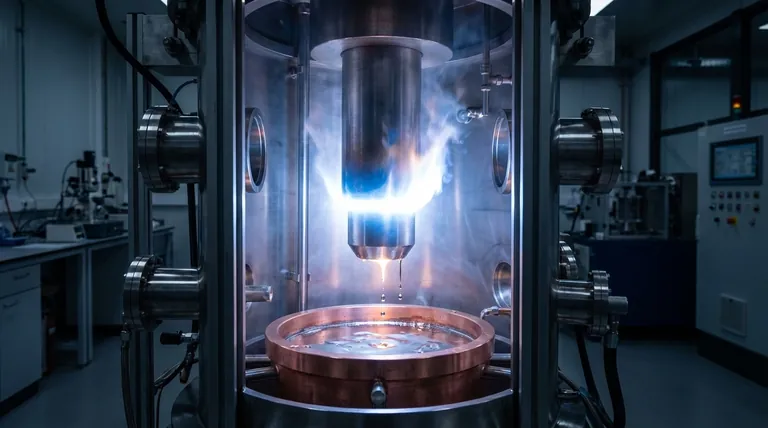
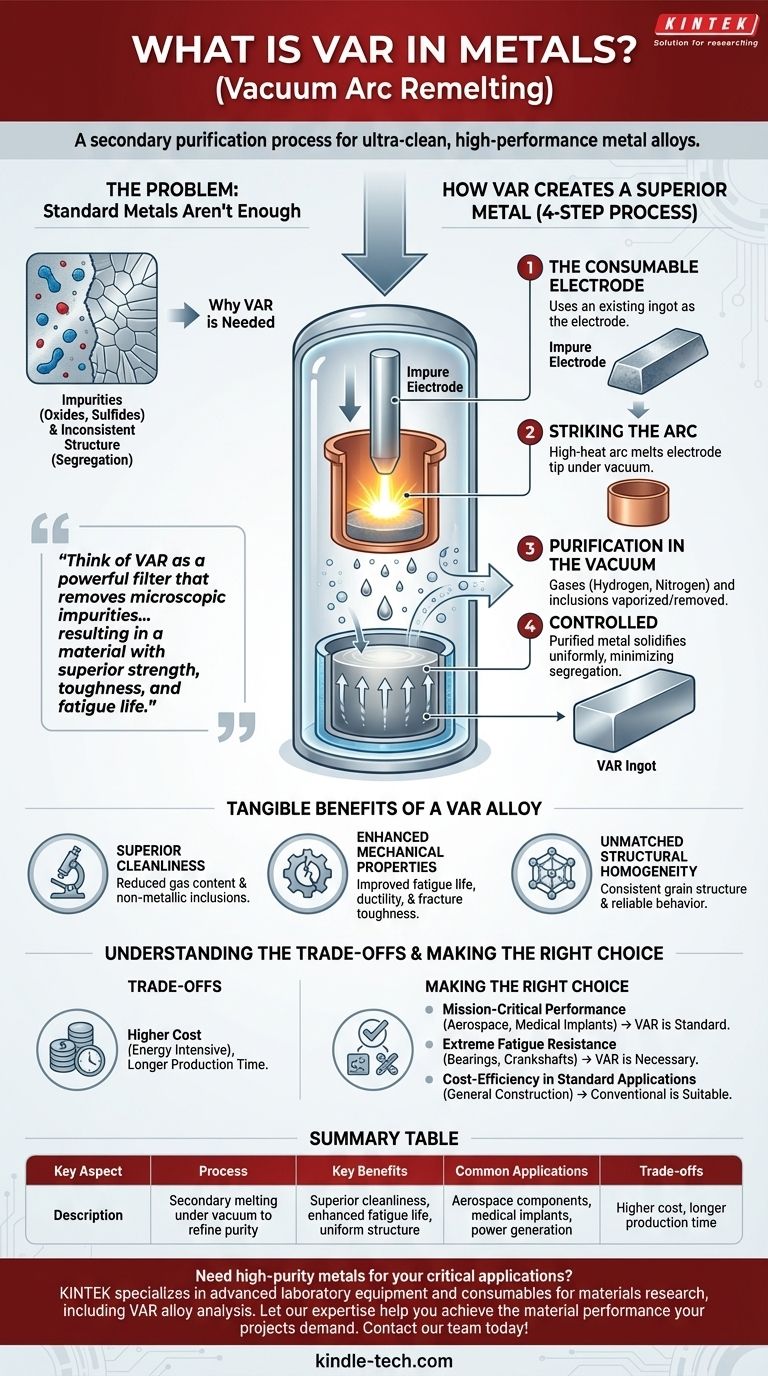
In the world of high-performance metals, "VAR" stands for Vacuum Arc Remelting. It is not a type of metal, but rather a secondary melting process used to produce exceptionally clean, high-strength, and uniform metal alloys. This purification technique is essential for materials used in the most demanding environments, such as aerospace, power generation, and medical implants.
