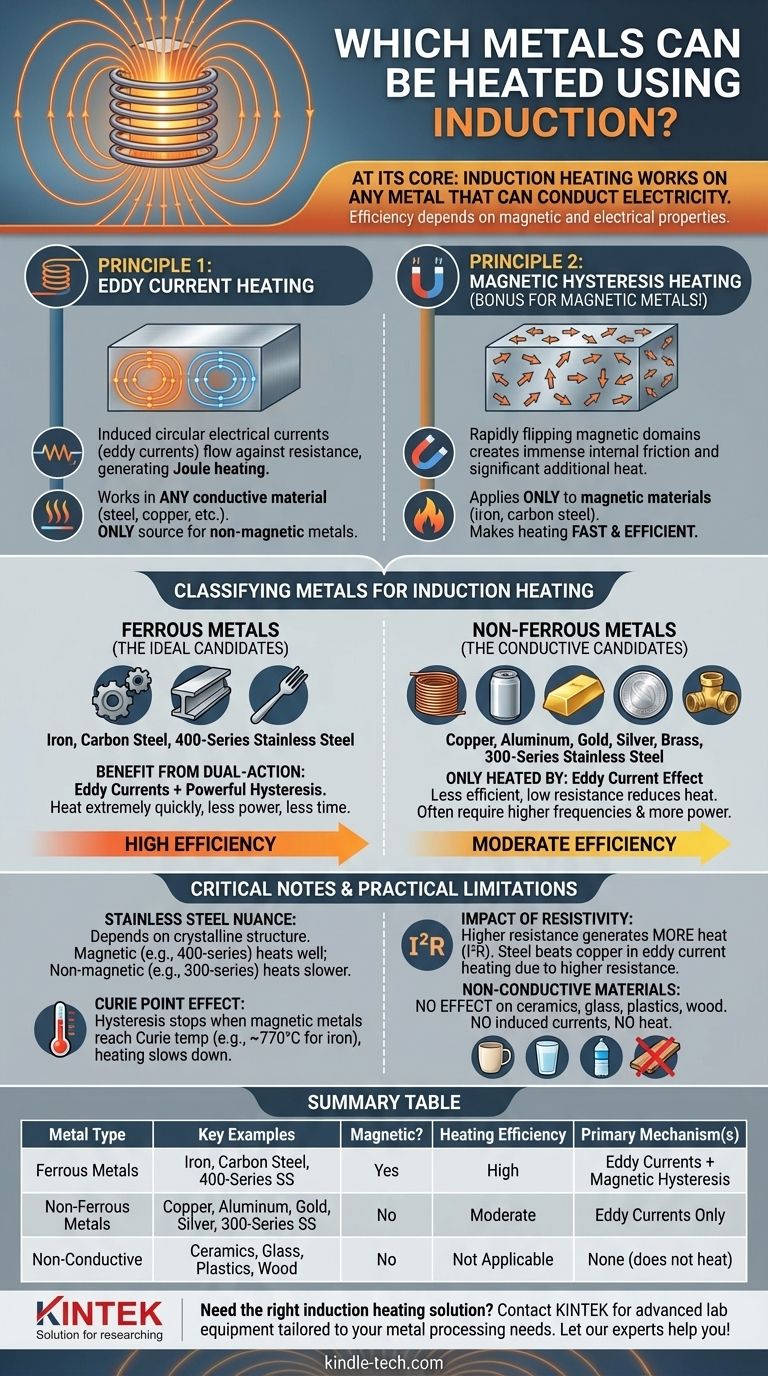
At its core, induction heating works on any metal that can conduct electricity. This includes common ferrous metals like iron and steel, non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum, and precious metals such as gold and silver. The critical factor is not just if a metal can be heated, but how efficiently and quickly the process occurs, which depends entirely on the metal's magnetic and electrical properties.
While any conductive material is a candidate for induction, magnetic metals like iron and steel heat far more efficiently than non-magnetic metals like copper or aluminum. This is because they benefit from two separate heating mechanisms, while non-magnetic metals only rely on one.

The Two Pillars of Induction Heating
To understand which metals are best suited for induction, you must first understand the two physical principles that generate the heat. The effectiveness of induction heating is determined by how well a material can leverage these phenomena.
Principle 1: Eddy Current Heating
An induction coil generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When a conductive material like any metal is placed inside this field, it induces small, circular electrical currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents.
These currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance, and this friction generates precise, localized heat. This mechanism, known as Joule heating, works in any electrically conductive material, from steel to copper. For non-magnetic metals, this is the only source of induction heat.
