To solder stainless steel, you cannot use standard rosin-core or plumbing solder. You must use a high-tin content solder, such as a 95/5 tin-antimony or a silver-bearing alloy, in combination with a highly aggressive, acidic flux specifically designed for stainless steel. This special flux is the most critical component, as it is required to chemically remove the tough oxide layer that prevents solder from adhering to the surface.
The success of soldering stainless steel depends almost entirely on the flux, not the solder itself. Standard fluxes are ineffective, and only a specialized acidic flux can break through the metal's protective layer to allow a solder bond to form.

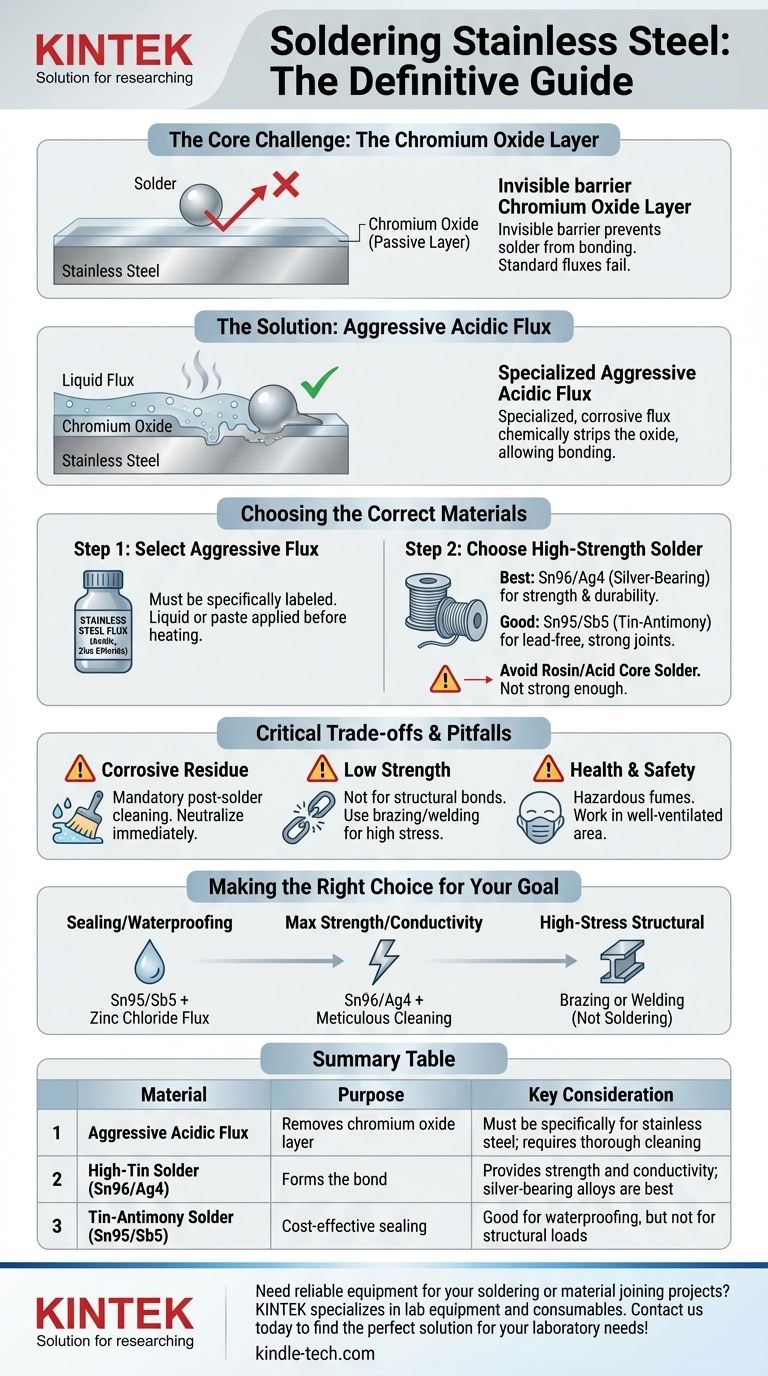
Why Stainless Steel is Difficult to Solder
Understanding the challenge of stainless steel is the first step toward overcoming it. The properties that make it "stainless" are the same ones that make it resistant to soldering.
The Problem: The Chromium Oxide Layer
Stainless steel contains chromium, which reacts with oxygen to form a passive, transparent, and self-healing layer of chromium oxide.
