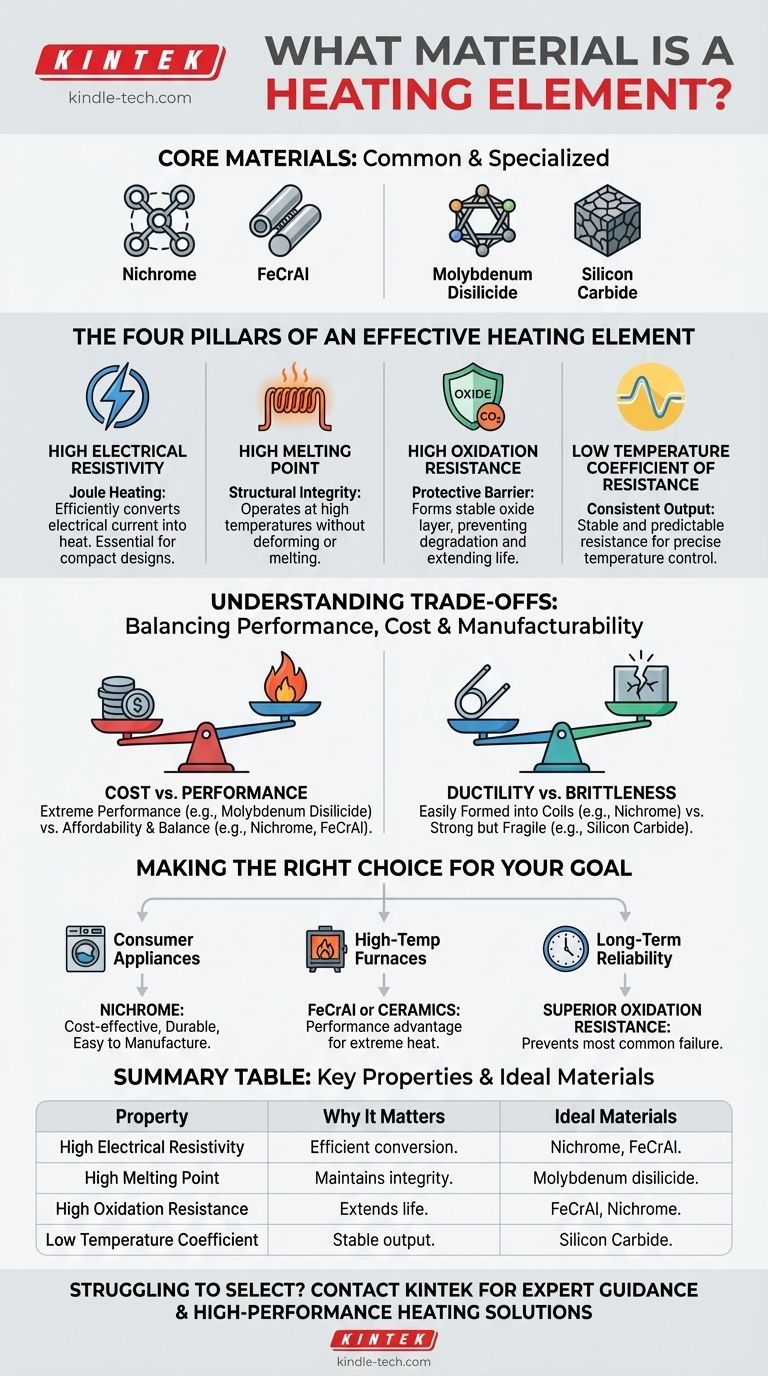
The most common heating elements are not made from a single material, but from specialized metal alloys or ceramic composites. The most widely used are nickel-chromium (Nichrome) and iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys, with materials like molybdenum disilicide and silicon carbide used for more extreme industrial applications.
The specific material used for a heating element is less important than the properties it possesses. The selection is a deliberate engineering choice based on four critical characteristics: high electrical resistance, a high melting point, stability at temperature, and resistance to oxidation.
