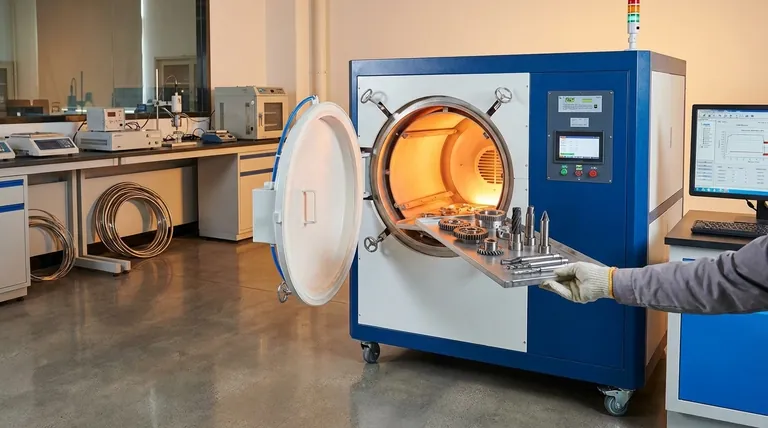
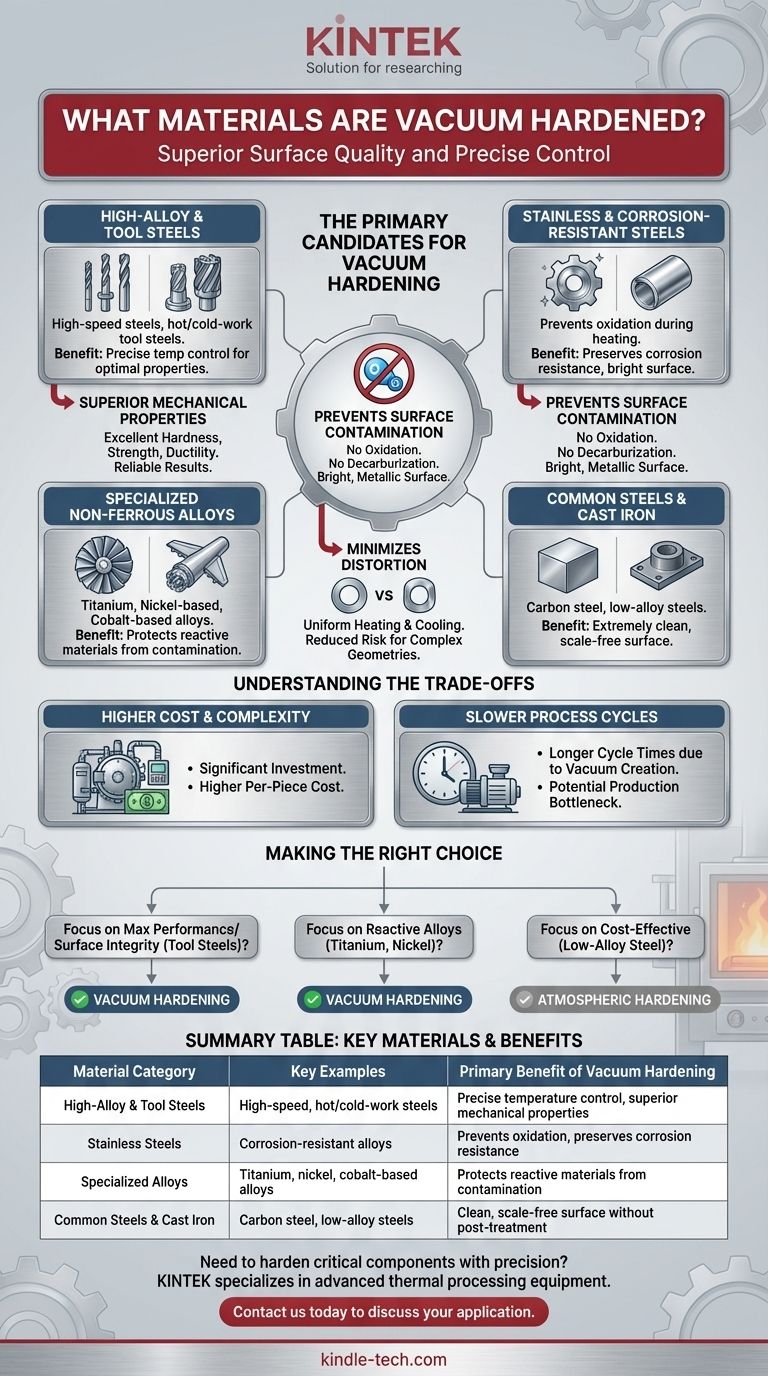
In short, vacuum hardening is suitable for a wide range of materials, including nearly all technically significant steel alloys, specialized non-ferrous alloys, and even cast iron. The primary candidates are high-alloy steels, tool steels, stainless steels, and sensitive metals like titanium or nickel-based alloys where a clean, bright surface finish and minimal distortion are critical.
