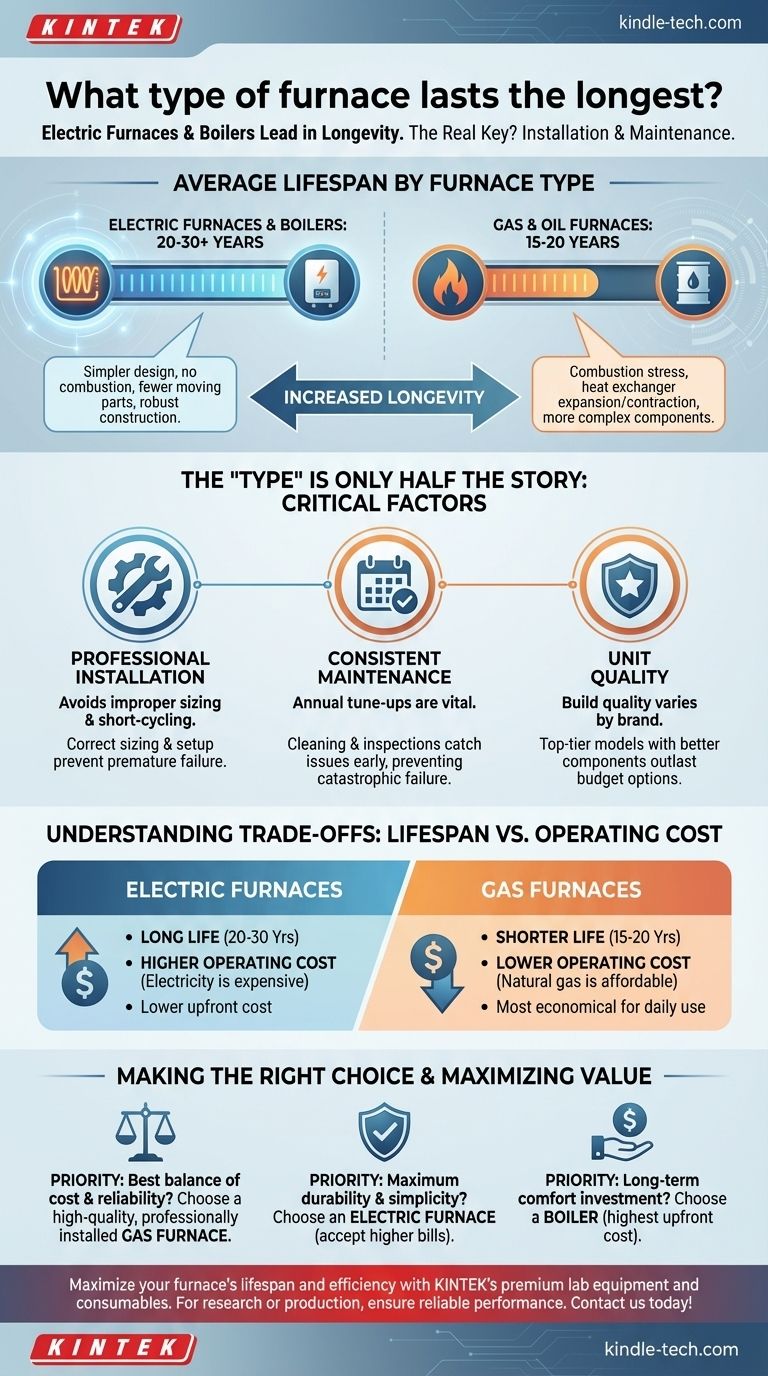
On average, electric furnaces and boilers last the longest. While a typical gas or oil furnace has a lifespan of 15 to 20 years, a well-maintained electric furnace or boiler can often operate effectively for 20 to 30 years. This increased longevity is primarily due to their simpler design with fewer complex, high-stress components.
The type of furnace sets a general expectation for its lifespan, but this is not the most important factor. The actual longevity of any heating system is determined far more by the quality of its installation, the consistency of its maintenance, and whether it was correctly sized for your home.

Baseline Lifespans by Furnace Type
The fuel a furnace uses directly impacts its mechanical complexity and the stresses it endures. This is the primary reason for the difference in average lifespans.
Electric Furnaces (20-30 Years)
An electric furnace has the simplest design. It uses heating elements—much like the coils in a toaster—to heat the air.