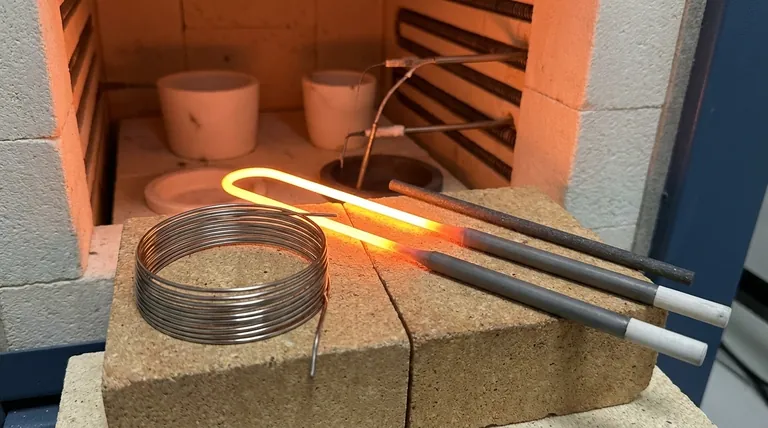

The Four Pillars of an Effective Heating Element
A material's ability to efficiently and reliably generate heat is not an accident. It is the result of a specific combination of physical properties that allow it to convert electrical energy into thermal energy without destroying itself in the process.
High Electrical Resistivity
A heating element works by resisting the flow of electricity, a principle known as Joule heating. High resistivity means the material is very effective at converting electrical current into heat.
This property allows a relatively short and thin wire to generate a significant amount of heat efficiently, which is essential for compact designs in appliances like toasters and hair dryers.
High Melting Point
This is a fundamental requirement. The material must operate at extremely high temperatures—often glowing red-hot or white-hot—without melting, softening, or deforming.
A high melting point ensures the element maintains its structural integrity and operational safety throughout its intended temperature range.
High Oxidation Resistance
At high temperatures, most metals react with oxygen in the air, causing them to degrade and fail. This process is called oxidation.
Effective heating element materials like Nichrome form a stable, protective outer layer of oxide. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing further oxidation and dramatically extending the element's service life.
Low Temperature Coefficient of Resistance
This property ensures the element's performance is stable and predictable. It means that as the material heats up, its electrical resistance does not change significantly.
An element with a low coefficient provides consistent heat output, preventing power surges or drops as it cycles through different temperatures. This is crucial for precise temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element material is an exercise in balancing performance, cost, and manufacturability. No single material is perfect for every application.
Cost vs. Performance
Materials designed for extreme industrial temperatures, like molybdenum disilicide, offer incredible performance but come at a significant cost.
For consumer goods, alloys like Nichrome and FeCrAl provide an excellent balance of high performance and affordability, making them ubiquitous.
Ductility vs. Brittleness
Metal alloys like Nichrome are highly ductile, meaning they can be easily drawn into wires and formed into complex coil shapes without breaking.
In contrast, ceramic elements like silicon carbide are very strong at high temperatures but are also brittle. They cannot be easily formed and are more susceptible to physical shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal material is always dictated by the specific requirements of the application, from everyday appliances to specialized industrial equipment.
- If your primary focus is consumer appliances: Nichrome is the standard choice, offering an ideal mix of cost-effectiveness, durability, and ease of manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature furnaces: FeCrAl alloys provide a performance advantage over Nichrome, while ceramics are necessary for the most extreme heat applications.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: A material with superior oxidation resistance is paramount, as this is the most common cause of element failure.
Understanding these core material properties empowers you to evaluate a heating element based on its true performance capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters | Ideal Materials |
|---|---|---|
| High Electrical Resistivity | Efficiently converts electricity to heat | Nichrome, FeCrAl |
| High Melting Point | Maintains integrity at high temperatures | Molybdenum disilicide |
| High Oxidation Resistance | Extends service life by preventing degradation | FeCrAl, Nichrome |
| Low Temperature Coefficient | Provides stable, predictable heat output | Silicon Carbide |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-performance heating solutions tailored to your laboratory's specific needs—whether for consumer appliances, high-temperature furnaces, or demanding industrial processes. Contact our experts today to ensure optimal efficiency, reliability, and longevity for your heating systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Which is better quartz or ceramic heating element? Choose the Right Heat for Your Application
- Which material is suitable for use in the heating element? Match the Right Material to Your Application
- What is the core function of resistance wire heating elements in a magnesium alloy waste recovery furnace? Expert Guide
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- How hot can resistance heating get? Unlock Temperatures from 1,200°C to Over 3,000°C
- What role do Carbon-Carbon composite heaters play within densification equipment? High-Temp Thermal Stability Solutions
- Why is a K-type thermocouple used to monitor substrate temperature during plasma treatment? Protect Material Integrity
- How effective is electrical resistance heating? It's 100% efficient at the point of use.



