Principle 2: Magnetic Hysteresis Heating
This second mechanism is a powerful bonus that only applies to magnetic materials, such as iron and carbon steel.
Magnetic metals are composed of microscopic magnetic regions, or "domains." The rapidly alternating magnetic field from the induction coil causes these domains to rapidly flip their polarity, trying to align with the field.
This frantic flipping—happening millions of time per second—creates immense internal friction, which generates significant additional heat. This hysteresis effect is what makes induction heating on ferrous metals so remarkably fast and efficient.
Classifying Metals for Induction Heating
Based on these principles, we can group metals into two practical categories for induction applications.
Ferrous Metals: The Ideal Candidates
Ferrous metals like iron, carbon steel, and certain stainless steels are the best candidates for induction heating.
They benefit from both eddy currents and the powerful hysteresis effect. This dual-action heating makes them heat extremely quickly, requiring less power and time to reach a target temperature for applications like melting, forging, or hardening.
Non-Ferrous Metals: The Conductive Candidates
Non-ferrous metals like copper, aluminum, gold, silver, and brass are not magnetic.
Therefore, they can only be heated by the eddy current effect. While effective, the process is less efficient than with ferrous metals. Because many of these metals (like copper and aluminum) are highly conductive, they have very low electrical resistance, which reduces the amount of heat generated by eddy currents.
Heating these materials often requires higher frequencies and more power to achieve the desired result.
A Critical Note on Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is not a single material. Its suitability for induction depends entirely on its crystalline structure.
- Ferritic/Martensitic (e.g., 400 Series): These grades are magnetic and heat exceptionally well, behaving much like carbon steel.
- Austenitic (e.g., 304, 316): These common grades are non-magnetic. They can be heated by induction, but they will respond much more slowly, similar to other non-ferrous metals.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
Knowing the principles reveals key trade-offs and limitations you must consider in any real-world application.
The Curie Point Effect
The hysteresis heating effect only works as long as the material is magnetic. Every magnetic metal has a "Curie temperature"—the point at which it loses its magnetic properties. For iron, this is approximately 770°C (1420°F).
When a piece of steel is heated past this point, the highly efficient hysteresis effect instantly stops. The metal will continue to heat via eddy currents alone, but the rate of temperature increase will noticeably slow down.
The Impact of Resistivity
Heat from eddy currents is a product of the current squared and the material's resistance (I²R). Therefore, a metal with higher electrical resistance will generate more heat from the same induced current.
This is why steel, which has a relatively high resistance, heats more effectively via eddy currents than copper, which has a very low resistance. Copper's excellent conductivity actually works against it in an induction heating scenario.
Non-Conductive Materials
It is crucial to remember that induction heating has no effect on non-conductive materials. Materials like ceramics, glass, plastics, and wood cannot have currents induced within them and will not heat up in an induction field.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of material must be aligned with the capabilities of induction technology.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating of steel or iron (e.g., hardening, forging): Induction is an exceptionally efficient choice due to the powerful combination of hysteresis and eddy current heating.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, copper, gold): Induction is a very clean and controllable method, but you must account for higher power requirements and potentially longer cycle times compared to ferrous metals.
- If your primary focus is working with stainless steel: You must identify the specific alloy; magnetic 400-series grades will heat far more readily than non-magnetic 300-series grades.
By understanding the physics at play, you can confidently determine whether induction heating is the right tool for your material and your process.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Key Examples | Magnetic? | Heating Efficiency | Primary Heating Mechanism(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Iron, Carbon Steel, 400-Series Stainless Steel | Yes | High | Eddy Currents + Magnetic Hysteresis |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Copper, Aluminum, Gold, Silver, 300-Series Stainless Steel | No | Moderate (requires more power) | Eddy Currents Only |
| Non-Conductive Materials | Ceramics, Glass, Plastics, Wood | No | Not Applicable | None (does not heat) |
Need the right induction heating solution for your specific metal processing? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're working with ferrous or non-ferrous metals, our induction heating systems deliver precise temperature control, rapid heating, and energy efficiency. Let our experts help you select the ideal equipment for melting, forging, hardening, or any other thermal process. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's productivity and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why must a high vacuum be maintained during Cu-CNT sintering? Ensure Optimal Bonding and Material Integrity
- What is the core role of a vacuum hot press furnace in composites? Master Precision Bonding and Densification
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- What functions does the vacuum environment of a vacuum hot pressing furnace serve? Optimize Cu/WC Composite Performance
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?



