Because there is no combustion, there are no corrosive byproducts, no gas valves, and no heat exchanger to crack. With fewer moving parts and a less stressful operation, there are simply fewer components that can fail.
Boilers (20-30+ Years)
While boilers heat water for hydronic systems rather than air, they are a common alternative to furnaces. They are known for exceptional durability.
Their longevity comes from robust construction, often using cast-iron heat exchangers, and a sealed, low-stress system. This durability, however, comes with a significantly higher upfront installation cost.
Gas & Oil Furnaces (15-20 Years)
Gas and oil furnaces are the most common heating systems. They generate intense heat through combustion, a process that inherently causes wear and tear.
The constant expansion and contraction of the metal heat exchanger is the primary limiting factor. Over time, this stress can cause cracks, which is a serious safety hazard and a terminal diagnosis for the furnace.
Why a Furnace's "Type" Is Only Half the Story
Focusing solely on the average lifespan of a furnace type can be misleading. The following factors have a much greater impact on how long your specific unit will actually last.
The Critical Role of Professional Installation
Improper installation is a primary cause of premature furnace failure. A unit that is oversized or undersized for your home will work inefficiently and wear out quickly.
An oversized furnace will "short-cycle," turning on and off frequently, which stresses components. An undersized unit will run constantly, leading to excessive wear.
The Power of Consistent Maintenance
Neglecting annual maintenance is the single most effective way to shorten a furnace's life.
Changing filters, cleaning sensors, and ensuring burners are clear of debris prevents the system from overworking. An annual professional tune-up can catch small issues before they cascade into catastrophic (and expensive) failures.
Quality of the Unit Itself
Within each furnace category (gas, electric, etc.), there are significant differences in build quality between manufacturers and models.
A top-tier gas furnace from a reputable brand, built with higher-quality components, has a greater chance of outlasting a budget-grade electric model.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Lifespan vs. Operating Cost
A longer lifespan does not always mean a lower total cost of ownership. The price of fuel is a critical piece of the puzzle.
Electric Furnaces: Long Life, Higher Cost
While electric furnaces last a long time and are often cheaper to purchase and install, electricity is typically the most expensive heating fuel. The high monthly operating costs can easily offset the benefit of a longer lifespan.
Gas Furnaces: Shorter Life, Lower Cost
Natural gas is the most affordable heating fuel in most regions. This makes gas furnaces the most economical choice for day-to-day operation, which is why they are the most popular type despite not having the longest absolute lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace is about balancing durability, upfront cost, and long-term operating expenses.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and simplicity: An electric furnace is an excellent choice, but only if you can accept significantly higher monthly energy bills.
- If your primary focus is the best balance of operating cost and reliability: A high-quality, professionally installed gas furnace is the most practical and economical solution for most homeowners.
- If your primary focus is a long-term investment in comfort and you have the budget: A boiler provides exceptional durability and heating quality, but with the highest initial installation cost.
Ultimately, committing to professional installation and annual maintenance is the most powerful way to maximize the life and efficiency of whichever furnace you choose.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Average Lifespan | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Furnace | 20-30 Years | Simple design, no combustion, fewer moving parts |
| Boiler | 20-30+ Years | Robust construction, sealed low-stress system |
| Gas & Oil Furnace | 15-20 Years | Combustion process, heat exchanger stress |
Maximize your furnace's lifespan and efficiency with KINTEK's premium lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're managing a research facility or a production lab, our heating systems and maintenance solutions ensure reliable performance and longevity. Contact us today to explore how KINTEK can support your laboratory's heating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM
- How can I improve my filter press performance? Optimize Slurry, Cycle, and Maintenance for Peak Efficiency
- What mechanical properties are affected by heat treatment? Master Hardness, Strength, and Toughness
- Is pyrolysis bad for the Environment? A Guide to Maximizing Benefits and Minimizing Risks
- What is the difference between thermal evaporation and molecular beam epitaxy? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- Which materials are used as high temperature resistance materials? A Guide to Superalloys, Ceramics & Composites
- Is glass made by sintering? The Truth About How Glass is Formed
- What is the sintering process? A Guide to Manufacturing with Powdered Materials



















