In short, a hydraulic press is used in nearly every industry that requires shaping, forming, crushing, or compressing materials with immense and controlled force. Its applications range from manufacturing car parts and forging metal to compacting powders for ceramics and testing the strength of concrete.
The true value of a hydraulic press isn't just its raw power, but its versatility. Its ability to deliver sustained, uniform pressure makes it the go-to solution for a vast range of tasks, from high-precision molding to heavy-duty crushing.

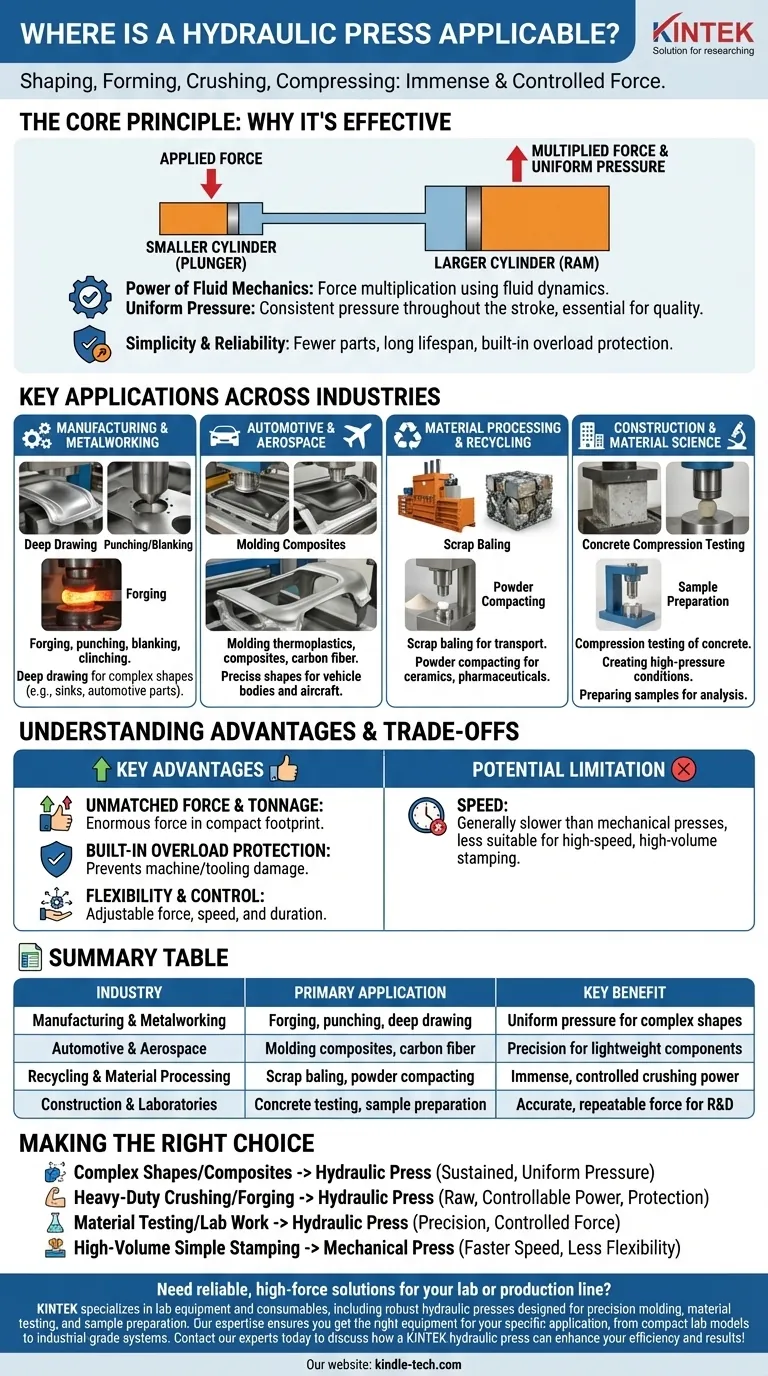
The Core Principle: Why Hydraulic Power is So Effective
To understand where a hydraulic press is used, you must first understand why it works so well. The machine's design is simple but profoundly effective, leveraging basic fluid dynamics.
