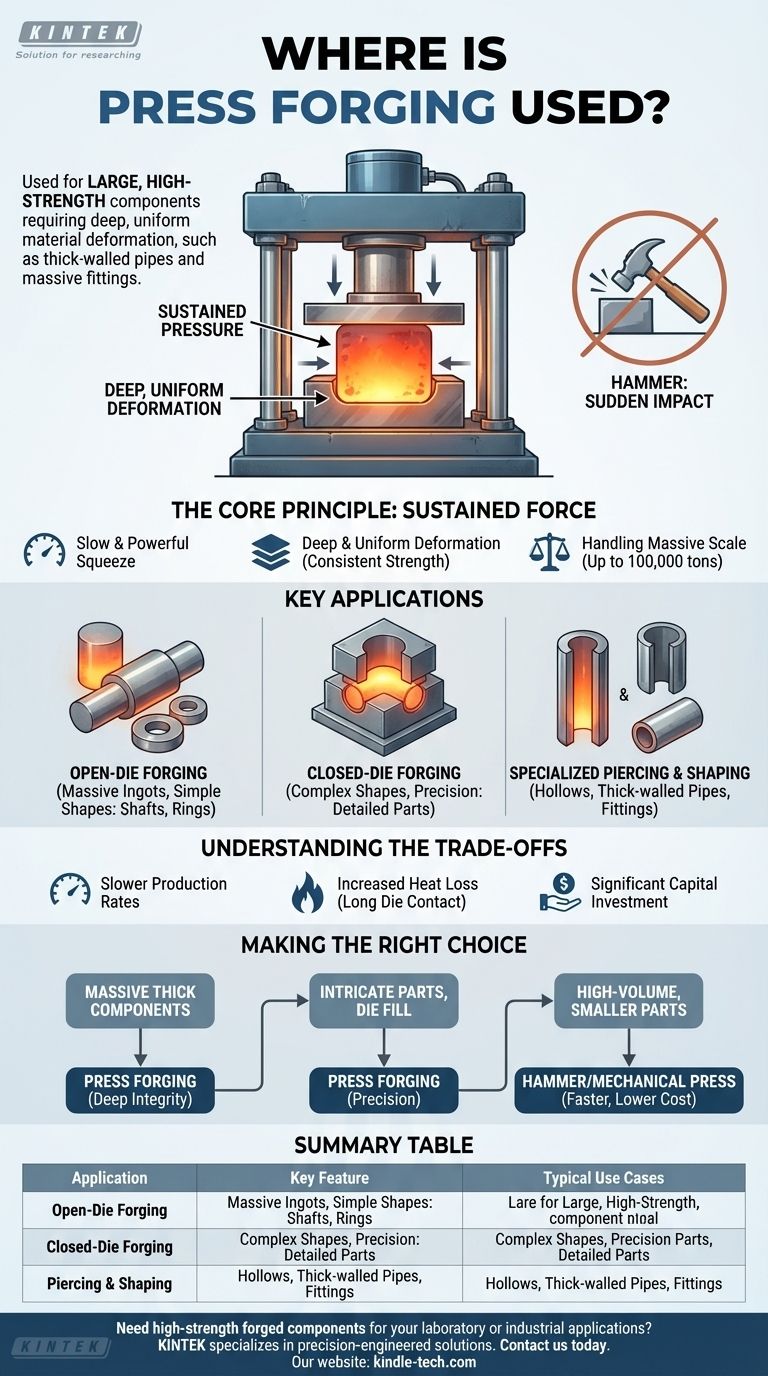
In short, press forging is used to manufacture large, high-strength metal components where deep and uniform material deformation is critical. This process is essential for applications like creating thick-walled pipes, industrial fittings, and other massive parts that demand consistent internal quality from surface to core.
The core principle is simple: press forging applies massive, sustained pressure rather than a sudden impact. This controlled squeeze ensures the force penetrates completely through large workpieces, making it the definitive method for shaping heavy-duty components where structural integrity is non-negotiable.

The Core Principle: Sustained Force vs. Impact
To understand where press forging is used, you must first understand how it works. Unlike the rapid, sharp blow of a forging hammer, a hydraulic press uses a slow, controlled application of immense force.
A Slow and Powerful Squeeze
A press moves a ram at a controlled, slower speed, squeezing the metal workpiece into its final shape. This continuous pressure is what distinguishes it from all other forging methods.
Deep and Uniform Deformation
The sustained pressure ensures the force doesn't just shape the surface but travels deep into the material's core. This results in a uniform grain structure and consistent strength throughout the entire part, which is critical for thick components.
Handling Massive Scale
Presses are defined by their sheer power and size. With force capacities reaching 100,000 tons and working strokes of up to 4 meters, they are engineered to handle workpieces that are simply too large for other forging techniques.
Key Applications Driven by Press Capabilities
The unique capabilities of press forging directly dictate its primary applications. It is the go-to process when the workpiece is large, the material is thick, or the required deformation is significant.
Open-Die Forging
This is the primary application for the largest forging presses. In open-die forging, the workpiece is not fully enclosed by the die. The press is used to incrementally shape massive ingots into simpler forms like shafts, rings, or blocks, often for heavy industrial machinery.
Closed-Die (Impression) Forging
For more complex shapes, closed-die forging uses a press to squeeze the metal into a die that acts as a mold. The immense force, with capacities up to 82,000 tons, ensures the metal flows and completely fills every detail of the die cavity, creating precise, high-strength parts.
Specialized Piercing and Shaping
The long, powerful stroke of a hydraulic press makes it ideal for specialized tasks. It is frequently used for piercing operations to create hollows in thick components and for the partial forging of heavy-duty fittings and thick-walled pipes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, press forging is not the universal solution. Its specific characteristics create clear operational trade-offs.
Slower Production Rates
The deliberate, controlled squeeze of a press is inherently slower than the rapid blows of a forging hammer. This makes it less suitable for high-volume manufacturing of smaller parts where speed is the primary driver of cost-efficiency.
Increased Die Contact and Heat Loss
Because the press holds the workpiece under pressure for a longer duration, there is more time for heat to transfer from the hot metal to the cooler dies. This can be a disadvantage, requiring careful management of workpiece temperature during the forging process.
Significant Capital Investment
Hydraulic forging presses are massive, complex, and expensive machines. Their scale and cost mean they are typically reserved for applications where their unique ability to forge large, high-integrity parts justifies the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a forging process depends entirely on the component's size, complexity, and required properties.
- If your primary focus is on massive components with thick cross-sections: Press forging is the only method that guarantees deep, uniform material deformation and structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is on creating intricate parts that require complete die fill: The sustained, high force of a press is ideal for ensuring precision in complex closed-die forgings.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of smaller parts: A forging hammer or a mechanical press will likely offer a more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, press forging is the definitive solution when the size, strength, and internal quality of the final component cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Feature | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Die Forging | Handles massive ingots | Shafts, rings, blocks for heavy machinery |
| Closed-Die Forging | Creates complex, precise shapes | High-strength components with detailed features |
| Piercing & Shaping | Forms hollows in thick materials | Thick-walled pipes, industrial fittings |
Need high-strength forged components for your laboratory or industrial applications? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision-engineered solutions. Our expertise in material processing ensures you get components with the structural integrity and uniform quality your applications demand. Contact us today to discuss how our forging solutions can enhance your project's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















