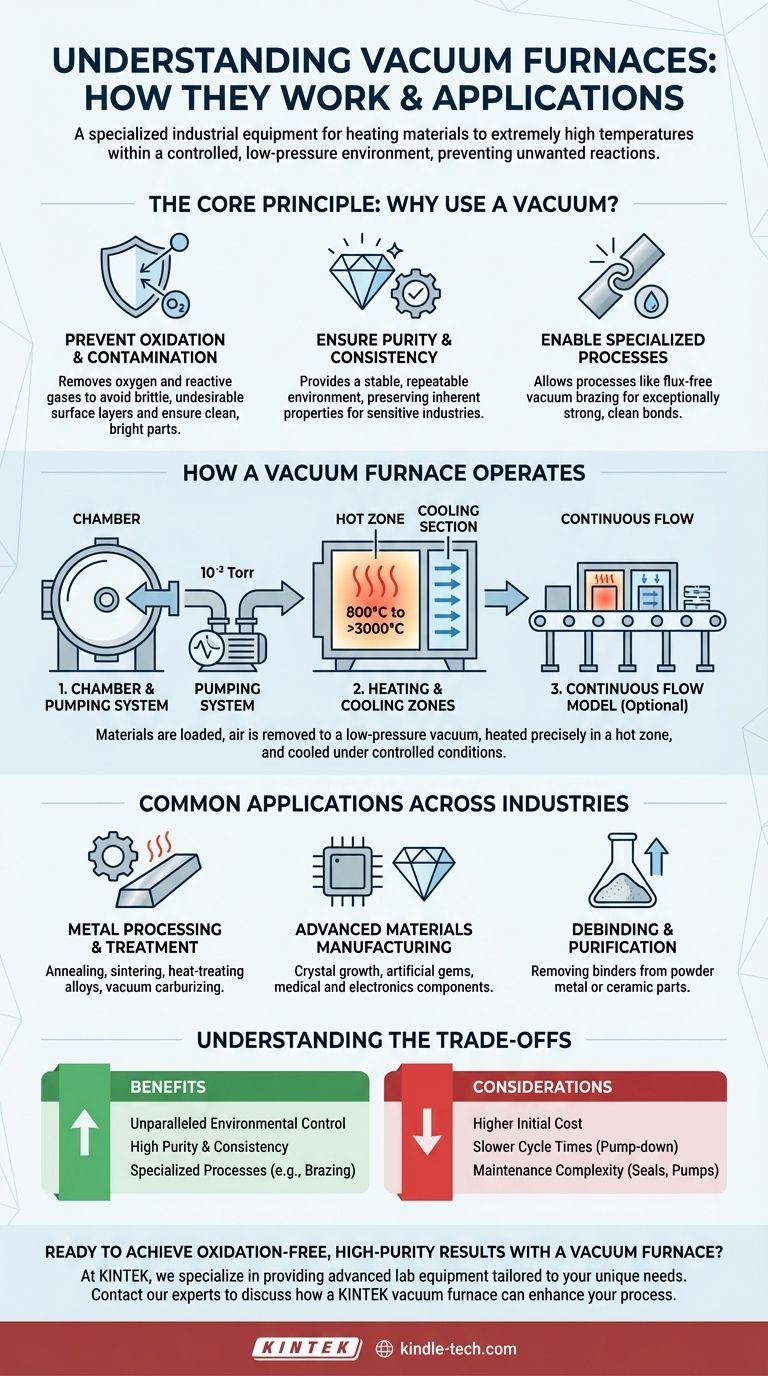
In short, a vacuum furnace is a specialized piece of industrial equipment used to heat materials to extremely high temperatures within a controlled, low-pressure environment. By removing air and other gases, these furnaces prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and contamination. This allows for the processing of materials that require exceptional purity, strength, and consistency.
The fundamental advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just the heat it provides, but the pristine, non-reactive environment it creates. This control over the atmosphere enables material treatments and joining processes that are simply not possible in a conventional furnace.