The Power of Fluid Mechanics
A hydraulic press operates using two interconnected cylinders filled with fluid. When a small amount of force is applied to the smaller cylinder (the plunger), that pressure is transmitted equally throughout the fluid, generating a massively multiplied force on the larger cylinder (the ram).
This principle allows a relatively small motor to generate immense tonnage, making it an efficient way to achieve incredible pressing power.
Delivering Uniform, Controlled Pressure
Unlike a mechanical press that delivers force at a specific point in its stroke, a hydraulic press can apply full, consistent pressure throughout the entire ram stroke. This is critical for applications like deep drawing or molding complex composite materials, where uniform pressure is essential for a quality result.
Simplicity and Reliability
With fewer moving parts than their mechanical counterparts, hydraulic presses often have a longer operational lifespan and require less maintenance. The hydraulic fluid itself acts as a lubricant, and the system has built-in overload protection—it simply won't apply more pressure than it's designed for, protecting both the machine and the tooling.
Key Applications Across Industries
The combination of power, control, and reliability makes the hydraulic press a cornerstone tool in numerous sectors. Its applications can be grouped by the primary function it serves.
Manufacturing and Metalworking
This is the most common domain for hydraulic presses. They are used for forging, punching, blanking, and clinching metal sheets. Their ability to perform deep drawing—forming a flat piece of metal into a deep, cup-like shape—is particularly valuable in producing parts like kitchen sinks or automotive components.
Automotive and Aerospace
These industries rely on hydraulic presses for forming high-strength, lightweight materials. The controlled pressure is ideal for molding thermoplastics, composites, and carbon fiber into complex, precise shapes needed for vehicle bodies and aircraft components.
Material Processing and Recycling
The raw crushing power of a hydraulic press is essential here. Giant presses are used for scrap baling, compacting old vehicles and other scrap metal into dense, manageable blocks for transport and recycling. They are also used for powder compacting in the production of ceramics or pharmaceuticals.
Construction and Material Science
In laboratory settings, hydraulic presses are fundamental tools for quality control. They are used for the compression testing of concrete samples to verify their strength and for creating high-pressure conditions to study material properties. They are also used to prepare samples for analysis by pressing powders into thin, uniform pellets.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
No single tool is perfect for every job. Understanding the unique benefits and potential limitations of a hydraulic press is key to making an informed decision.
Key Advantage: Unmatched Force and Tonnage
The primary benefit is the ability to generate enormous amounts of force, often measured in hundreds or thousands of tons, within a relatively compact footprint.
Key Advantage: Built-in Overload Protection
A hydraulic system is pressure-limited by its nature. This inherent safety feature prevents damage to the machine and the expensive dies used for forming and molding, extending their lifespan.
Key Advantage: Flexibility and Control
The force, speed, and duration of the press stroke are all fully adjustable. This high degree of control allows for greater adaptability across different materials and applications, from delicate forming to intense crushing.
Potential Limitation: Speed
Compared to mechanical presses, hydraulic presses are generally slower. The time it takes to build and release hydraulic pressure makes them less suitable for high-speed, high-volume stamping operations where cycle time is the most critical factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use a hydraulic press depends entirely on the specific requirements of the task.
- If your primary focus is forming complex shapes or advanced composites: The sustained, uniform pressure of a hydraulic press is essential for quality and consistency.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty crushing, baling, or forging: The raw, controllable power and inherent overload protection of a hydraulic press make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is material testing or laboratory work: A hydraulic press provides the precision and controlled force necessary for accurate, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is extremely high-volume production of simple stamped parts: A faster mechanical press may be a more efficient solution, though you will sacrifice the flexibility of a hydraulic system.
The hydraulic press is chosen wherever controlled, immense force is the key to transforming a material.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Metalworking | Forging, punching, deep drawing | Uniform pressure for complex shapes |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Molding composites, carbon fiber | Precision for lightweight components |
| Recycling & Material Processing | Scrap baling, powder compacting | Immense, controlled crushing power |
| Construction & Laboratories | Concrete testing, sample preparation | Accurate, repeatable force for R&D |
Need reliable, high-force solutions for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including robust hydraulic presses designed for precision molding, material testing, and sample preparation. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific application, from compact lab models to industrial-grade systems. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hydraulic press can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples



