The core purpose of Vacuum Arc Remelting is to take a good quality metal and refine it into an elite one. Think of it as a powerful filter that removes microscopic impurities and structural inconsistencies, resulting in a material with superior strength, toughness, and fatigue life.
Why Standard Metal Isn't Always Enough
To understand the value of VAR, you must first understand the inherent limitations of conventional primary melting processes.
The Problem of Impurities
When metals are first produced from ore, they are melted in air. This process can trap undesirable elements like oxygen and nitrogen within the metal structure. It also introduces non-metallic inclusions—tiny particles of oxides, sulfides, or nitrides—that act as microscopic stress points.
The Challenge of Inconsistent Structure
As a large ingot of molten metal cools and solidifies, different alloying elements can cool at slightly different rates. This leads to segregation, where concentrations of certain elements vary throughout the ingot, creating an inconsistent internal structure with unpredictable weak spots.
How VAR Creates a Superior Metal
Vacuum Arc Remelting is a solution specifically designed to eliminate these problems. The process takes a solid ingot produced by conventional means and refines it.
Step 1: The Consumable Electrode
The process begins by taking an already-formed alloy ingot and using it as a giant consumable electrode. This electrode is placed inside a sealed, water-cooled copper crucible from which all the air has been removed, creating a vacuum.
Step 2: Striking the Arc
A powerful electric arc is initiated between the bottom of the electrode and a small amount of starting material at the base of the crucible. The intense heat of the arc, which can exceed the temperature of the sun's surface, progressively melts the tip of the electrode, one drop at a time.
Step 3: Purification in the Vacuum
As the molten metal droplets travel through the vacuum, dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen are pulled out. The extreme heat also vaporizes or breaks down many non-metallic inclusions. These lighter impurities are drawn away by the vacuum system.
Step 4: Controlled Solidification
The purified molten metal falls into the water-cooled copper crucible below and solidifies in a highly controlled, directional manner from the bottom up. This controlled solidification creates a very uniform and fine-grained structure, minimizing the chemical segregation that weakens standard ingots. The final product is a new, ultra-clean VAR ingot.
The Tangible Benefits of a VAR Alloy
The result of this intensive process is a material with measurably superior characteristics.
Superior Cleanliness and Chemical Purity
VAR dramatically reduces the gas content and the number of non-metallic inclusions in an alloy. This "cleanliness" is the primary source of its enhanced performance.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
By removing the microscopic weak points (inclusions) where cracks initiate, VAR significantly improves a material's fatigue life, ductility, and fracture toughness. The material can withstand more stress cycles and resist catastrophic failure.
Unmatched Structural Homogeneity
The controlled, directional solidification ensures a consistent grain structure and chemical composition from top to bottom. This makes the material's behavior highly predictable and reliable under stress, which is critical for safety-focused applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VAR produces exceptional materials, it is not a universal solution due to its inherent compromises.
The Primary Factor: Cost
Vacuum Arc Remelting is an additional, energy-intensive manufacturing step. The specialized equipment, vacuum technology, and high electricity consumption make VAR-processed materials significantly more expensive than their conventionally melted counterparts.
Production Time and Yield
The process is slower than primary melting, which limits throughput. Furthermore, a portion of the material at the top and bottom of the remelted ingot must be cropped off, slightly reducing the final material yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a VAR material is a decision driven entirely by the performance demands of the end-use application.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: For components like jet engine turbine disks, airframes, or surgical implants where failure is not an option, VAR is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is extreme fatigue resistance: For parts like high-performance bearings, crankshafts, or connecting rods that endure millions of stress cycles, VAR provides the necessary lifespan.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency in a standard application: For general construction, automotive bodies, or consumer products, the cost of VAR is not justified, and conventional alloys are perfectly suitable.
Ultimately, specifying a VAR material is an engineering decision to invest in metallurgical purity to guarantee performance and reliability under the most severe conditions.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Secondary melting under vacuum to refine metal purity and structure. |
| Key Benefits | Superior cleanliness, enhanced fatigue life, and uniform grain structure. |
| Common Applications | Aerospace components, medical implants, power generation turbines. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost and longer production time compared to conventional melting. |
Need high-purity metals for your critical applications? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables to support materials research and development, including the analysis of VAR-processed alloys. Let our expertise help you achieve the material performance your projects demand. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity
- What is the VAR melting process? The Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is a remelting process? A Guide to High-Purity Metal Refinement



















