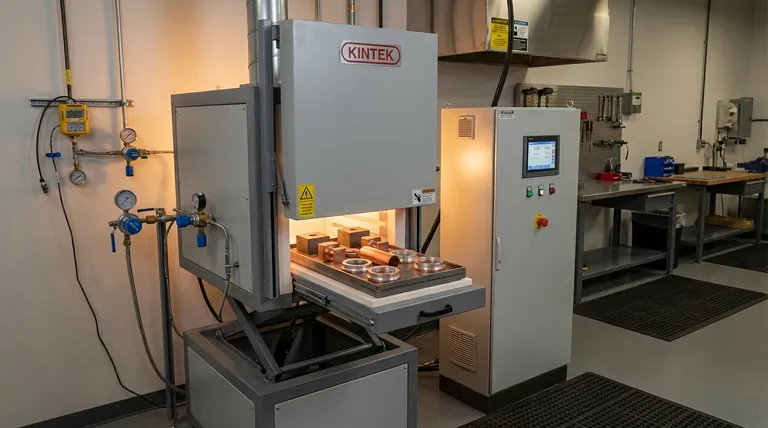
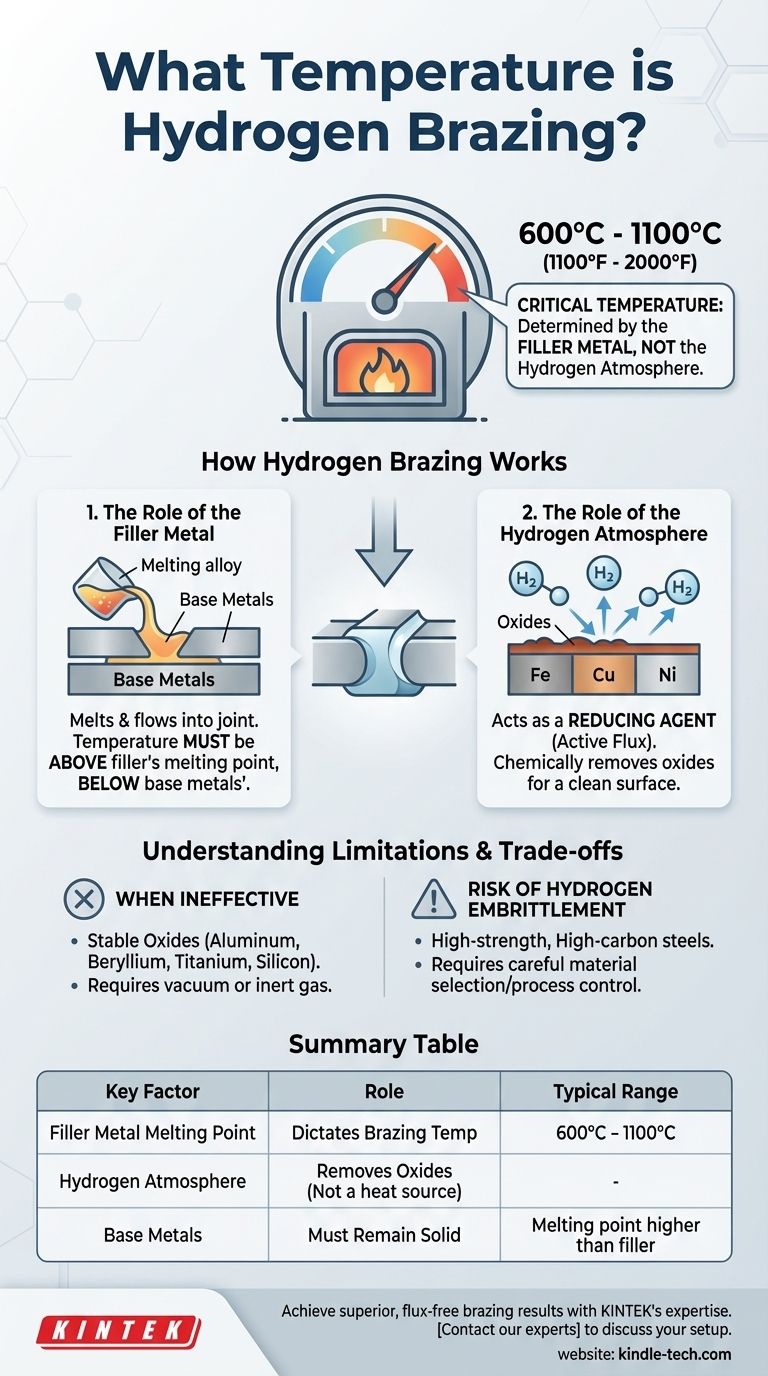
In hydrogen brazing, the critical temperature is determined by the filler metal, not the hydrogen atmosphere itself. While the process takes place at elevated temperatures, there is no single "hydrogen brazing temperature." Instead, the temperature must be set high enough to melt the specific brazing filler alloy being used, which typically ranges from 600°C to over 1100°C (1100°F to 2000°F).