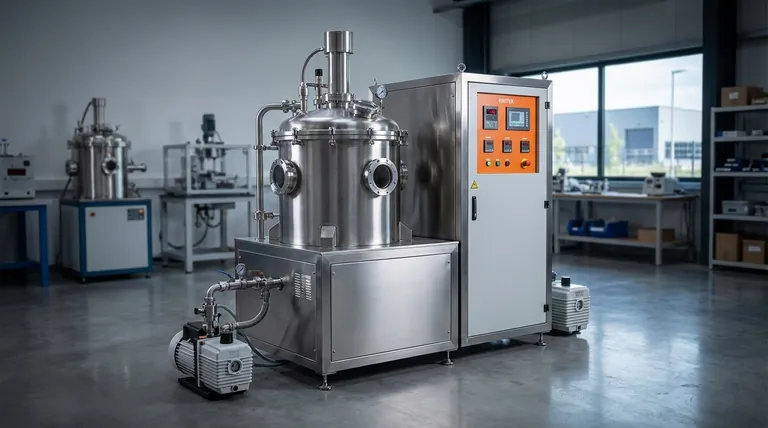

The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
To understand how a vacuum furnace works, you must first understand why removing the atmosphere is so critical. The vacuum itself is the key enabling technology for several high-performance manufacturing processes.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The primary reason to use a vacuum is to remove oxygen and other reactive gases. At high temperatures, most metals will rapidly oxidize in the presence of air, forming a brittle, undesirable layer on their surface. A vacuum eliminates this risk, resulting in a clean, bright, and structurally sound finished part.
Ensuring Purity and Consistency
A vacuum provides a highly stable and repeatable environment. This is essential for industries like medical, aerospace, and electronics, where even microscopic impurities can cause component failure. The process ensures that the material's inherent properties are preserved and enhanced without introducing external contaminants.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain processes, such as vacuum brazing, rely on a vacuum to function. Brazing joins two materials using a filler metal that melts and flows into the joint. In a vacuum, this can be done without flux, creating an exceptionally strong and clean bond that is free of corrosive residues.
How a Vacuum Furnace Operates
A vacuum furnace integrates several key systems to achieve its precise control over both temperature and pressure.
The Chamber and Pumping System
The process begins with placing materials inside a sealed, robust chamber. A powerful vacuum pump system then removes the air, reducing the internal pressure to a specific vacuum level, often less than 10⁻³ Torr. This step is what creates the controlled processing environment.
The Heating and Cooling Zones
Once the desired vacuum level is reached, electric heating elements within a "hot zone" raise the temperature, which can range from 800°C to over 3000°C. After the heating cycle, parts can be cooled in a controlled manner, sometimes within a dedicated cooling section of the furnace, to achieve specific material properties.
The Continuous Flow Model
For high-volume production, continuous vacuum furnaces offer a straight-through design. Operators load materials at the entry side, and they travel through various heating and cooling zones at a constant speed before being unloaded at the exit. This method ensures highly consistent and even heating for every individual part, improving efficiency.
Common Applications Across Industries
The precise control offered by vacuum furnaces makes them indispensable in a wide range of demanding fields.
Metal Processing and Treatment
The most common applications involve metals. This includes annealing (softening metal), sintering (fusing powdered material into a solid mass), heat-treating steel alloys, and vacuum carburizing for surface hardening.
Advanced Materials Manufacturing
Industries requiring ultra-pure materials rely heavily on this technology. Key applications include crystal growth for semiconductors, producing artificial gems, and manufacturing components for the medical, energy, and electronics sectors.
Debinding and Purification
Vacuum furnaces are also used for debinding, a process that removes binder materials used in parts made from metal or ceramic powders. The vacuum helps extract the vaporized binders cleanly and efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the solution for every heating application. It's important to recognize their limitations.
Higher Initial Cost
The complexity of the sealed chamber, high-performance heating elements, and vacuum pumping systems makes these furnaces significantly more expensive to purchase and install than their atmospheric counterparts.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber before the heating cycle can begin often results in longer overall processing times compared to conventional furnaces, particularly for batch operations.
Maintenance Complexity
Maintaining a perfect seal and ensuring the optimal performance of vacuum pumps requires specialized knowledge and regular maintenance. Leaks can compromise the entire process, so system integrity is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your end goal and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-purity components: A vacuum furnace is essential for preventing contamination in sensitive applications like medical implants or aerospace electronics.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies: Vacuum brazing provides superior, flux-free joints for intricate parts that cannot be welded.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent heat treatment: A continuous vacuum furnace offers unmatched repeatability and efficiency for mass production.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace provides an unparalleled level of environmental control, making it an essential tool for creating the world's most demanding and advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber & Pumping System | Removes air to create a low-pressure, non-reactive environment |
| Heating Elements (Hot Zone) | Heats materials to precise temperatures (800°C to 3000°C) |
| Controlled Cooling System | Cools materials to achieve specific properties |
| Continuous Flow Design (Optional) | Enables high-volume, consistent processing for mass production |
Ready to achieve oxidation-free, high-purity results with a vacuum furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, electronics, or materials research, our vacuum furnaces deliver the precise environmental control required for critical processes like brazing, sintering, and annealing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your process purity, consistency, and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