The decision to use vacuum hardening is driven less by a material's basic ability to be hardened and more by the need for superior surface quality and precise control over the final mechanical properties, especially for high-value or sensitive alloys.

The Primary Candidates for Vacuum Hardening
Vacuum hardening is a versatile process, but it provides the most significant benefits for specific categories of metals that are sensitive to atmospheric exposure at high temperatures.
High-Alloy and Tool Steels
This is the most common application for vacuum hardening. These materials contain significant amounts of alloying elements that require precise temperature control to achieve their desired properties.
Examples include high-speed steels (used for drills and milling cutters), hot-work and cold-work tool steels, and steels used for forging tools, die casting tools, and industrial knives.
Stainless and Corrosion-Resistant Steels
The vacuum environment is critical for stainless steels because it prevents oxidation during the heating cycle. This preserves the material's chromium content at the surface, which is essential for its corrosion resistance.
This ensures the part emerges from the furnace with a bright, clean, and uncompromised surface.
Specialized and Non-Ferrous Alloys
The protective nature of the vacuum makes it ideal for hardening advanced materials that react readily with oxygen.
This includes titanium alloys, nickel-based alloys, and cobalt-based alloys. These materials are often used in demanding aerospace, medical, and industrial applications where material integrity is paramount.
Common Steels and Cast Iron
While often hardened in atmospheric furnaces, materials like carbon steel, low-alloy steels, and cast-iron alloys can also be vacuum hardened.
The process is typically chosen for these materials when the final application demands an exceptionally clean surface free of scale or decarburization, eliminating the need for post-heat-treat cleaning operations.
Why These Materials Benefit from a Vacuum Environment
The choice to use a vacuum furnace is directly linked to the unique advantages the environment provides during the high-temperature hardening process.
Preventing Surface Contamination
The core benefit of a vacuum is the absence of oxygen. This completely prevents oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface layer of steel), which can weaken the final part.
The result is a bright, metallic surface that often requires no further finishing.
Achieving Superior Mechanical Properties
Precise, uniform heating and controlled inert gas quenching lead to highly predictable results.
Parts treated in a vacuum furnace exhibit excellent hardness, high tensile and shear strength, and improved ductility and elasticity, making them more durable and reliable in service.
Minimizing Distortion
Vacuum furnaces provide extremely uniform heating and cooling. This controlled environment significantly reduces the risk of part distortion, which is a critical concern for complex geometries or components with tight dimensional tolerances.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hardening is not the default solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment and are more complex to operate and maintain than traditional atmospheric furnaces. This can translate to a higher per-piece cost for the heat treatment.
Slower Process Cycles
The need to pump the air out of the chamber to create a vacuum adds time to the overall process cycle. For high-volume production of simple parts, this can be a significant bottleneck compared to faster atmospheric methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct hardening process depends entirely on your material and the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and surface integrity for tool steels or high-alloy steels: Vacuum hardening is the superior choice, delivering a clean finish and optimal properties.
- If your primary focus is hardening sensitive, reactive alloys like titanium or nickel: The protective vacuum environment is essential to prevent material degradation.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective hardening of low-alloy steel where surface scale is acceptable: A conventional atmospheric hardening process is likely more economical.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum hardening is an investment in quality, ensuring that your most critical components achieve their maximum potential without compromise.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefit of Vacuum Hardening |
|---|---|---|
| High-Alloy & Tool Steels | High-speed steels, hot-work/cold-work tool steels | Precise temperature control, superior mechanical properties |
| Stainless Steels | Corrosion-resistant alloys | Prevents oxidation, preserves chromium for corrosion resistance |
| Specialized Non-Ferrous Alloys | Titanium, nickel, cobalt-based alloys | Protects reactive materials from contamination |
| Common Steels & Cast Iron | Carbon steel, low-alloy steels | Clean, scale-free surface without post-treatment cleaning |
Need to harden critical components with precision and superior surface quality?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Our vacuum hardening solutions are designed to help you achieve exceptional results for high-value materials like tool steels, stainless steels, and sensitive alloys—ensuring bright, clean finishes and minimal distortion.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver reliable, high-performance outcomes for your most demanding applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials



