The essential takeaway is that the hydrogen atmosphere serves as a cleaning agent, not a heat source. Its role is to chemically remove oxides from the base metals at high temperatures, allowing the molten filler metal to form a clean, strong bond. The correct temperature is dictated entirely by the melting point of your chosen filler.

How Hydrogen Brazing Works
The Role of the Filler Metal
The core of any brazing operation is the filler metal. This is the alloy that melts, flows into the gap between the two base parts through capillary action, and then solidifies to create the joint.
The process temperature must be set above the melting point of the filler metal but below the melting point of the base metals being joined.
The Role of the Hydrogen Atmosphere
At the high temperatures required for brazing, metals rapidly oxidize. These oxide layers prevent the filler metal from "wetting" the surfaces, which would result in a weak or non-existent joint.
Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent or active flux. It reacts with the oxides of many common metals—such as iron, copper, nickel, and cobalt—and reduces them back to their pure metallic state, creating a perfectly clean surface for the filler metal to bond with.
Why Temperature and Atmosphere Work Together
The process is a synergistic one. The furnace provides the thermal energy to melt the filler alloy, while the hydrogen atmosphere simultaneously prepares the metal surfaces, ensuring the molten filler can create a continuous, high-integrity metallurgical bond.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
When Hydrogen is Ineffective
Hydrogen is not a universal solution. It is not powerful enough to reduce the highly stable oxides that form on certain metals.
This includes metals like aluminum, beryllium, titanium, and silicon. For these materials, hydrogen brazing is unsuitable, and processes like vacuum brazing or brazing in an inert gas (like argon) are required.
Risk of Hydrogen Embrittlement
Certain materials, particularly high-strength and high-carbon steels, can absorb atomic hydrogen at brazing temperatures. This can lead to a significant loss of ductility and premature failure, a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement.
Careful material selection and procedural controls are necessary to mitigate this risk when brazing susceptible alloys.
Safety Considerations
Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires specialized, sealed furnaces and strict safety protocols to handle correctly. It is an industrial process that demands a controlled environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Materials
- If your primary focus is joining common steels, copper, or nickel alloys: Hydrogen brazing is an excellent choice for creating clean, flux-free joints. The temperature will be dictated by the appropriate copper, silver, or nickel-based filler metal for your application.
- If your primary focus is joining materials with stable oxides (e.g., aluminum, titanium): You must use an alternative process like vacuum brazing, as the hydrogen atmosphere will not be effective at cleaning these surfaces.
- If your primary focus is joining high-carbon or hardened steels: You must evaluate the risk of hydrogen embrittlement. A different atmosphere or post-brazing heat treatment may be required.
Ultimately, selecting the correct brazing temperature begins with selecting the right filler metal for your specific base materials and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Hydrogen Brazing | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Filler Metal Melting Point | Dictates the brazing temperature | 600°C - 1100°C (1100°F - 2000°F) |
| Hydrogen Atmosphere | Removes oxides from base metals | Not a heat source |
| Base Metals | Must remain solid during brazing | Melting point higher than filler |
Achieve superior, flux-free brazing results with KINTEK's expertise.
Struggling with oxide contamination or weak joints in your lab? Our hydrogen brazing solutions provide the clean, controlled atmosphere needed for strong metallurgical bonds in materials like steel, copper, and nickel alloys.
We specialize in lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research and production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal brazing setup for your materials and ensure joint integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What affects the melting point of a substance? Uncover the Key Factors & Forces
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- What hazard is involved when using a furnace? Protect Your Home from the Silent Killer
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model



