Think of this layer as a coat of invisible, non-stick paint. Solder simply cannot "wet" or bond to this surface. While copper also oxidizes, its oxide layer is easily removed by the mild rosin or water-soluble fluxes used in electronics and plumbing. The chromium oxide on stainless steel is far more resilient.
The Solution: Aggressive Flux
To solder stainless steel, you must chemically strip this oxide layer away. This requires a flux that is significantly more powerful than what is used for copper or brass.
These are highly acidic and corrosive fluxes, often containing zinc chloride, hydrochloric acid, or phosphoric acid. They aggressively etch the surface, removing the oxide and exposing the raw steel underneath for the solder to bond with.
Choosing the Correct Materials
Success requires two components: the right flux and the right solder. They must work together.
Step 1: Select an Aggressive Flux
Your first priority is finding a flux explicitly labeled "for stainless steel" or "for nickel/chrome alloys." Standard electronics or plumbing flux will fail every time.
These fluxes are liquid or paste and must be applied separately to the joint before heating.
Step 2: Choose a High-Strength Solder
Once you have the right flux, you can select an appropriate solder. Since you are already working on a strong material, using a strong solder alloy is best practice.
- Silver-Bearing Solder (Best): Alloys like Sn96/Ag4 (96% tin, 4% silver) offer excellent strength, durability, and wetting characteristics once the flux has activated.
- Tin-Antimony Solder (Good): An alloy like Sn95/Sb5 (95% tin, 5% antimony) is another strong, lead-free choice that works very well.
- Tin-Lead Solder (Usable): Traditional 60/40 or 63/37 tin-lead solders can work, but only if used with the correct aggressive flux. They offer no real advantage and are being phased out for health reasons.
Avoid solders that have a built-in rosin or acid core, as this core flux is never strong enough for stainless steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Using aggressive flux introduces critical risks that you must manage for a successful and lasting joint.
The Danger of Corrosive Residue
The acids in stainless steel flux are highly corrosive. If any residue is left on the joint after soldering, it will continue to attack the metal, leading to corrosion and eventual joint failure.
Post-solder cleaning is not optional. You must neutralize and thoroughly clean the area immediately after the joint cools. A common method is to scrub the area with a paste of baking soda and water, followed by a final rinse with clean water.
Strength Limitations
A soldered joint is a low-temperature bond. It is suitable for sealing seams, creating waterproof joints, or for electrical connections.
However, soldering does not create a structural bond on steel. For applications requiring high mechanical strength, you must use a high-temperature process like brazing or welding.
Health and Safety
The fumes produced when heating acidic flux are hazardous and should not be inhaled. Always work in a well-ventilated area and consider using a fume extractor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your materials based on the objective of your project.
- If your primary focus is sealing or waterproofing: A tin-antimony solder (Sn95/Sb5) combined with a zinc chloride-based flux is a cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength or electrical conductivity: A silver-bearing solder (Sn96/Ag4) provides the strongest possible soldered bond, but remember to be meticulous with post-solder cleaning.
- If your primary focus is a high-stress structural connection: Soldering is the wrong process entirely. You must move to brazing or welding to achieve the necessary strength and safety.
Ultimately, a successful stainless steel solder joint is the result of using an aggressive flux to prepare the surface and a quality solder to form the bond.
Summary Table:
| Material | Purpose | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Aggressive Acidic Flux | Removes chromium oxide layer | Must be specifically for stainless steel; requires thorough cleaning |
| High-Tin Solder (e.g., Sn96/Ag4) | Forms the bond | Provides strength and conductivity; silver-bearing alloys are best |
| Tin-Antimony Solder (e.g., Sn95/Sb5) | Cost-effective sealing | Good for waterproofing, but not for structural loads |
Need reliable equipment for your soldering or material joining projects? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that require precision and durability. Whether you're working with stainless steel or other challenging materials, our products ensure you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three-Section Clamp
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using PTFE capillaries in a ten-channel parallel aging reactor? Master Flow Uniformity
- What technical advantages does a PTFE-based flow reaction platform offer? Speed Up Lignin Depolymerization by 95%
- What are the primary reasons for selecting PTFE as a matrix? Enhance Composites with Carbon Nanotube Reinforcement
- How does PTFE aqueous dispersion contribute to the performance of modified MFC anodes? Boost Stability and Durability
- Is PTFE corrosion resistant? Discover the Ultimate Chemical Resistance for Your Lab



















